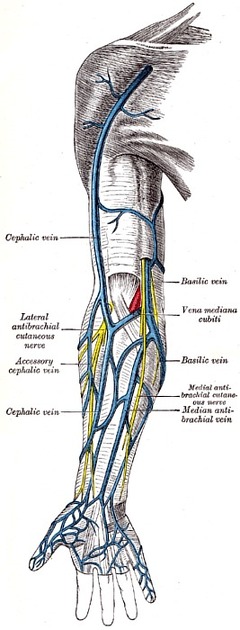
The basilic vein, along with the cephalic vein, is one of the primary superficial veins that drain the upper limb 1. It courses through both the forearm and arm, and contributes to the formation of the axillary vein.
On this page:
Images:
Summary
origin: ulnar aspect of the superficial venous network of the dorsum of the hand
location: courses upwards on the medial aspect of the forearm and arm
drainage: palm of the hand, medial aspect of the forearm and arm
tributaries: median cubital vein and median antebrachial vein
termination: joins the brachial vein in the axilla to form the axillary vein
Gross anatomy
Origin
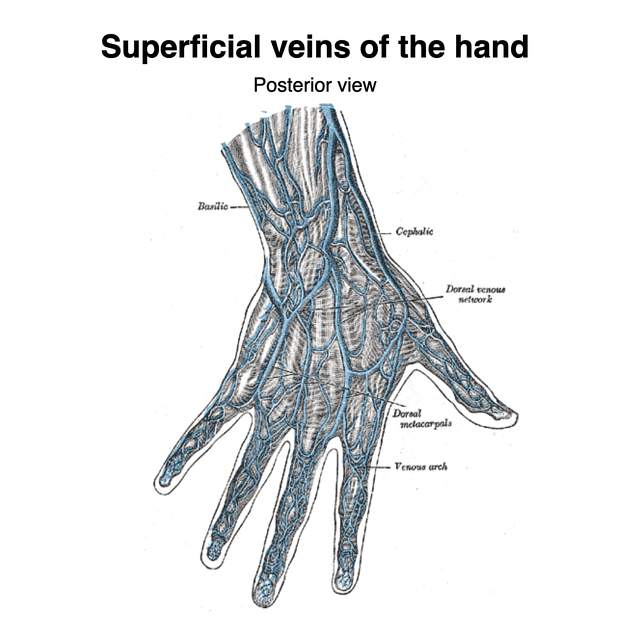
The basilic vein arises from the ulnar side of the superficial venous network of the dorsum of the hand 2.
Course
From the ulnar aspect of the superficial venous network, the basilic vein ascends posteromedially in the forearm towards the anterior elbow region to pass anterior to the medial epicondyle of the humerus 1,3. In the brachium it continues to ascend anteromedially until it penetrates the brachial fascia at the basilic hiatus, halfway between the elbow and axilla 2,3. The basilic vein then courses medial to the brachial artery until it unites with the brachial veins in the axilla to form the axillary vein 1,4.
Tributaries
Superficial veins of the upper limb are highly variable and have multiple superficial tributaries which drain into them 5. Two such variable tributaries of the basilic vein include:
-
connects the basilic vein to the cephalic vein in the anterior aspect of the cubital fossa 1,3.
it is a common site for venipuncture 5.
-
arises from the palmar venous plexus on the palm of the hand, which drains the palmar digital veins. It courses anteriorly in the forearm and drains the subcutaneous tissue of the anterior wrist and forearm 2.
it terminates into the basilic or median cubital veins (1,3).
in some cases the median antebrachial vein divides into median cephalic and median basilic veins at the elbow, which then drain into the cephalic and basilic veins respectively 2.
Termination
The basilic vein terminates by uniting with the paired brachial veins to form the axillary vein at the inferior border of the teres major muscle 4.
Drainage
The basilic vein drains the medial side of the superficial venous network of the dorsum of the hand, which in turn drains blood from the palm of the hand 2. As it ascends in the forearm and arm, the basilic vein drains the medial aspect of the upper limb via numerous superficial veins 1.
Radiographic features
Ultrasound
Basilic vein is a frequent venipuncture site. It is located at 1.2 cm (0.4 to 3.5 cm) medial to the brachial artery at the antecubital fossa 6. The visibility basilic vein after tourniquet application is 65% 6.






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.