Bladder outlet obstruction
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Nasir Siddiqui had no recorded disclosures.
View Nasir Siddiqui's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Khalid Alhusseiny had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Khalid Alhusseiny's current disclosures- Bladder outlet obstruction (BOO)
- Primary bladder neck obstruction
- Bladder neck obstruction
- Chronic bladder outlet obstruction
Bladder outlet obstruction can arise from a number of conditions affecting the urethra and/or bladder outlet but is most commonly encountered in elderly men due to prostate enlargement.
On this page:
Clinical presentation
Patients often present with difficulty in urination, retention, and urinary discomfort 2,7.
Pathology
Obstruction can be caused by a wide range both functional and anatomical causes that varies by sex, a non-exhaustive list includes:
-
anatomical
iatrogenic, e.g. anti-incontinence surgery (in females) 6,7
-
mass lesions within the periurethral region
-
benign
in males: prostate enlargement (most common cause) 1,7
in females: ovarian cyst, uterine fibroid 7
malignant, e.g. urethral cancer, vaginal cancer, cervical cancer 7
-
urethral strictures: more common in males than females 1,7
-
functional
-
sphincteric dyssynergia
from neurogenic cause, e.g. multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury 7
without neurogenic cause, i.e. primary bladder neck obstruction 7
-
sphincteric pseudodyssynergia
from dysfunctional voiding related to learned behaviour or pain syndromes 7
-
Radiographic features
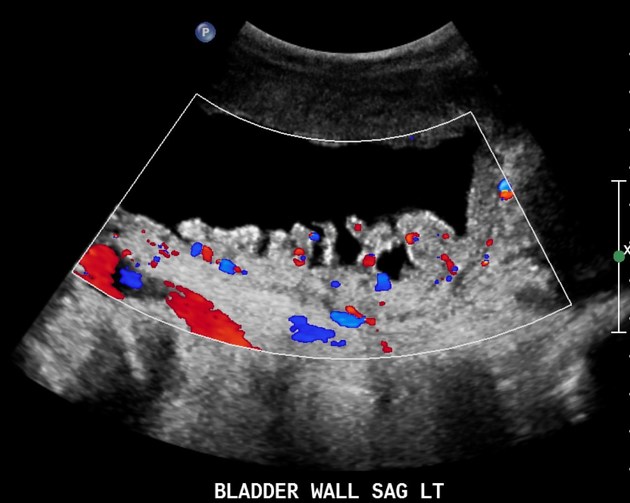
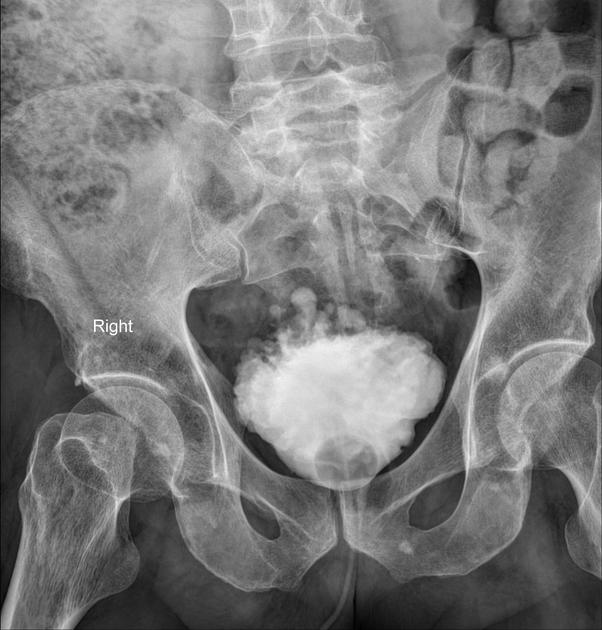
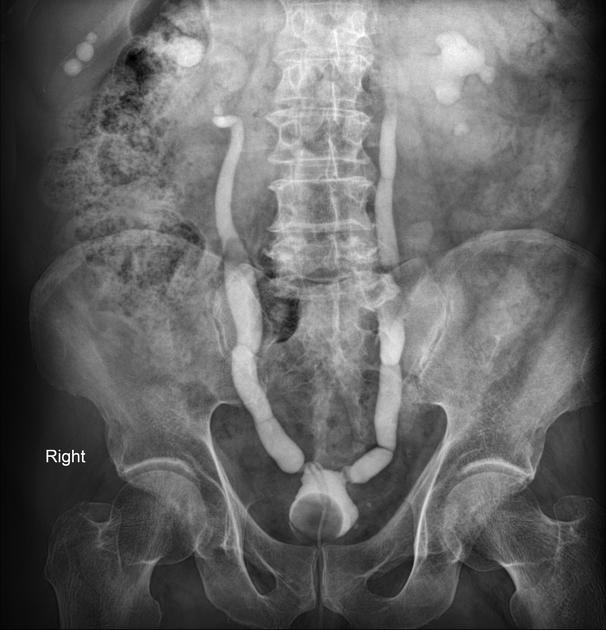
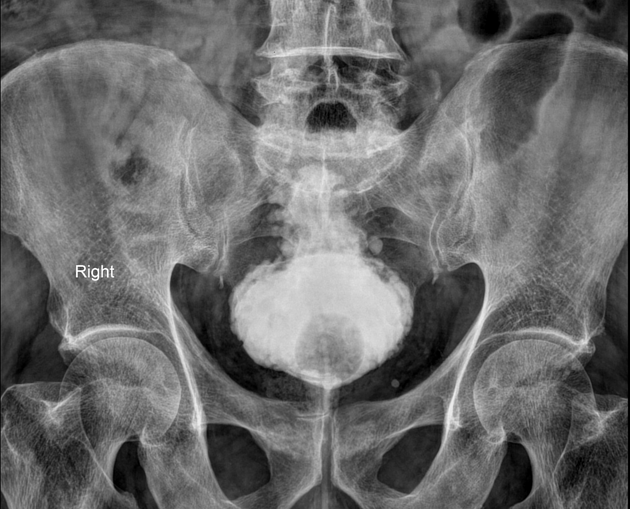
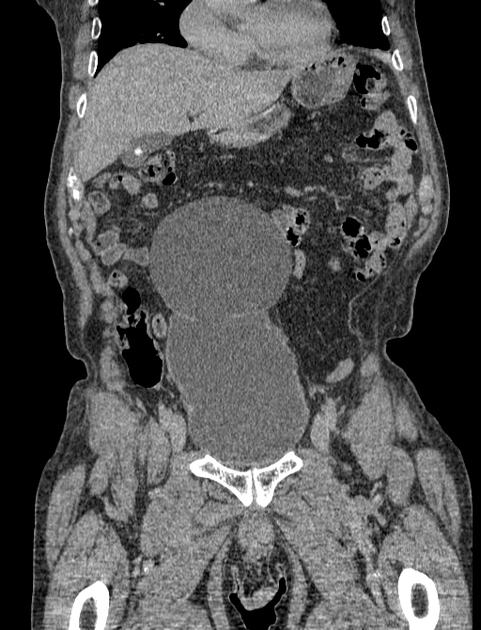
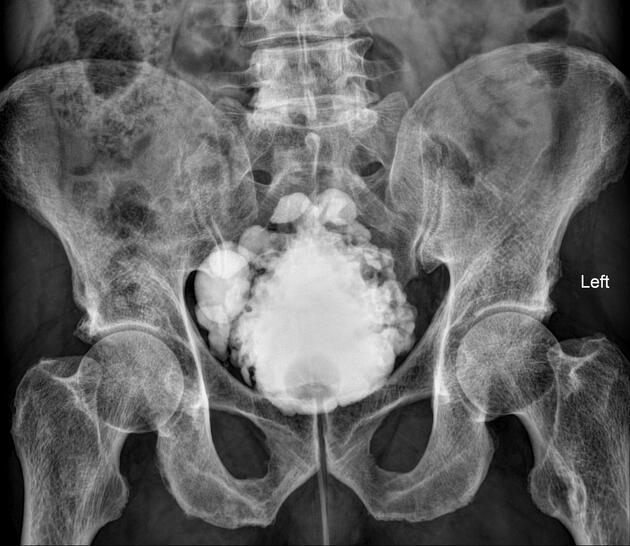
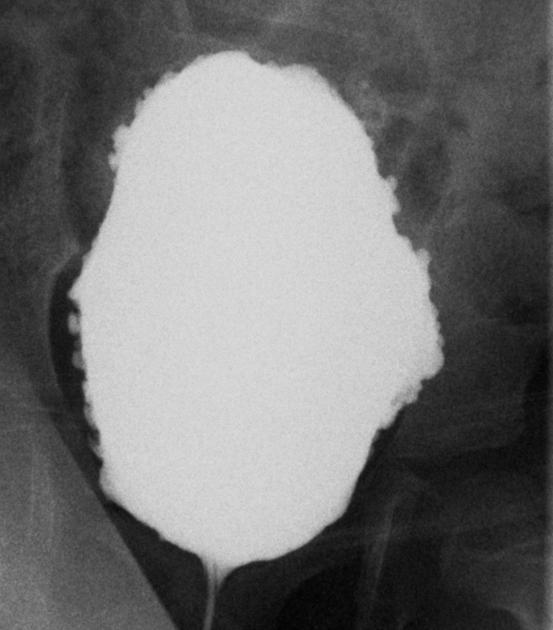
On radiographic evaluation, the bladder wall appears thickened and trabeculated. Urinary retention is noted with increased post-void residual on sonographic or voiding studies.
