Balthazar score (acute pancreatitis)
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Ayush Goel had no recorded disclosures.
View Ayush Goel's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Henry Knipe had the following disclosures:
- Micro-X Ltd, Shareholder (past)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosures- Balthazar's score
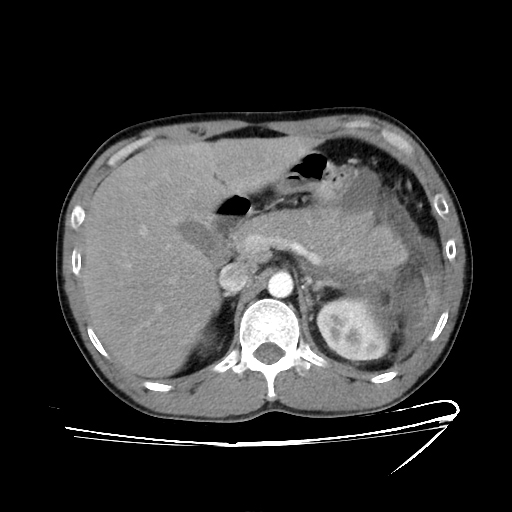
The Balthazar score is a subscore within the CT severity index (CTSI) for grading acute pancreatitis.
The CTSI sums two scores:
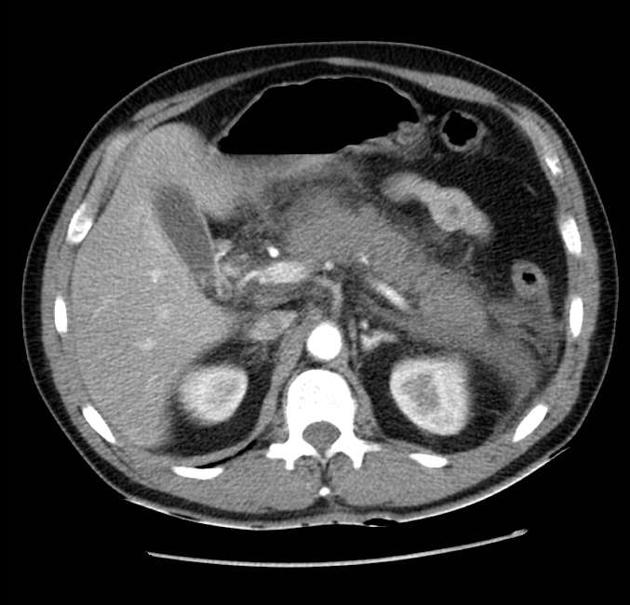
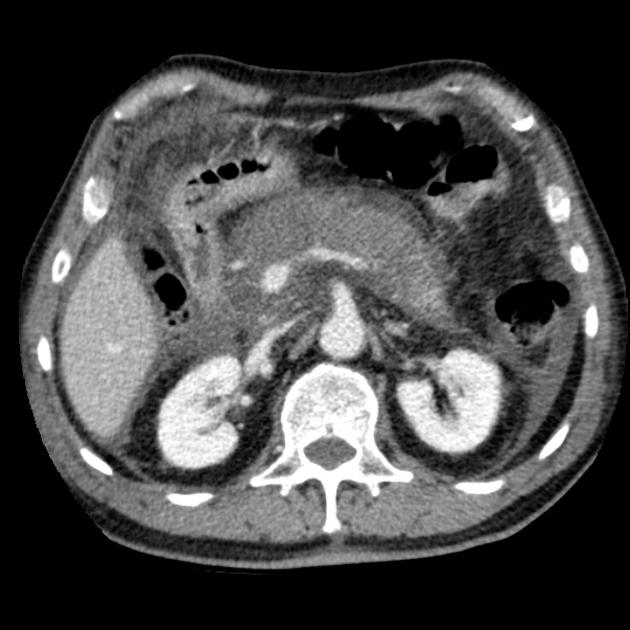
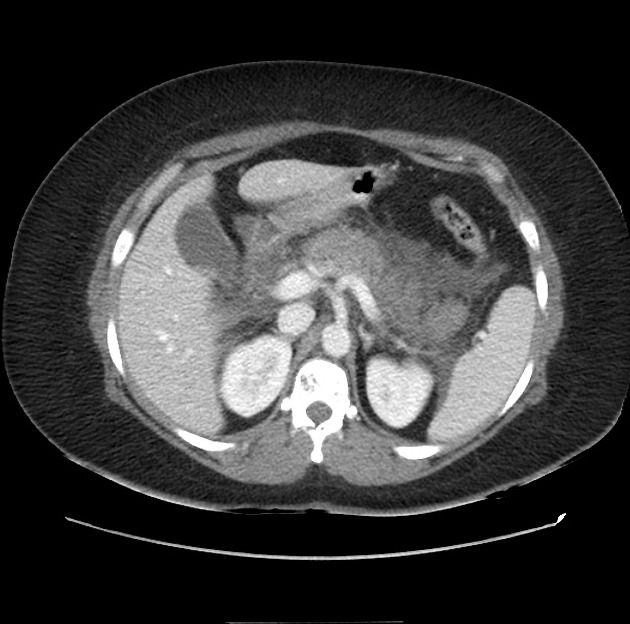
Balthazar score: grading of pancreatitis (A-E)
grading the extent of pancreatic necrosis
The Balthazar score was originally used alone, but adding a score for pancreatic necrosis improved the correlation with clinical severity scores.
