Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction complications are common, occurring in 10-25% of patients.
On this page:
Images:
Clinical presentation
Patients with complications of ACL reconstruction can present with decreased range of motion (impingement or arthrofibrosis) and/or laxity (graft rupture or stretching) 2.
Pathology
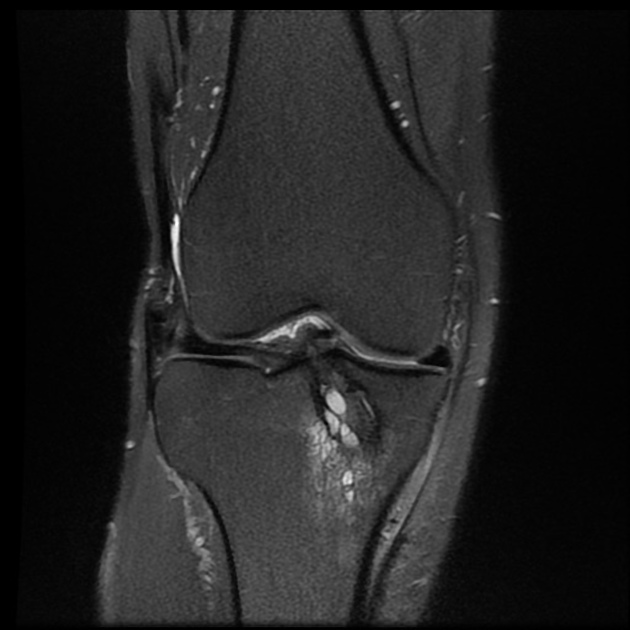
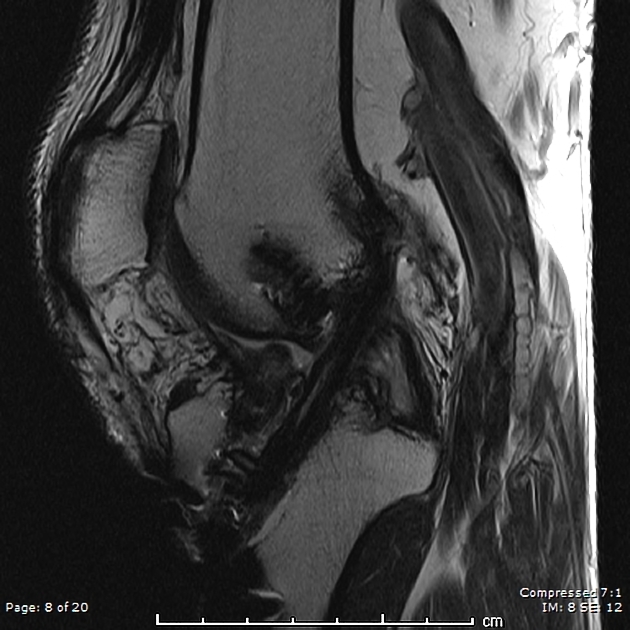
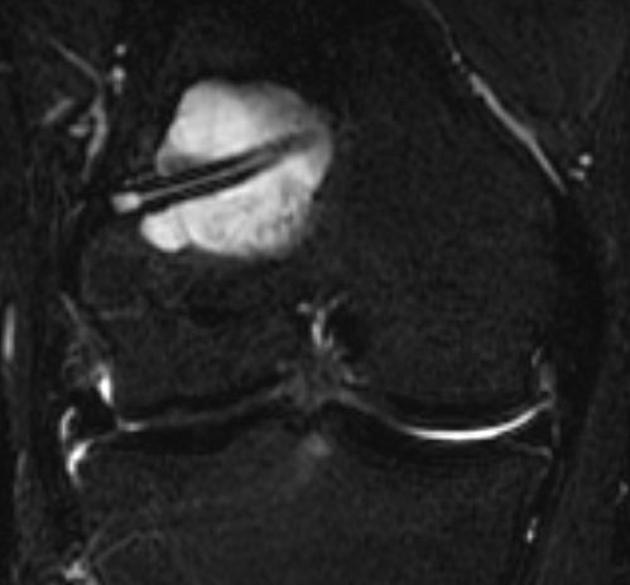
Complications include 1-3:
-
decreased range of motion
-
femoral or tibial tunnel cyst
more common on the tibial side
-
post-operative laxity: occurs in 1-8% of patients 3
-
acute or chronic: in chronic rupture the graft is not visible on MRI due to resorption over time
-
miscellaneous
fixation material complication: e.g. migration, displacement, fragmentation, screw extrusion
inflammatory reaction/rejection
infection
tunnel osteolysis: defined as tunnel widening >14 mm; may require two-stage revision ACL reconstruction 5
septic arthritis: ~0.5% (range 0.1-0.9%)
retractile capsulitis
donor tendon complication: e.g. rupture, shortening
vascular complications: e.g. inferior geniculate artery pseudoaneurysms at donor tendon sites
stress fractures: more common on the femoral side





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.