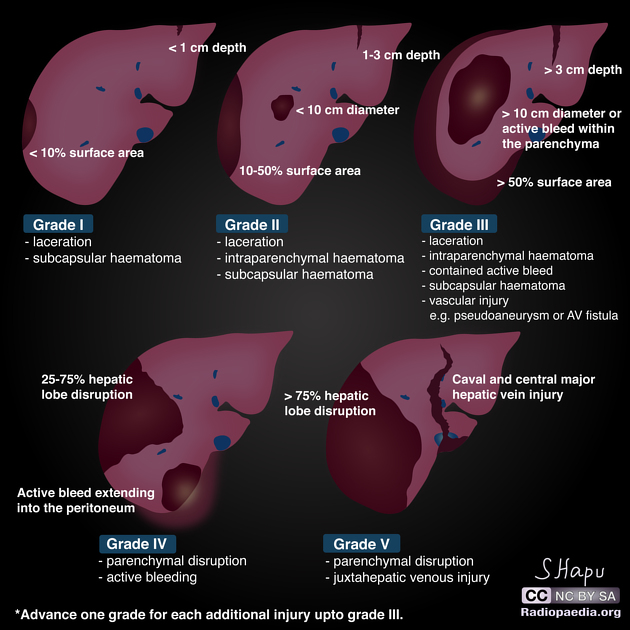
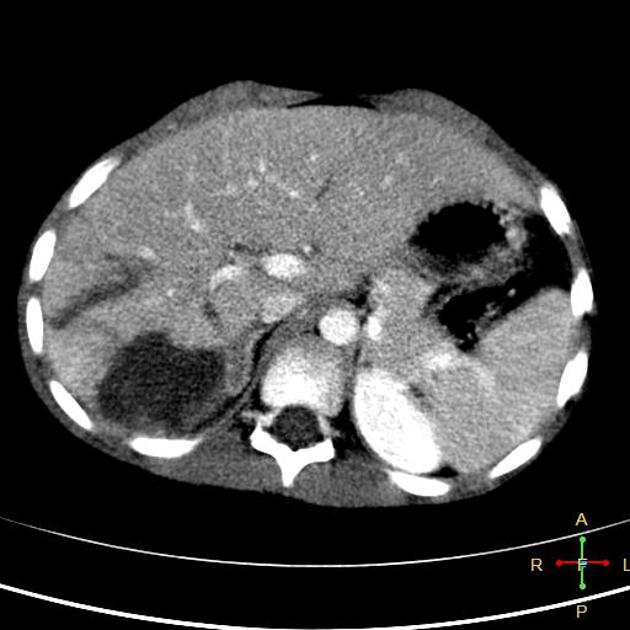
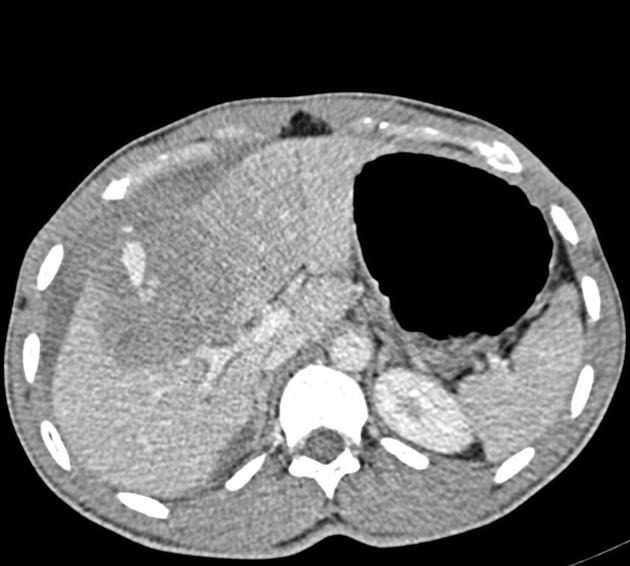
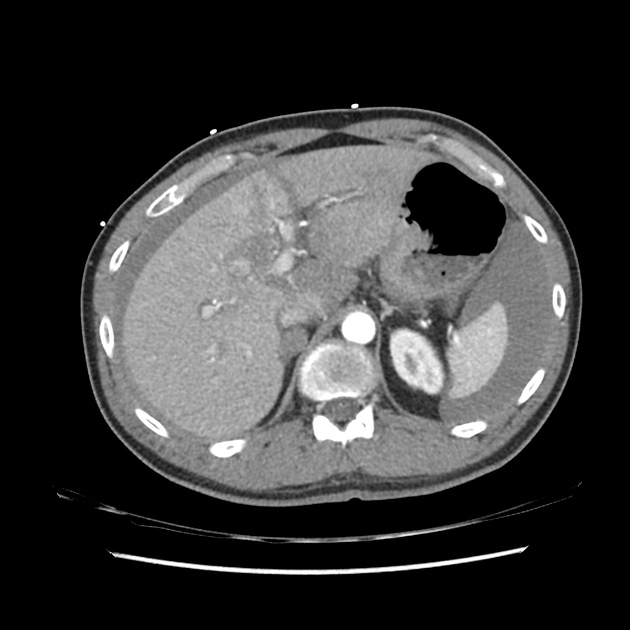
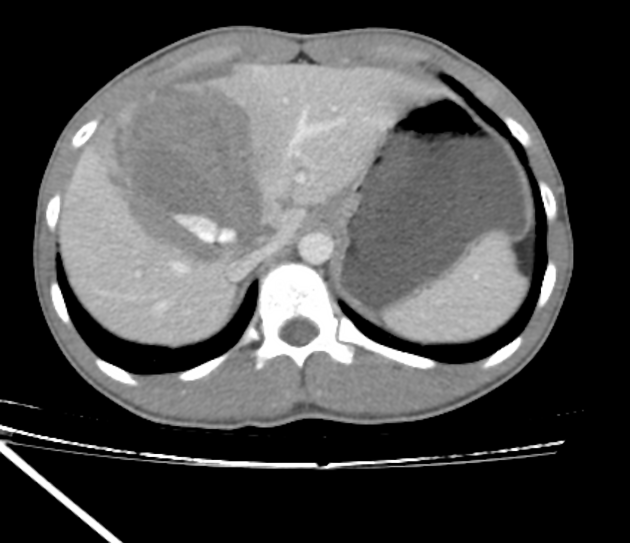
The AAST (American Association for the Surgery of Trauma) liver injury scale, revised in 2018, is the most widely used liver injury grading system 3.
The 2018 update incorporates "vascular injury" (i.e. pseudoaneurysm, arteriovenous fistula) into the imaging criteria for visceral injury 3. Couinaud hepatic segments are also no longer used to quantify injury 5.
There are imaging, surgical, and pathologic criteria which can be used to grade injury 3. This page highlights the imaging criteria.
On this page:
Classification
-
grade I
haematoma: subcapsular, <10% surface area
laceration: capsular tear, <1 cm parenchymal depth
-
grade II
haematoma: subcapsular, 10-50% surface area
haematoma: intraparenchymal <10 cm diameter
laceration: capsular tear 1-3 cm parenchymal depth, <10 cm length
-
grade III
haematoma: subcapsular, >50% surface area; ruptured subcapsular or parenchymal haematoma
haematoma: intraparenchymal >10 cm
laceration: capsular tear >3 cm parenchymal depth
vascular injury with active bleeding contained within liver parenchyma
-
grade IV
laceration: parenchymal disruption involving 25-75% of a hepatic lobe
vascular injury with active bleeding breaching the liver parenchyma into the peritoneum
-
grade V
laceration: parenchymal disruption involving >75% of hepatic lobe
vascular: juxtahepatic venous injuries (retrohepatic vena cava / central major hepatic veins)
Additional points
advance one grade for multiple injuries up to grade III
for each grade, the worst feature is chosen, either haematoma or laceration (no need for both/all to coexist)
vascular injury (i.e. pseudoaneurysm or AV fistula): appears as a focal collection of vascular contrast which decreases in attenuation on delayed images
active bleeding: focal or diffuse collection of vascular contrast which increases in size or attenuation on a delayed phase
Imaging technique
The AAST guidelines recommend dual arterial/portal venous phase imaging to evaluate a vascular injury of the liver, spleen, or kidney 3.
External links
If any of these links are broken or for other problems and questions, please contact editors@radiopaedia.org.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.