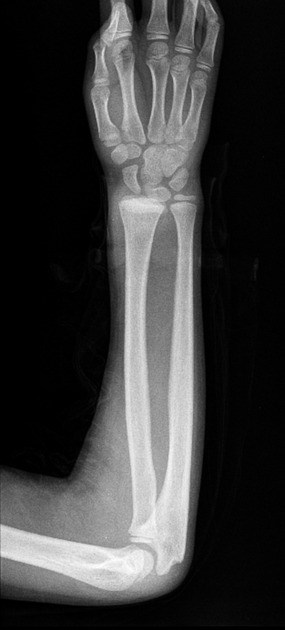
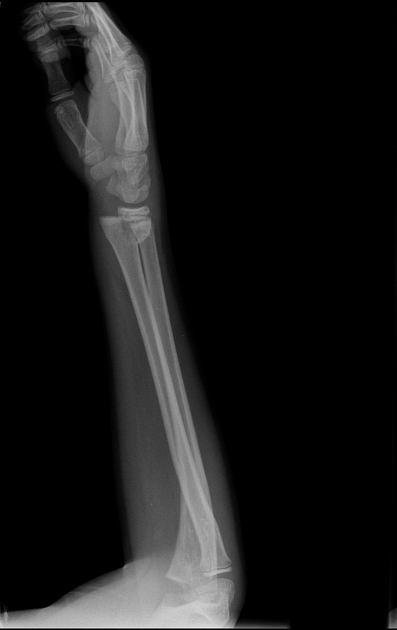
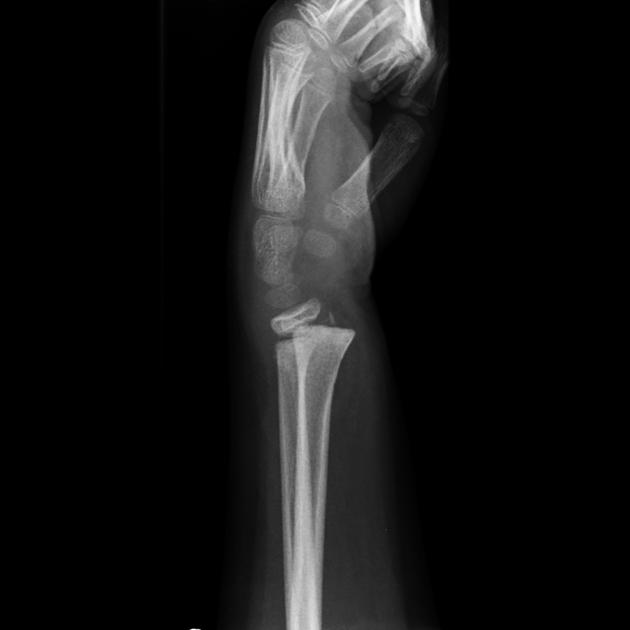
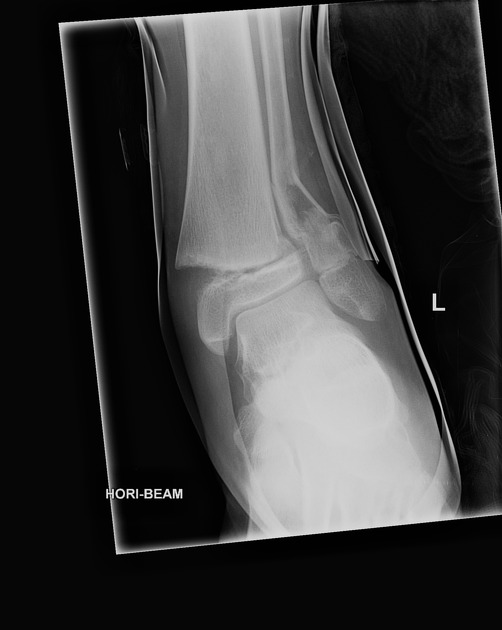
Salter-Harris classification
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Liz Silverstone had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Liz Silverstone's current disclosures- Salter-Harris fracture classification
- SH types
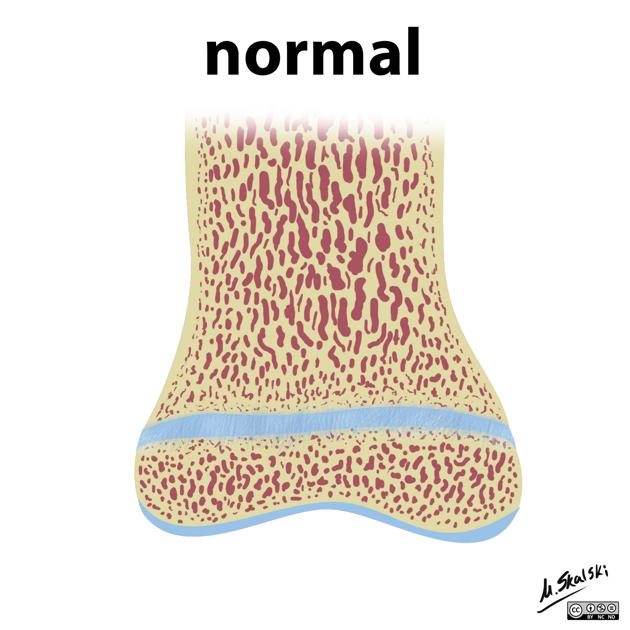
The Salter-Harris classification was proposed by Salter and Harris in 1963 1 and is the most widely used (c. 2023) system for describing physeal fractures.
Classification
Conveniently, the Salter-Harris types can be remembered by the mnemonic SALTR.
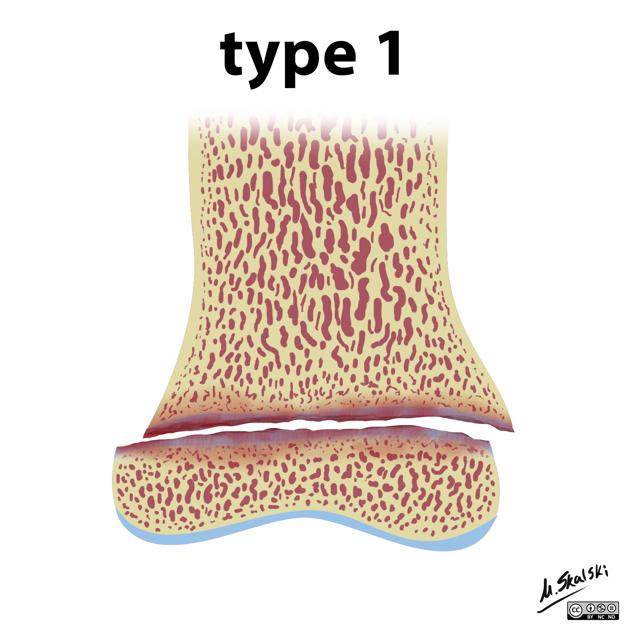
-
slipped
5-7%
fracture plane passes all the way through the growth plate, not involving bone
cannot occur if the growth plate is fused cit
good prognosis
-
above
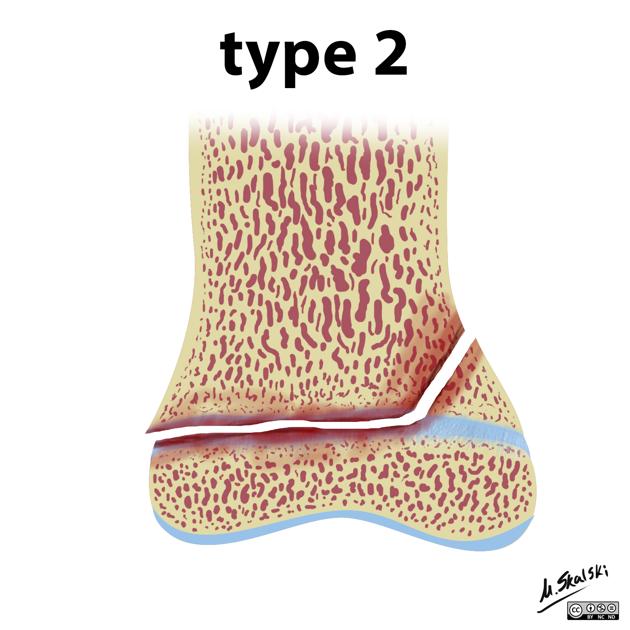
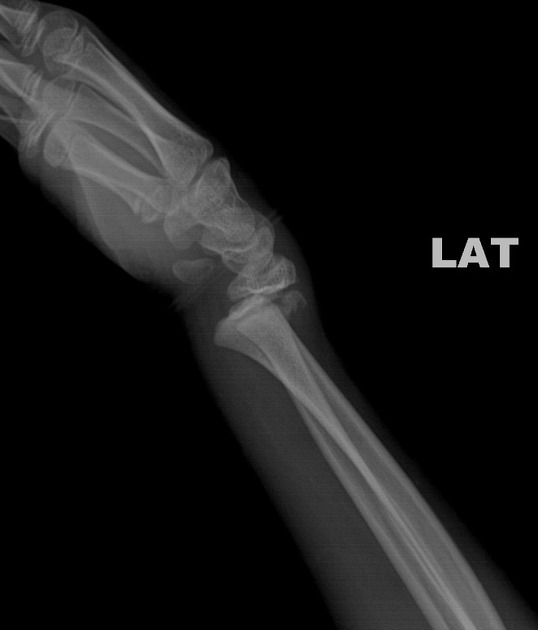
~75% (by far the most common)
fracture passes across most of the growth plate and up through the metaphysis
good prognosis
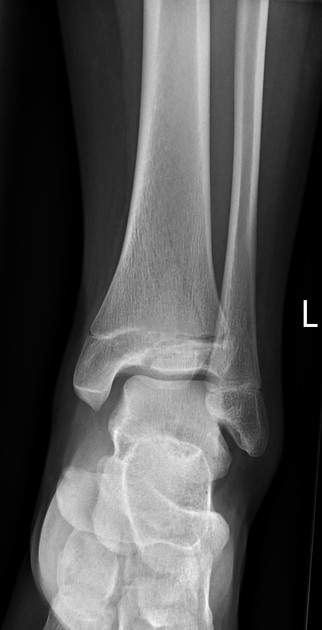
-
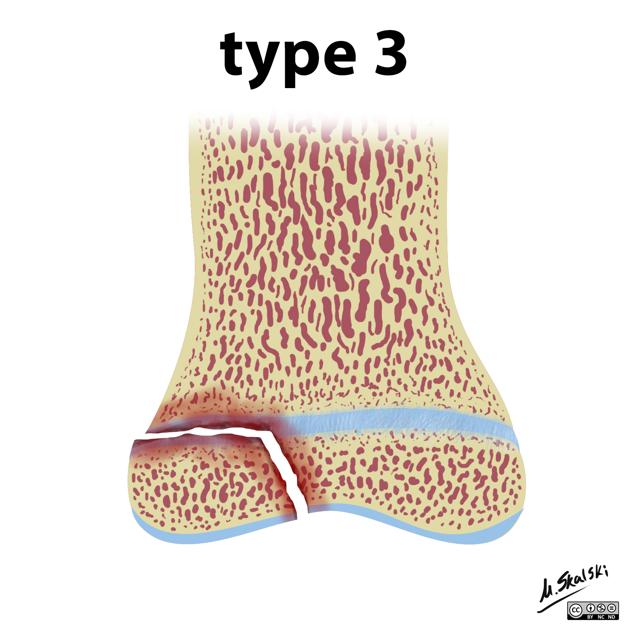
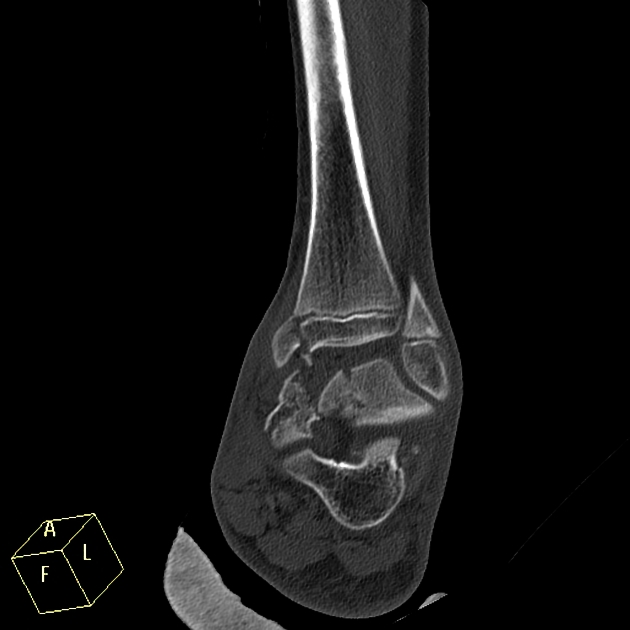
lower
7-10%
