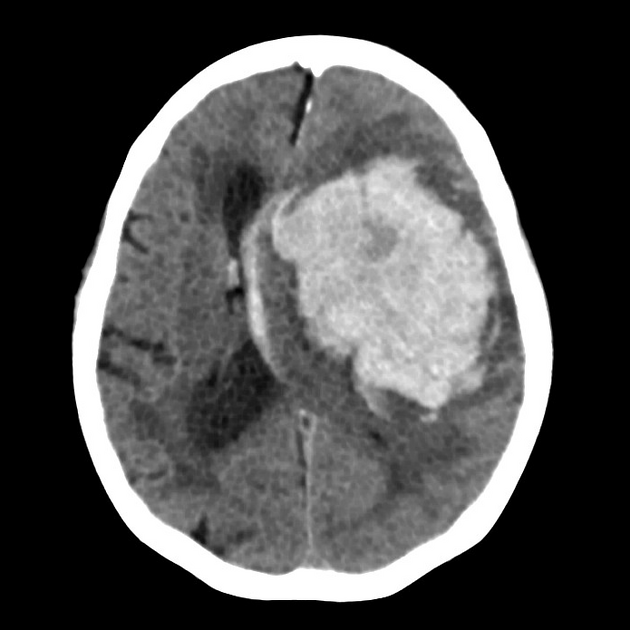
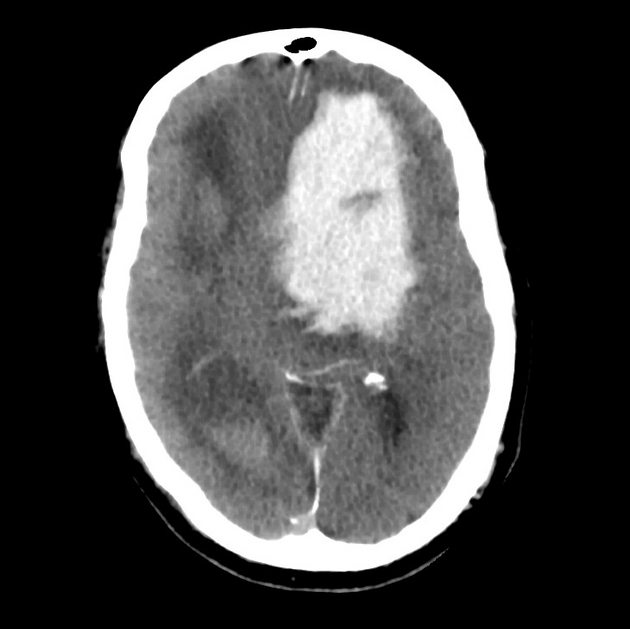
Black hole sign (intracerebral haemorrhage)
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Khalid Alhusseiny had no recorded disclosures.
View Khalid Alhusseiny's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Rohit Sharma had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Rohit Sharma's current disclosures- CT black hole sign
The black hole sign refers to the non-contrast CT appearance of acute extravasation of blood into a haematoma, for example, an intracerebral haemorrhage, and therefore is a predictor of haemorrhage expansion 3. It can be thought of as an encapsulated swirl sign.
Radiographic features
The black hole sign represents a well-defined hypodense region within a hyperdense haematoma that is not connected to the nearby brain parenchyma 1,3. It may have a variable shape (e.g. round, oval, rod-like). There should be at least a 28 Hounsfield unit (HU) difference between the black hole and the surrounding haemorrhage 1,3.
Some data suggest this sign to be more specific in patients taking warfarin than direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) 4.
References
- 1. Li Q, Zhang G, Xiong X et al. Black Hole Sign. Stroke. 2016;47(7):1777-81. doi:10.1161/strokeaha.116.013186
- 2. Shakya M, Fu F, Zhang M et al. Comparison of Black Hole Sign, Satellite Sign, and Iodine Sign to Predict Hematoma Expansion in Patients with Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage. BioMed Research International. 2021;2021:1-8. doi:https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/3919710
- 3. Morotti A, Boulouis G, Dowlatshahi D et al. Standards for Detecting, Interpreting, and Reporting Noncontrast Computed Tomographic Markers of Intracerebral Hemorrhage Expansion. Ann Neurol. 2019;86(4):480-92. doi:10.1002/ana.25563 - Pubmed
- 4. Sato H, Kinoshita M, Takano T et al. Black Hole Sign Under Anticoagulant Therapy: A Retrospective Comparison of Warfarin and Direct Oral Anticoagulants. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2024;:ajnr.A8528. doi:10.3174/ajnr.a8528 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Stroke and intracranial haemorrhage
-
stroke and intracranial haemorrhage
- general articles
-
ischaemic stroke
- general discussions
- scoring and classification systems
- Alberta stroke program early CT score (ASPECTS)
- ASCOD classification
- Canadian Neurological Scale
- Heidelberg bleeding classification
- NIH Stroke Scale
- Mathew stroke scale
- modified Rankin scale
- Orgogozo Stroke Scale
- Scandinavian Stroke Scale
- thrombolysis in cerebral infarction (TICI) scale
- TOAST classification
- collateral vessel scores
- signs
- by region
- hemispheric infarcts
- frontal lobe infarct
- parietal lobe infarct
- temporal lobe infarct
- occipital lobe infarct
- alexia without agraphia syndrome: PCA
- cortical blindness syndrome (Anton syndrome): top of basilar or bilateral PCA
- Balint syndrome: bilateral PCA
- lacunar infarct
-
thalamic infarct
- artery of Percheron infarct
- Déjerine-Roussy syndrome (thalamic pain syndrome): thalamoperforators of PCA
- top of the basilar syndrome
- striatocapsular infarct
- choroid plexus infarct
- cerebellar infarct
-
brainstem infarct
- midbrain infarct
- Benedikt syndrome: PCA
- Claude syndrome: PCA
- Nothnagel syndrome: PCA
- Weber syndrome: PCA
- Wernekink commissure syndrome
- pontine infarct
- Brissaud-Sicard syndrome
- facial colliculus syndrome
- Gasperini syndrome: basilar artery or AICA
- inferior medial pontine syndrome (Foville syndrome): basilar artery
- lateral pontine syndrome (Marie-Foix syndrome): basilar artery or AICA
- locked-in syndrome: basilar artery
- Millard-Gubler syndrome: basilar artery
- Raymond syndrome: basilar artery
- medullary infarct
- Babinski-Nageotte syndrome
- Cestan-Chenais syndrome
- hemimedullary syndrome (Reinhold syndrome)
- lateral medullary stroke syndrome (Wallenberg syndrome)
- medial medullary syndrome (Déjerine syndrome)
- Opalski syndrome
- midbrain infarct
- acute spinal cord ischaemia syndrome
- hemispheric infarcts
- by vascular territory
- by vessel size
- treatment options
- complications
-
intracranial haemorrhage
-
intra-axial haemorrhage
- signs and formulas
- ABC/2 (volume estimation)
- black hole sign
- blend sign
- cashew nut sign
- CTA spot sign
- island sign
- satellite sign
- swirl sign
- zebra sign
- by type
- by location
- signs and formulas
- extra-axial haemorrhage
- extradural haemorrhage (EDH)
- intralaminar dural haemorrhage
- subdural haemorrhage (SDH)
-
subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH)
- types
- complications
- grading systems
- subpial haemorrhage
-
intra-axial haemorrhage




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.