Bronchial carcinoid tumour
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Yuranga Weerakkody had no recorded disclosures.
View Yuranga Weerakkody's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Liz Silverstone had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Liz Silverstone's current disclosures- Bronchial carcinoid
- Bronchial carcinoid tumours
- Bronchial carcinoid tumor
- Bronchial carcinoid tumors
- Bronchial carcinoids
- Carcinoid tumours involving the bronchi
- Primary bronchial carcinoid tumour
- Bronchial carcinoid tumors (BCT's)
- Bronchial carcinoid tumor (BCT)
- Bronchial carcinoid tumours (BCT's)
- Bronchial carcinoid tumour (BCT)
- Bronchial adenoma
- Bronchial adenomas
- Central pulmonary carcinoid
- Central carcinoid tumour of the lung
- Central carcinoid tumours of the lung
- Central carcinoid tumor of the lung
- Central carcinoid tumors of the lung
Bronchial carcinoid tumours are carcinoid tumours primarily occurring in relation to a bronchus. They were previously incorrectly termed bronchial adenomas. They usually occur in association with a segmental or larger bronchus.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Typically affects patients from the 3rd to 7th decades with the mean age around 45 years 7,10.
Associations
Cushing syndrome: due to ACTH-producing carcinoid tumour types 1
Clinical presentation
The presentation can vary depending on location. Central neoplasms can cause bronchial obstruction and distal pneumonia, atelectasis, bronchiectasis, air-trapping or lung abscess. Partial airway obstruction can cause cough, wheezing and recurrent pulmonary infections. Peripheral tumours are generally asymptomatic and can cause air-trapping. Presentation with carcinoid syndrome is rare (~2-5%) 5,10.
Pathology
They are neuroendocrine neoplasms that range from low-grade typical carcinoids to more aggressive atypical carcinoids.
Location
Most (~60%) occur centrally within the major bronchi, or rarely within the trachea 4.
Radiographic features
Plain radiograph
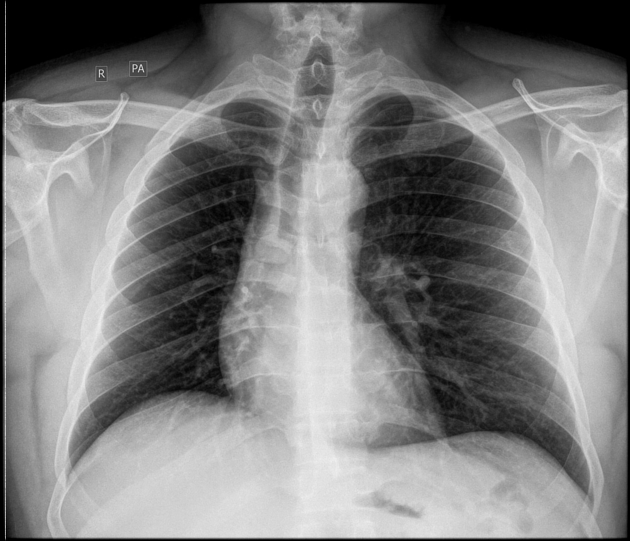
Tumours may be seen as filling defects in the main bronchi or trachea with sharp, possibly notched margins 2. Associated airway stenosis with pulmonary atelectasis may be also seen.