fracture plane passes some distance along with the growth plate and down through the epiphysis
poorer prognosis as the proliferative and reserve zones are interrupted
-
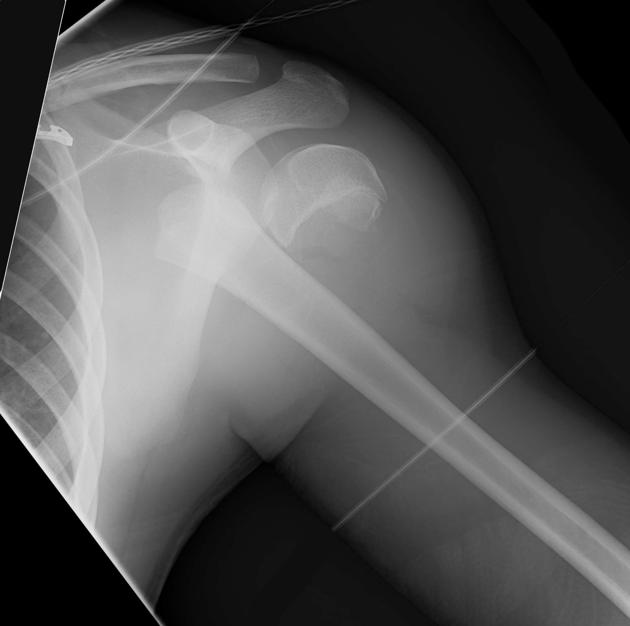
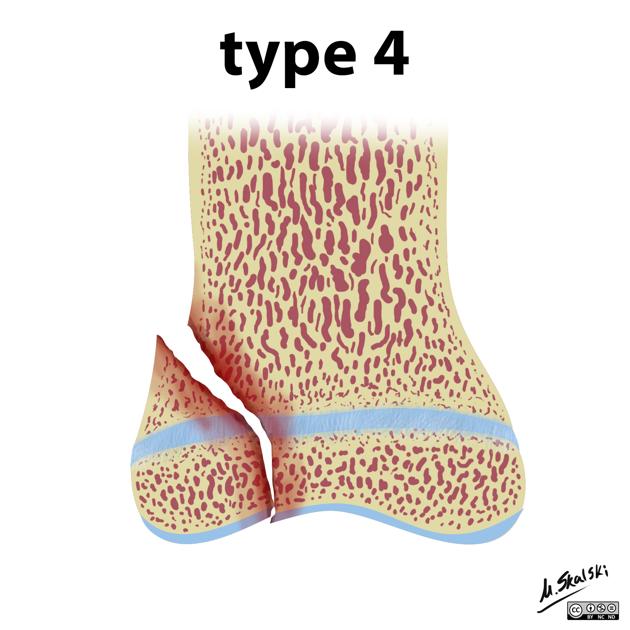
through or transverse or together
intra-articular
10%
fracture plane passes directly through the metaphysis, growth plate and down through the epiphysis
poor prognosis as the proliferative and reserve zones are interrupted
-
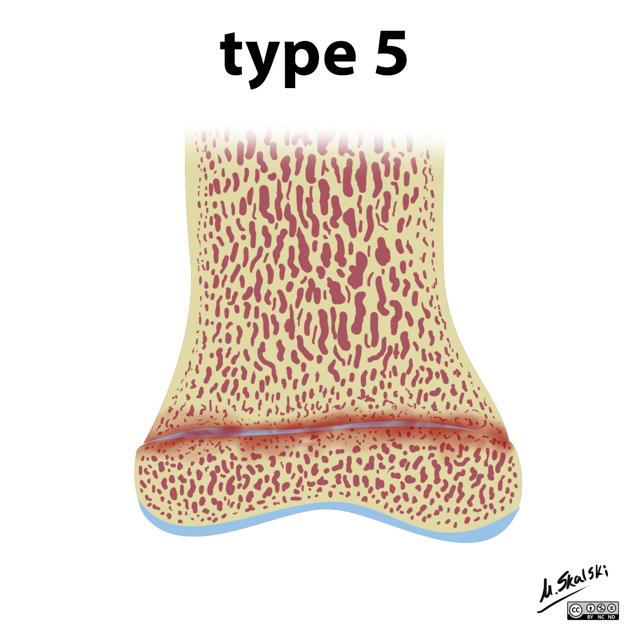
ruined or rammed or crush
uncommon <1%
crushing type injury does not displace the growth plate but damages it by direct compression
worst prognosis
Others
There are a few other rare types that you should probably never include in a report, as almost no one will know what you are talking about. Nonetheless, they are:
type VI: injury to the perichondral structures
type VII: isolated injury to the epiphyseal plate
type VIII: isolated injury to the metaphysis, with a potential injury related to endochondral ossification
type IX: injury to the periosteum that may interfere with membranous growth
Fractures that involve the physis can present with trapped periosteum and this should be considered when one aspect of the physis is widened 5.