Treatment and prognosis
The goal of treatment is to relieve the obstruction and prevent urinary tract infections and renal compromise. This can be done by either catheterisation or surgical intervention depending on the aetiology of the obstruction 2.
Differential diagnosis
On imaging consider:
References
- 1. Abrams. Bladder Outlet Obstruction Index, Bladder Contractility Index and Bladder Voiding Efficiency: Three Simple Indices to Define Bladder Voiding Function. BJU Int. 1999;84(1):14-5. doi:10.1046/j.1464-410x.1999.00121.x
- 2. Blaivas J & Groutz A. Bladder Outlet Obstruction Nomogram for Women with Lower Urinary Tract Symptomatology. Neurourol Urodyn. 2000;19(5):553-64. doi:10.1002/1520-6777(2000)19:5<553::aid-nau2>3.0.co;2-b
- 3. Dmochowski R. Bladder Outlet Obstruction: Etiology and Evaluation. Rev Urol. 2005;7 Suppl 6:S3-S13. PMC1477620
- 4. Malde S, Solomon E, Spilotros M et al. Female Bladder Outlet Obstruction: Common Symptoms Masking an Uncommon Cause. Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2019;11(1):72-7. doi:10.1111/luts.12196 - Pubmed
- 5. Malde S, Nambiar A, Umbach R et al. Systematic Review of the Performance of Noninvasive Tests in Diagnosing Bladder Outlet Obstruction in Men with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. Eur Urol. 2017;71(3):391-402. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2016.09.026 - Pubmed
- 6. Malde S, Solomon E, Spilotros M et al. Female Bladder Outlet Obstruction: Common Symptoms Masking an Uncommon Cause. Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2019;11(1):72-7. doi:10.1111/luts.12196 - Pubmed
- 7. Dmochowski R. Bladder Outlet Obstruction: Etiology and Evaluation. Rev Urol. 2005;7 Suppl 6(Suppl 6):S3-S13. PMC1477620 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Voiding cystourethrography
- Uterine artery embolisation
- Pine cone bladder
- Cystography
- Cystitis cystica
- Intravesical prostatic protrusion
- Urinary bladder diverticula (causes)
- Urinary bladder wall thickening
- Patent urachus
- Emphysematous cystitis
- Urinoma
- Prostatomegaly
- Medical abbreviations and acronyms (B)
- Detrusor muscle
- Urinary bladder diverticulum
- Post-void residual
- Brunn's cyst of the urinary bladder
- Bladder calculus
- Adenocarcinoma (urinary bladder)
- Neurogenic bladder
- Urinary bladder diverticulum
- Scrotal cystocele - bladder herniation into scrotum
- Prostatomegaly
- Giant urinary bladder diverticulum
- Urethral stricture - high-grade
- Grade IV bilateral hydronephrosis
- Urethral stricture
- Chronic bladder outlet obstruction
- Urinary bladder diverticulum
- Bladder calculus
- Urinary bladder stone
- Gross bladder diverticula secondary to outlet obstruction
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta praevia
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynaecology
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumours
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumours of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumours
- mixed germ cell tumour
- yolk sac tumour (endodermal sinus tumour)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumour
- sex cord / stromal tumours of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumour of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumours (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumours
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys










 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.