Anconeus epitrochlearis muscle
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Imran Jindani had no recorded disclosures.
View Imran Jindani's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Daniel J Bell had no recorded disclosures.
View Daniel J Bell's current disclosures- Anconeus epitrochlearis muscle
- Accessory anconeus muscle
- Accessory anconeus epitrochlearis muscle
- Epitrochleoanconeus muscle
The anconeus epitrochlearis muscle is an accessory muscle of the upper limb at the medial aspect of the elbow. It is also known as the accessory anconeus muscle or epitrochleoanconeus muscle and should not be confused with the anconeus muscle which is present at the lateral aspect of the elbow.
On this page:
Epidemiology
The muscle may be unilateral but has been found to be bilateral in one of four patients with cubital tunnel syndrome 2. It is present in ~15% (range 3-28%) of the population 3.
Clinical presentation
It can be asymptomatic or symptomatic when there is compression of the ulnar nerve within the cubital tunnel, leading to ulnar neuritis.
Gross anatomy
Origin
- medial epicondyle (inferior surface)
Insertion
- olecranon (medial cortex)
The anconeus epitrochlearis muscle contributes to the roof of the cubital tunnel when present, running superficial to the ulnar nerve in the posteromedial aspect of the elbow.
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Radiographic features
Ultrasound
Thin hypoechoic mass superficial to the ulnar nerve. May also demonstrate underlying ulnar nerve changes (thickening and edema) suggestive of cubital tunnel syndrome 4.
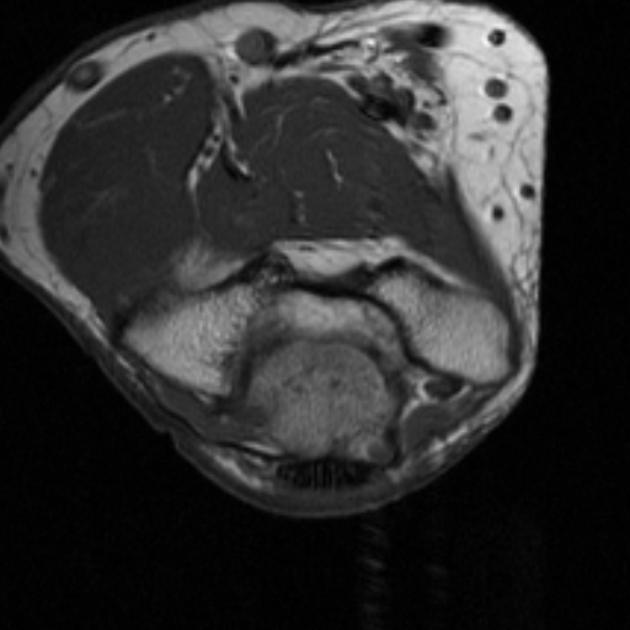
MRI
Axial MR images may demonstrate a mass superficial to the cubital tunnel, where there should normally only be fat.
References
- 1. Stoller DW. Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Orthopaedics and Sports Medicine, 3e. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. (2007) ISBN:0781773571. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Sookur PA, Naraghi AM, Bleakney RR et-al. Accessory muscles: anatomy, symptoms, and radiologic evaluation. Radiographics. 2008;28 (2): 481-99. Radiographics (full text) - doi:10.1148/rg.282075064 - Pubmed citation
- 3. Stein JM, Cook TS, Simonson S et-al. Normal and variant anatomy of the elbow on magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2011;19 (3): 609-19. doi:10.1016/j.mric.2011.05.002 - Pubmed citation
- 4. Okamoto M, Abe M, Shirai H, Ueda N. Diagnostic ultrasonography of the ulnar nerve in cubital tunnel syndrome. (2000) Journal of hand surgery (Edinburgh, Scotland). 25 (5): 499-502. doi:10.1054/jhsb.1999.0350 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Anconeus epitrochlearis accessory muscle - symptomatic
- Cubital tunnel syndrome
- Cubital tunnel syndrome
- Cubital tunnel syndrome due to anconeus epitrochlearis
- Anconeus epitrochlearis
- Superficial thrombophlebitis and anconeus epitrochlearis
- Cubital tunnel syndrome
- Anconeus epitrochlearis
- Anconeus epitrochlearis
- Anconeus epitrochlearis muscle
Related articles: Anatomy: Upper limb
-
skeleton of the upper limb
- clavicle
- scapula
- humerus
- radius
- ulna
- hand
- accessory ossicles of the upper limb
- accessory ossicles of the shoulder
- accessory ossicles of the elbow
-
accessory ossicles of the wrist (mnemonic)
- os centrale carpi
- os epilunate
- os epitriquetrum
- os styloideum
- os hamuli proprium
- lunula
- os triangulare
- trapezium secondarium
- os paratrapezium
- os radiostyloideum (persistent radial styloid)
- joints of the upper limb
-
pectoral girdle
-
shoulder joint
- articulations
- associated structures
- joint capsule
- bursae
- ligaments
- movements
- scapulothoracic joint
-
glenohumeral joint
- arm flexion
- arm extension
- arm abduction
- arm adduction
- arm internal rotation (medial rotation)
- arm external rotation (lateral rotation)
- circumduction
- arterial supply - scapular anastomosis
- ossification centers
-
shoulder joint
-
elbow joint
- proximal radioulnar joint
- ligaments
- associated structures
- movements
- alignment
- arterial supply - elbow anastomosis
- development
-
wrist joint
- articulations
-
ligaments
- intrinsic ligaments
- extrinsic ligaments
- radioscaphoid ligament
- dorsal intercarpal ligament
- dorsal radiotriquetral ligament
- dorsal radioulnar ligament
- volar radioulnar ligament
- radioscaphocapitate ligament
- long radiolunate ligament
- Vickers ligament
- short radiolunate ligament
- ulnolunate ligament
- ulnotriquetral ligament
- ulnocapitate ligament
- ulnar collateral ligament
- associated structures
- extensor retinaculum
- flexor retinaculum
- joint capsule
- movements
- alignment
- ossification centers
-
hand joints
- articulations
- carpometacarpal joint
-
metacarpophalangeal joints
- palmar ligament (plate)
- collateral ligament
-
interphalangeal joints
- palmar ligament (plate)
- collateral ligament
- movements
- ossification centers
- articulations
-
pectoral girdle
- spaces of the upper limb
- muscles of the upper limb
- shoulder girdle
- anterior compartment of the arm
- posterior compartment of the arm
-
anterior compartment of the forearm
- superficial
- intermediate
- deep
-
posterior compartment of the forearm (extensors)
- superficial
- deep
- muscles of the hand
-
accessory muscles
- elbow
- volar wrist midline
- palmaris longus profundus
- aberrant palmaris longus
- volar wrist radial-side
- accessory flexor digitorum superficialis indicis
- flexor indicis profundus
- flexor carpi radialis vel profundus
- accessory head of the flexor pollicis longus (Gantzer muscle, common)
- volar wrist ulnar-side
- dorsal wrist
- blood supply to the upper limb
-
arteries
- subclavian artery (mnemonic)
- axillary artery
- brachial artery (proximal portion)
- ulnar artery
- radial artery
- veins
-
arteries
- innervation of the upper limb
- intercostobrachial nerve
-
brachial plexus (mnemonic)
- branches from the roots
- branches from the trunks
- branches from the cords
- lateral cord
- posterior cord
- medial cord
- terminal branches
- lymphatic drainage of the upper limb







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.