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Salter R, Harris WR. Injuries Involving the Epiphyseal Plate. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1963. 45 (3) 587-622. Read at J Bone Joint Surg Am
- 2. Primer of Diagnostic Imaging. (2002) ISBN: 0323023282 - Google Books
- 3. Mercer Rang, Maya E. Pring, Dennis Ray Wenger. Rang's Children's Fractures. (2005) ISBN: 9780781752862 - Google Books
- 4. Little J, Klionsky N, Chaturvedi A, Soral A, Chaturvedi A. Pediatric Distal Forearm and Wrist Injury: An Imaging Review. Radiographics. 2014;34(2):472-90. doi:10.1148/rg.342135073 - Pubmed
- 5. Chen J, Abel M, Fox M. Imaging Appearance of Entrapped Periosteum Within a Distal Femoral Salter-Harris II Fracture. Skeletal Radiol. 2015;44(10):1547-51. doi:10.1007/s00256-015-2201-x - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Describing a fracture (an approach)
- Salter-Harris fracture classification (mnemonic)
- Tillaux fracture
- Metaphyseal fracture
- Physeal fracture
- Salter-Harris type V fracture
- Physeal arrest
- Triplane fracture
- Physis
- Thurstan Holland fragment
- Eponymous fractures
- Greenstick fracture
- Paediatric shoulder radiograph (an approach)
- Salter-Harris type IV fracture
- Delbet classification
- Salter-Harris type III fracture
- Medical abbreviations and acronyms (S)
- Focal periphyseal oedema zone