The CTSI has since been updated to the modified CTSI (2004).
On this page:
CTSI
Grading of pancreatitis (Balthazar score)
A: normal pancreas: 0
B: enlargement of pancreas: 1
C: inflammatory changes in pancreas and peripancreatic fat: 2
D: ill-defined single peripancreatic fluid collection: 3
E: two or more poorly defined peripancreatic fluid collections: 4
Pancreatic necrosis
none: 0
≤30%: 2
>30-50%: 4
>50%: 6
The maximum score that can be obtained is 10.
Stratification of pancreatitis severity
mild pancreatitis (interstitial pancreatitis): Balthazar B or C, without pancreatic or extrapancreatic necrosis
intermediate (exudative pancreatitis): Balthazar D or E, without pancreatic necrosis; peripancreatic collections are due to extrapancreatic necrosis
severe pancreatitis (necrotizing): necrosis of the pancreas (non-enhancing areas in the pancreas on contrast-enhanced CT)
Treatment and prognosis
There is good correlation of clinical pancreatitis scores and current CT pancreatitis severity scores (such as the CTSI and modified CTSI) so imaging is not always necessary to assess the severity of pancreatitis 3.
See also
References
- 1. Balthazar EJ, Freeny PC, Vansonnenberg E. Imaging and intervention in acute pancreatitis. Radiology. 1994;193 (2): 297-306. Radiology (abstract) - Pubmed citation
- 2. Balthazar EJ. Acute pancreatitis: assessment of severity with clinical and CT evaluation. Radiology. 2002;223 (3): 603-13. Radiology (full text) - doi:10.1148/radiol.2233010680 - Pubmed citation
- 3. Bollen TL, Singh VK, Maurer R et-al. A comparative evaluation of radiologic and clinical scoring systems in the early prediction of severity in acute pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011;107 (4): 612-9. doi:10.1038/ajg.2011.438 - Pubmed citation
Incoming Links
- Acute pancreatitis
- Necrotising pancreatitis with hypoperfusion complex
- Necrotising pancreatitis
- Acute pancreatitis - Balthazar C
- Acute pancreatitis - Balthazar E
- Acute pancreatitis
- Acute pancreatitis - Balthazar C
- Necrotising emphysematous pancreatitis
- Acute pancreatitis - Balthazar E
- Acute pancreatitis - Balthazar E
- Acute pancreatitis
Related articles: Pathology: Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary
- liver
- depositional disorders
- infection and inflammation
- liver abscess
- hepatic hydatid infection
- cirrhosis
- hepatitis
- cholecystitis
- cholangitis
- malignancy
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumors
- benign epithelial tumors
- hepatocellular hyperplasia
- hepatocellular adenoma
- hepatic/biliary cysts
- benign nonepithelial tumors
- primary malignant epithelial tumors
- hepatocellular carcinoma
- hepatocellular carcinoma variants
-
cholangiocarcinoma
- intra-hepatic
- mass-forming type
- periductal infiltrating type - Klatskin tumors
- intraductal growing type
- extra-hepatic/large duct type
- intra-hepatic
- biliary cystadenocarcinoma
- combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma
- hepatoblastoma
- undifferentiated carcinoma
- primary malignant nonepithelial tumors
- hematopoietic and lymphoid tumors
- primary hepatic lymphoma
- hepatic myeloid sarcoma (hepatic chloroma)
- secondary tumors
- miscellaneous
- adrenal rest tumors
- hepatic carcinosarcoma
- hepatic fibroma
- hepatic hemangioma
- hepatic Kaposi sarcoma
- hepatic lipoma
- hepatic mesenchymal hamartoma
- hepatic myxoma
- hepatic rhabdoid tumor
- hepatic solitary fibrous tumor
- hepatic teratoma
- hepatic yolk sac tumor
- inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (inflammatory pseudotumor)
- nodular regenerative hyperplasia
- pancreatic rest tumors
- primary hepatic carcinoid
- benign epithelial tumors
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumors
- metabolic
- trauma
-
vascular and perfusion disorders
- portal vein related
- hepatic artery related
- hepatic veins related
- inferior vena cava related
- other
- third inflow
- liver thrombotic angiitis
- infra diaphragmatic total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR)
- hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease)
- pancreas
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- cystic neoplasm (cystic pancreatic mass differential diagnosis)
- solid neoplasm
- non-epithelial pancreatic neoplasms
- others
- simple pancreatic cyst
-
pancreatitis (mnemonic for the causes)
- acute pancreatitis
- chronic pancreatitis
- Ascaris-induced pancreatitis
- tropical pancreatitis
- autoimmune pancreatitis
- emphysematous pancreatitis
- hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis
- hereditary pancreatitis
- pancreatitis associated with cystic fibrosis
- pancreaticopleural fistula
- segmental pancreatitis
- pancreatic atrophy
- pancreatic lipomatosis
- pancreatic trauma
- pancreatic transplant
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- gallbladder and biliary
- congenital malformations and anatomical variants
- gallstones
- gallbladder inflammation
- bile ducts inflammation
- gallbladder wall abnormalities
- other gallbladder abnormalities
- bile duct dilatation (differential)
- bile duct wall thickening (differential)
- bile ducts neoplasms




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.