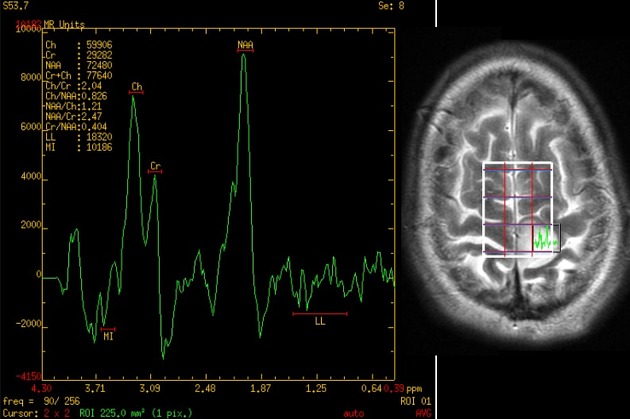
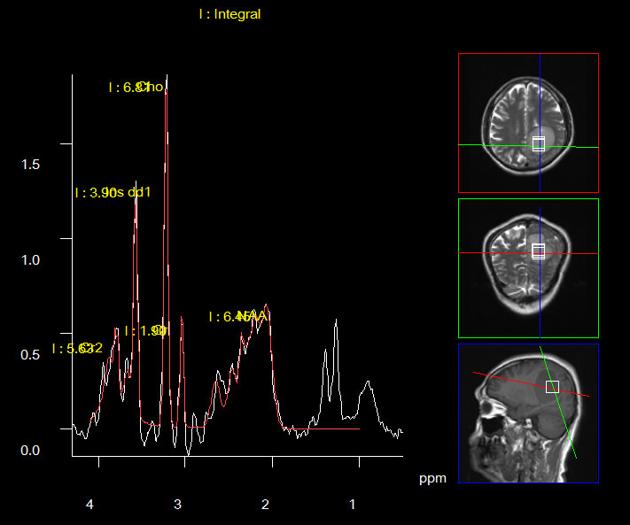
Choline peak
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Jeremy Jones had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresCholine is a precursor of acetylcholine (ACH) and a cell membrane component which is commonly examined in MR spectroscopy. It resonates at 3.2 ppm chemical shift.
Choline is a marker of cellular membrane turnover and therefore elevated in neoplasms, demyelination, inflammation and gliosis 1.
It is useful in a number of scenarios:
diffuse glioma vs metastasis: elevation in a region of high T2 signal surrounding an enhancing mass (edema) suggests an infiltrating diffuse glioma rather than a cerebral metastasis
glioblastoma progression vs pseudoprogression: elevation favors tumor progression over pseudoprogression, but can be elevated if a strong immune response is present as is seen in immunotherapy 1,2
toxoplasmosis vs lymphoma: lymphoma typically shows elevated choline peak, while it is reduced in toxoplasmosis
Due to active myelination with synthesis of membrane constituents, an infant’s brain shows high choline peaks compared to adult spectroscopy 3-6.
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Mader I, Rauer S, Gall P, Klose U. (1)H MR Spectroscopy of Inflammation, Infection and Ischemia of the Brain. Eur J Radiol. 2008;67(2):250-7. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2008.02.033 - Pubmed
- 2. Aquino D, Gioppo A, Finocchiaro G, Bruzzone M, Cuccarini V. MRI in Glioma Immunotherapy: Evidence, Pitfalls, and Perspectives. J Immunol Res. 2017;2017:5813951. doi:10.1155/2017/5813951 - Pubmed
- 3. Hüppi P, Posse S, Lazeyras F, Burri R, Bossi E, Herschkowitz N. Magnetic Resonance in Preterm and Term Newborns: 1H-Spectroscopy in Developing Human Brain. Pediatr Res. 1991;30(6):574-8. doi:10.1203/00006450-199112000-00017 - Pubmed
- 4. Progressi in RM. Spettroscopia Protonica Cerebrale. (1999) ISBN: 9788879472470 - Google Books
- 5. Groenendaal F, Veenhoven R, van der Grond J, Jansen G, Witkamp T, de Vries L. Cerebral Lactate and N-Acetyl-Aspartate/choline Ratios in Asphyxiated Full-Term Neonates Demonstrated in Vivo Using Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Pediatr Res. 1994;35(2):148-51. doi:10.1203/00006450-199402000-00004 - Pubmed
- 6. Peden C, Cowan F, Bryant D et al. Proton MR Spectroscopy of the Brain in Infants. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1990;14(6):886-94. doi:10.1097/00004728-199011000-00004 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Leigh syndrome
- Posterior fossa ependymoma
- Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumour
- MR spectroscopy
- Diffuse axonal injury
- Myo-inositol peak
- Hunter's angle
- Adult-onset leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids and pigmented glia
- Medulloblastoma
- Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
- HIV-associated dementia
- Valproate-induced hyperammonaemic encephalopathy
- Lymph node imaging
- Prostate cancer
- Multiple sclerosis
- Glioblastoma vs cerebral metastasis
- Embryonal tumour with multilayered rosettes
- Meningioma
- Atypical choroid plexus papilloma
- Baló concentric sclerosis
- AIDS-related diffuse large B-cell lymphoma - CNS
- Central neurocytoma
- Cerebral tuberculosis
- Embryonal tumour with multilayered rosettes (ETMR)
- Lhermitte-Duclos disease
- Diffuse glioma
- Brain metastasis as initial presentation of non-small cell lung cancer
- Brain metastasis (large cystic mass)
- Bilateral thalamic gliomata
- Solitary supratentorial metastasis
- Glioblastoma NOS
- Ependymoma - MRS
- Low grade glioma (MR spectroscopy)
- Low grade glioma with radiation necrosis
- High grade astrocytoma (MRS)
- Brain abscess - MR spectroscopy
- Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma
- Thalamic glioma
Related articles: Imaging technology
- imaging technology
- imaging physics
- imaging in practice
-
x-rays
- x-ray physics
- x-ray in practice
- x-ray production
- x-ray tube
- filters
- automatic exposure control (AEC)
- beam collimators
- grids
- air gap technique
- cassette
- intensifying screen