- Slipped upper femoral epiphysis
- Salter-Harris type I fracture
- Little finger proximal phalanx fracture
- Salter-Harris type III fracture
- Slipped upper femoral epiphysis
- Salter-Harris type II fracture - wrist
- Transphyseal fracture of the distal femur
- Salter-Harris type IV fracture
- Triplane fracture
- Salter Harris type II wrist injury
- Salter-Harris type II injury
- Distal radial fracture - Salter-Harris 2
- Triplane fracture
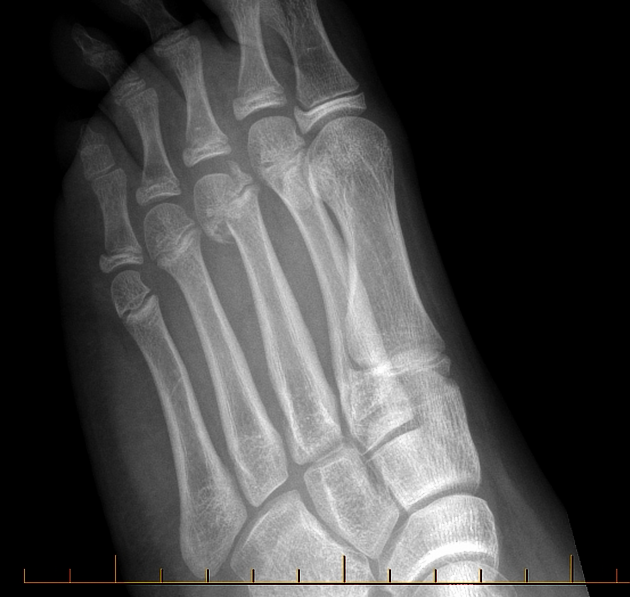
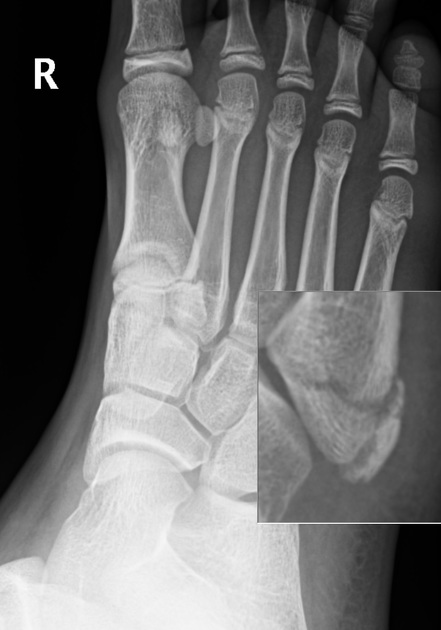
- Salter-Harris type II fracture of first metatarsal bone
- Proximal tibia metaphyseal fracture - Salter-Harris ΙΙ
- Distal fibula fracture - Salter-Harris type II
- Salter-Harris type II fracture
- Paediatric hand anatomy (illustration)
- Tillaux fracture
- Neonatal distal humeral fracture - ultrasound
- Lateral humeral condyle fracture - Milch type 2
- Salter-Harris type I fracture of distal radius
Related articles: Fractures
-
fracture
- terminology
- fracture location
- diaphyseal fracture
- metaphyseal fracture
- physeal fracture
- epiphyseal fracture
- fracture types[+][+]
- avulsion fracture
- articular surface injuries
- complete fracture
- incomplete fracture
- infraction
- compound fracture
- pathological fracture