CT
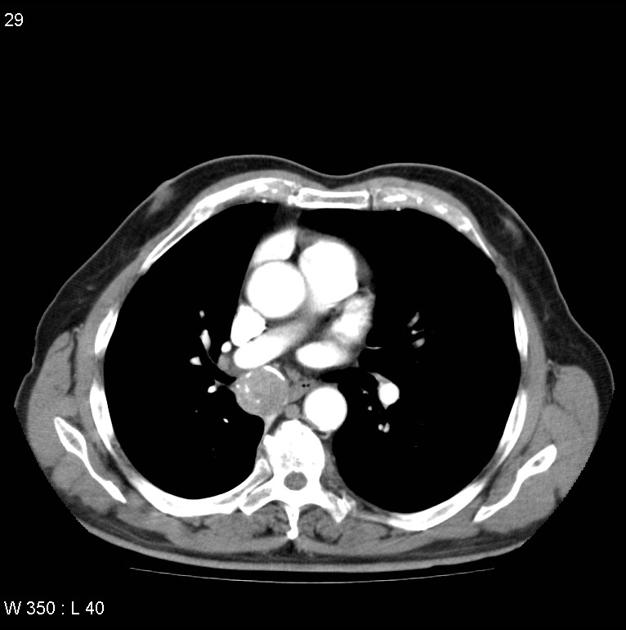
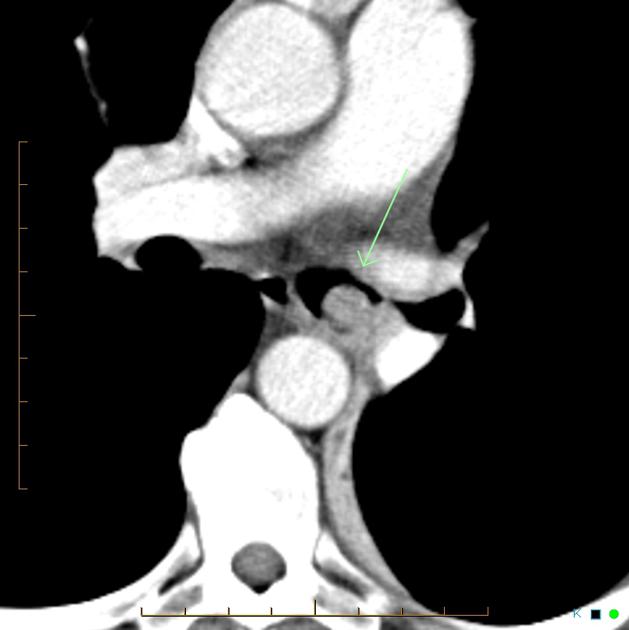
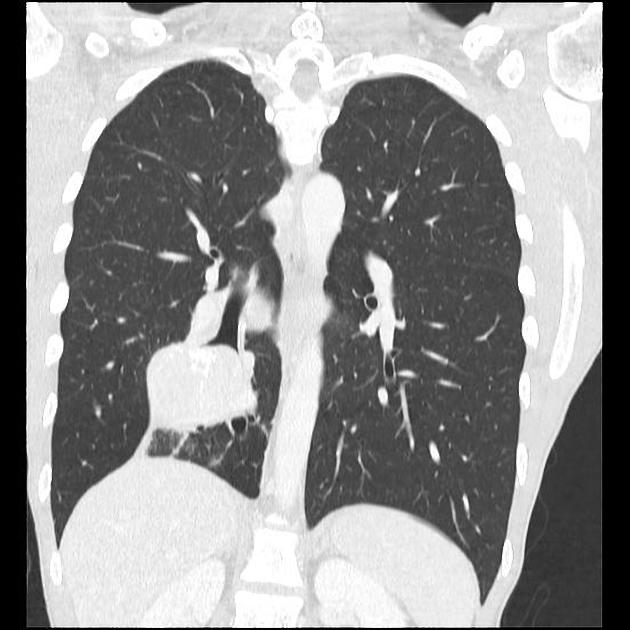
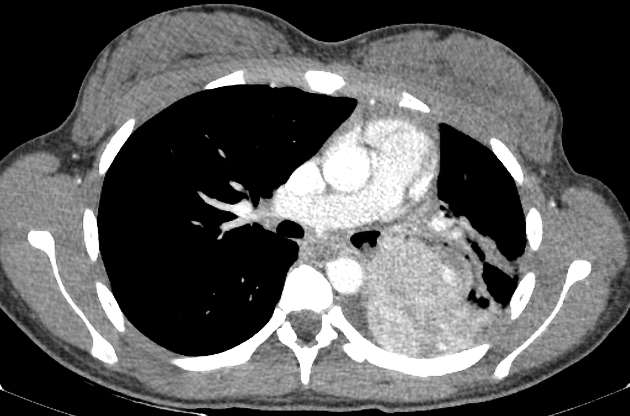
Central lesions are usually seen as:
a single hilar or perihilar mass that is usually well-defined, round or ovoid
can be of any size but are typically 2-5 cm
there is often marked homogeneous contrast enhancement due to high vascularity
calcification (usually eccentric) can occur but is not a common feature
Nuclear medicine
PET-CT
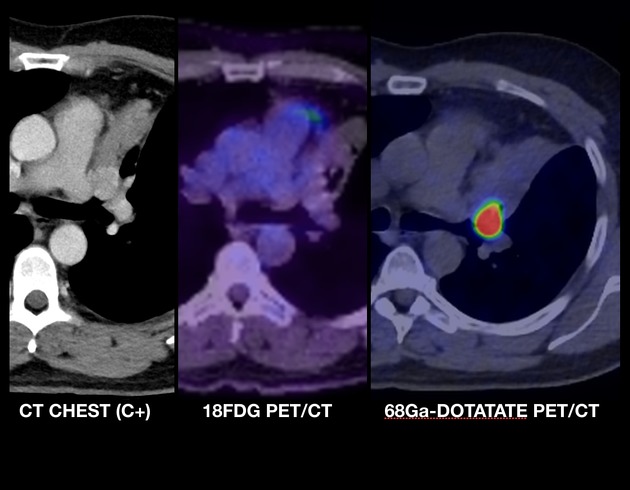
F18-FDG PET-CT helps to distinguish aggressive tumours: well-differentiated carcinoid tumours ususally show low FDG avidity. FDG avidity is increased in high-grade and poorly differentiated carcinoid tumours 14.