- stress fracture
- fracture displacement[+][+]
- fracture location
- fracture healing[+][+]
- skull fractures[+][+]
-
facial fractures[+][+]
- fractures involving a single facial buttress
- alveolar process fractures
- frontal sinus fracture
- isolated zygomatic arch fractures
- mandibular fracture
- nasal bone fracture
- orbital blow-out fracture
- paranasal sinus fractures
- complex fractures
- dental fractures
- fractures involving a single facial buttress
-
spinal fractures[+][+]
- classification (AO Spine classification systems)
-
cervical spine fracture classification systems
- AO classification of upper cervical injuries
- AO classification of subaxial injuries
- Anderson and D'Alonzo classification (odontoid fracture)
- Roy-Camille classification (odontoid process fracture)
- Gehweiler classifcation (atlas fractures)
- Levine and Edwards classification (hangman fracture)
- Allen and Ferguson classification (subaxial spine injuries)
- subaxial cervical spine injury classification (SLIC)
- thoracolumbar spinal fracture classification systems
- three column concept of spinal fractures (Denis classification)
- classification of sacral fractures
-
cervical spine fracture classification systems
- spinal fractures by region
- spinal fracture types
- classification (AO Spine classification systems)
- rib fractures[+][+]
- sternal fractures
-
upper limb fractures[+][+]
- classification
- Rockwood classification (acromioclavicular joint injury)
- AO classification (clavicle fracture)
- Neer classification (clavicle fracture)
- Neer classification (proximal humeral fracture)
- AO classification (proximal humeral fracture)
- AO/OTA classification of distal humeral fractures
- Milch classification (lateral humeral condyle fracture)
- Weiss classification (lateral humeral condyle fracture)
- Bado classification of Monteggia fracture-dislocations (radius-ulna)
- Mason classification (radial head fracture)
- Frykman classification (distal radial fracture)
- Mayo classification (scaphoid fracture)
- Hintermann classification (gamekeeper's thumb)
- Eaton classification (volar plate avulsion injury)
- Keifhaber-Stern classification (volar plate avulsion injury)
- upper limb fractures by region
- shoulder
- clavicular fracture
-
scapular fracture
- acromion fracture
- coracoid process fracture
- glenoid fracture
- humeral head fracture
- proximal humeral fracture
- humeral neck fracture
- arm
- elbow
- forearm
- wrist
-
carpal bones
- scaphoid fracture
- lunate fracture
- capitate fracture
- triquetral fracture
- pisiform fracture