Gallium-68 DOTATATE
Gallium-68 DOTATATE has shown high accuracy, better imaging quality and lower radiation dose than octreotide scan. Its sensitivity and specificity reaches 80% to 95% as it contains a synthetic somatostatin analogue that has high affinity for somatostatin 2 receptors on the surface membrane of well-differentiated primary and metastatic neuroendocrine tumours 14.
References
- 1. Doppman JL, Pass HI, Nieman LK et-al. Detection of ACTH-producing bronchial carcinoid tumors: MR imaging vs CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991;156 (1): 39-43. AJR Am J Roentgenol (abstract) - Pubmed citation
- 2. Nessi R, Basso ricci P, Basso ricci S et-al. Bronchial carcinoid tumors: radiologic observations in 49 cases. J Thorac Imaging. 1991;6 (2): 47-53. - Pubmed citation
- 3. Zwiebel BR, Austin JH, Grimes MM. Bronchial carcinoid tumors: assessment with CT of location and intratumoral calcification in 31 patients. Radiology. 1991;179 (2): 483-6. Radiology (abstract) - Pubmed citation
- 4. Anh-Vu H. Ngo, Christopher Michael Walker, Jonathan H. Chung, Julie E. Takasugi, Eric J. Stern, Jeffrey P. Kanne, Gautham P. Reddy, and J. David Godwin. Tumors and Tumorlike Conditions of the Large Airways. American Journal of Roentgenology 2013 201:2, 301-313. AJR
- 5. Ramachandran PV, Harigovind D, Shamsudeen H et-al. Imaging spectrum of bronchial carcinoid--a case of central bronchial obstructing lesion. J Indian Med Assoc. 2002;100 (7): 461-2, 464. - Pubmed citation
- 6. Squerzanti A, Basteri V, Antinolfi G et-al. Bronchial carcinoid tumors: clinical and radiological correlation. Radiol Med. 2003;104 (4): 273-84. Pubmed citation
- 7. Rosado de christenson ML, Abbott GF, Kirejczyk WM et-al. Thoracic carcinoids: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 19 (3): 707-36. Radiographics (citation) - Pubmed citation
- 8. Zwiebel BR, Austin JH, Grimes MM. Bronchial carcinoid tumors: assessment with CT of location and intratumoral calcification in 31 patients. Radiology. 1991;179 (2): 483-6. Radiology (abstract) - Pubmed citation
- 9. Meisinger QC, Klein JS, Butnor KJ et-al. CT features of peripheral pulmonary carcinoid tumors. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197 (5): 1073-80. doi:10.2214/AJR.10.5954 - Pubmed citation
- 10. Jeung MY, Gasser B, Gangi A et-al. Bronchial carcinoid tumors of the thorax: spectrum of radiologic findings. Radiographics. 2002;22 (2): 351-65. Radiographics (full text) - Pubmed citation
- 11. Davila DG, Dunn WF, Tazelaar HD et-al. Bronchial carcinoid tumors. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1993;68 (8): 795-803. - Pubmed citation
- 12. Morandi U, Casali C, Rossi G. Bronchial typical carcinoid tumors. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2006;18 (3): 191-8. doi:10.1053/j.semtcvs.2006.08.005 - Pubmed citation
- 13. Scarsbrook AF, Thakker RV, Wass JA et-al. Multiple endocrine neoplasia: spectrum of radiologic appearances and discussion of a multitechnique imaging approach. Radiographics. 2006;26 (2): 433-51. Radiographics (full text) - doi:10.1148/rg.262055073 - Pubmed citation
- 14. Foto N & Lee D. Pulmonary Carcinoid and the Importance of Correct Radiotracer Selection. TOJ. 2021;21(1):6-9. doi:10.31486/toj.20.0155 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Calcified mediastinal lymph nodes (differential)
- Carcinoid tumours of the lung
- Solitary pulmonary nodule
- Carcinoid heart disease
- Coin lesion (lung)
- Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome
- Peripheral pulmonary carcinoid tumour
- Mucoid impaction (lung)
- Finger in glove sign (lung)
- Tracheal masses
- Pulmonary neuroendocrine tumours
- Bronchiectasis
- Tracheal and endobronchial lesions
- Cushing syndrome
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the tracheobronchial tree
Related articles: Chest
- imaging techniques
-
chest radiograph
- radiography
-
approach
- ABCDE
- ABCDEFGHI
- congenital heart disease
- medical devices in the thorax
- common lines and tubes
- nasogastric tubes
- endotracheal tubes
- central venous catheters
- oesophageal temperature probe
- tracheostomy tube
- pleural catheters
- cardiac conduction devices
- prosthetic heart valve
- review areas