- hamate fracture
- trapezoid fracture
- trapezium fracture
- hand
- shoulder
- classification
- lower limb fractures[+][+]
- classification by region
- pelvic fractures
- hip fractures
- Pipkin classification (femoral head fracture)
- Garden classification (hip fracture)
- American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- Cooke and Newman classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- Johansson classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- Vancouver classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- femoral
- knee
- Schatzker classification (tibial plateau fracture)
- AO classification of distal femur fractures
- Meyers and McKeevers classification (anterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture)
- tibia/fibula
- Watson-Jones classification (tibial tuberosity avulsion fracture)
- ankle
- foot
- Berndt and Harty classification (osteochondral lesions of the talus)
- Sanders CT classification (calcaneal fracture)
- Hawkins classification (talar neck fracture)
- Myerson classification (Lisfranc injury)
- Nunley-Vertullo classification (Lisfranc injury)
- pelvis and lower limb fractures by region
- pelvic fracture
- sacral fracture
- coccygeal fracture
-
hip
- acetabular fracture
- femoral head fracture
-
femoral neck fracture
- subcapital fracture
- transcervical fracture
- basicervical fracture
-
trochanteric fracture
- pertrochanteric fracture
- intertrochanteric fracture
- subtrochanteric fracture
- femur
- mid-shaft fracture
- bisphosphonate-related fracture
- distal femoral fracture
- knee
- avulsion fractures
- Segond fracture
- reverse Segond fracture
- anterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture
- posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture
- arcuate complex avulsion fracture (arcuate sign)
- biceps femoris avulsion fracture
- iliotibial band avulsion fracture
- semimembranosus tendon avulsion fracture
- Stieda fracture (MCL avulsion fracture)
- patellar fracture
- tibial plateau fracture
- avulsion fractures
- leg
- tibial tuberosity avulsion fracture
- tibial shaft fracture
- fibular shaft fracture
- Maisonneuve fracture
- ankle
- foot
- tarsal bones
- metatarsal bones
- phalanges
- classification by region
- terminology





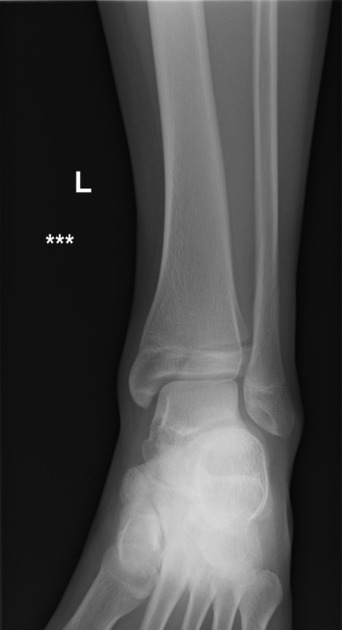
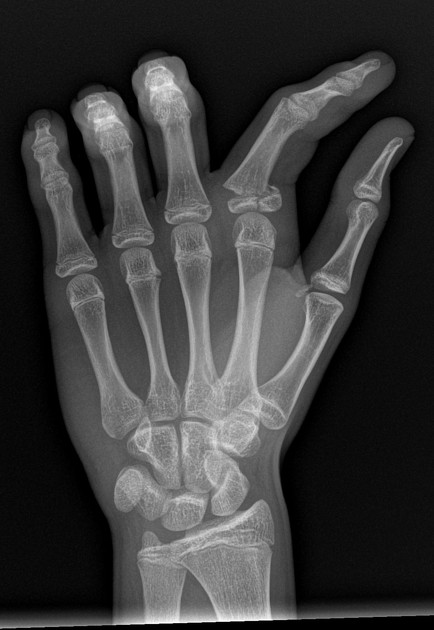
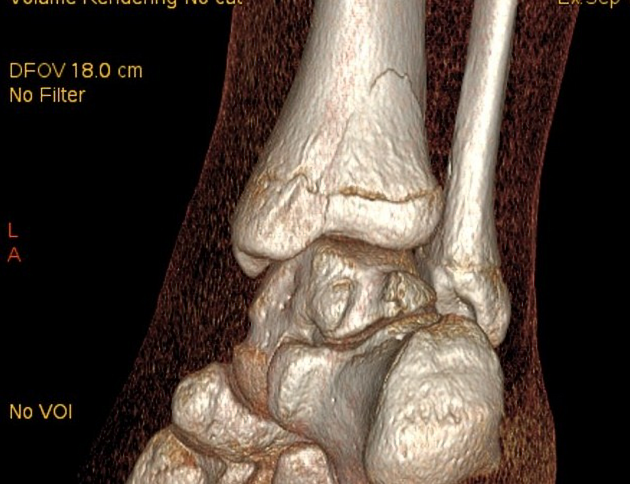
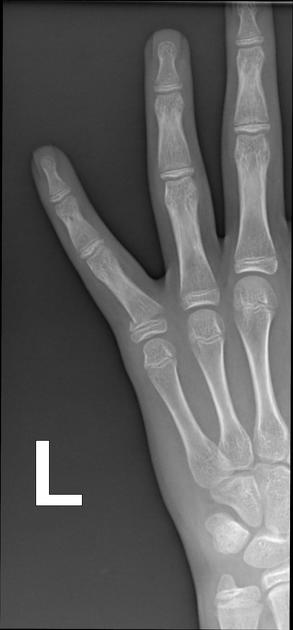
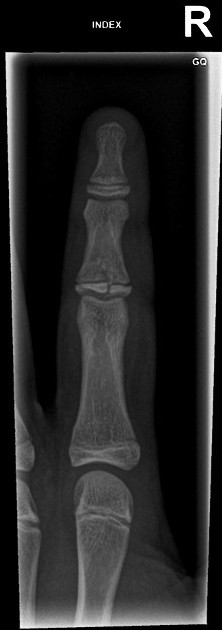
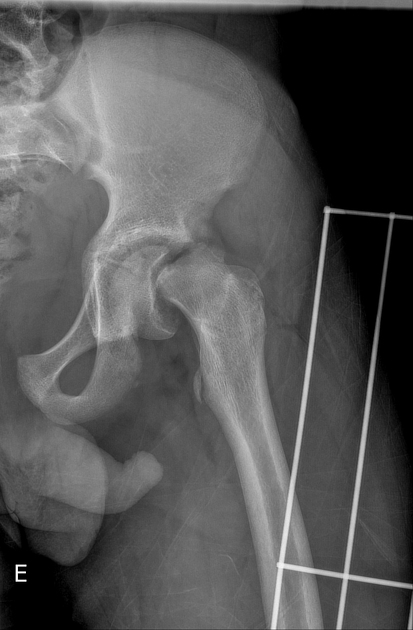


 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.