-
airspace opacification
- differential diagnoses of airspace opacification
- lobar consolidation
-
atelectasis
- mechanism-based
- morphology-based
- lobar lung collapse
- chest x-ray in the exam setting
- cardiomediastinal contour
- chest radiograph zones
- tracheal air column
- fissures
- normal chest x-ray appearance of the diaphragm
- nipple shadow
-
lines and stripes
- anterior junction line
- posterior junction line
- right paratracheal stripe
- left paratracheal stripe
- posterior tracheal stripe/tracheo-oesophageal stripe
- posterior wall of bronchus intermedius
- right paraspinal line
- left paraspinal line
- aortic-pulmonary stripe
- aortopulmonary window
- azygo-oesophageal recess
- spaces
- signs
- air bronchogram
- big rib sign
- Chang sign
- Chen sign
- coin lesion
- continuous diaphragm sign
- dense hilum sign
- double contour sign
- egg-on-a-string sign
- extrapleural sign
- finger in glove sign
- flat waist sign
- Fleischner sign
- ginkgo leaf sign
- Golden S sign
- Hampton hump
- haystack sign
- hilum convergence sign
- hilum overlay sign
- Hoffman-Rigler sign
- holly leaf sign
- incomplete border sign
- juxtaphrenic peak sign
- Kirklin sign
- medial stripe sign
- melting ice cube sign
- more black sign
- Naclerio V sign
- Palla sign
- pericardial fat tag sign
- Shmoo sign
- silhouette sign
- snowman sign
- spinnaker sign
- steeple sign
- straight left heart border sign
- third mogul sign
- tram-track sign
- walking man sign
- water bottle sign
- wave sign
- Westermark sign
- HRCT
-
chest radiograph
- airways
- bronchitis
- small airways disease
-
bronchiectasis
- broncho-arterial ratio
- related conditions
- differentials by distribution
- narrowing
-
tracheal stenosis
- diffuse tracheal narrowing (differential)
-
bronchial stenosis
- diffuse airway narrowing (differential)
-
tracheal stenosis
- diverticula
- pulmonary oedema
-
interstitial lung disease (ILD)
- Anti-Jo-1 antibody-positive interstitial lung disease
- drug-induced interstitial lung disease
-
hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- acute hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- subacute hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- aetiology
- bird fancier's lung: pigeon fancier's lung
- farmer's lung
- cheese workers' lung
- bagassosis
- mushroom worker’s lung
- malt worker’s lung
- maple bark disease
- hot tub lung
- wine maker’s lung
- woodsman’s disease
- thatched roof lung
- tobacco grower’s lung
- potato riddler’s lung
- summer-type pneumonitis
- dry rot lung
- machine operator’s lung
- humidifier lung
- shower curtain disease
- furrier’s lung
- miller’s lung
- lycoperdonosis
- saxophone lung
-
idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (mnemonic)
- acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP)
- cryptogenic organising pneumonia (COP)
- desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP)
- non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP)
- idiopathic pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis
- lymphoid interstitial pneumonia (LIP)
- respiratory bronchiolitis–associated interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD)
- usual interstitial pneumonia / idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (UIP/IPF)
-
pneumoconioses
- fibrotic
- non-fibrotic
-
lung cancer
-
non-small-cell lung cancer
-
adenocarcinoma
- pre-invasive tumours
- minimally invasive tumours
- invasive tumours
- variants of invasive carcinoma
- described imaging features
- adenosquamous carcinoma
- large cell carcinoma
- primary sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung
- squamous cell carcinoma
- salivary gland-type tumours
-
adenocarcinoma
- pulmonary neuroendocrine tumours
- preinvasive lesions
-
lung cancer invasion patterns
- tumour spread through air spaces (STAS)
- presence of non-lepidic patterns such as acinar, papillary, solid, or micropapillary
- myofibroblastic stroma associated with invasive tumour cells
- pleural invasion
- vascular invasion
- tumours by location
- benign neoplasms
- pulmonary metastases
- lung cancer screening
- lung cancer staging
-
non-small-cell lung cancer








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.