- x-ray film
- image intensifier
- digital radiography
- digital image
- mammography
- x-ray artifacts
- radiation units
- radiation safety
- radiation detectors
- fluoroscopy
-
computed tomography (CT)
- CT physics
- CT in practice
- CT technology
- CT image reconstruction
- CT image quality
- CT dose
-
CT contrast media
-
iodinated contrast media
- agents
- water soluble
- water insoluble
- vicarious contrast material excretion
- iodinated contrast media adverse reactions
- agents
- non-iodinated contrast media
-
iodinated contrast media
-
CT artifacts
- patient-based artifacts
- physics-based artifacts
- hardware-based artifacts
- ring artifact
- tube arcing
- out of field artifact
- air bubble artifact
- helical and multichannel artifacts
- CT safety
- history of CT
-
MRI
- MRI physics
- MRI in practice
- MRI hardware
- signal processing
-
MRI pulse sequences (basics | abbreviations | parameters)
- T1 weighted image
- T2 weighted image
- proton density weighted image
- chemical exchange saturation transfer
- CSF flow studies
- diffusion weighted imaging (DWI)
- echo-planar pulse sequences
- fat-suppressed imaging sequences
- gradient echo sequences
- inversion recovery sequences
- metal artifact reduction sequence (MARS)
-
perfusion-weighted imaging
- techniques
- derived values
- saturation recovery sequences
- spin echo sequences
- spiral pulse sequences
- susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI)
- T1 rho
- MR angiography (and venography)
-
MR spectroscopy (MRS)
- 2-hydroxyglutarate peak: resonates at 2.25 ppm
- alanine peak: resonates at 1.48 ppm
- choline peak: resonates at 3.2 ppm
- citrate peak: resonates at 2.6 ppm
- creatine peak: resonates at 3.0 ppm
- functional MRI (fMRI)
- gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) peak: resonates at 2.2-2.4 ppm
- glutamine-glutamate peak: resonates at 2.2-2.4 ppm
- Hunter's angle
- lactate peak: resonates at 1.3 ppm
- lipids peak: resonates at 1.3 ppm
- myoinositol peak: resonates at 3.5 ppm
- MR fingerprinting
- N-acetylaspartate (NAA) peak: resonates at 2.0 ppm
- propylene glycol peak: resonates at 1.13 ppm
-
MRI artifacts
- MRI hardware and room shielding
- MRI software
- patient and physiologic motion
- tissue heterogeneity and foreign bodies
- Fourier transform and Nyquist sampling theorem
- MRI contrast agents
- MRI safety
-
ultrasound
- ultrasound physics
-
transducers
- linear array
- convex array
- phased array
- frame averaging (frame persistence)
- ultrasound image resolution
- imaging modes and display
- pulse-echo imaging
- real-time imaging
-
Doppler imaging
- Doppler effect
- color Doppler
- power Doppler
- B flow
- color box
- Doppler angle
- pulse repetition frequency and scale
- wall filter
- color write priority
- packet size (dwell time)
- peak systolic velocity
- end-diastolic velocity
- resistive index
- pulsatility index
- Reynolds number
- panoramic imaging
- compound imaging
- harmonic imaging
- elastography
- scanning modes
- 2D ultrasound
- 3D ultrasound
- 4D ultrasound
- M-mode
-
ultrasound artifacts
- acoustic shadowing
- acoustic enhancement
- beam width artifact
- reverberation artifact
- ring down artifact
- mirror image artifact
- side lobe artifact
- speckle artifact
- speed displacement artifact
- refraction artifact
- multipath artifact
- anisotropy
- electrical interference artifact
- hardware-related artifacts
- Doppler artifacts
- aliasing
- tissue vibration
- spectral broadening
- blooming
- motion (flash) artifact
- twinkling artifact
- acoustic streaming
- biological effects of ultrasound
- history of ultrasound
-
nuclear medicine
- nuclear medicine physics
- detectors
- tissue to background ratio
-
radiopharmaceuticals
- fundamentals of radiopharmaceuticals
- radiopharmaceutical labeling
- radiopharmaceutical production
- nuclear reactor produced radionuclides
- cyclotron produced radionuclides
- radiation detection
- dosimetry
- specific agents
- carbon-11
- chromium-51
- fluorine agents
- gallium agents
- Ga-67 citrate
- Ga-68
- iodine agents
-
I-123
- I-123 iodide
- I-123 ioflupane (DaTSCAN)
- I-123 ortho-iodohippurate
- I-131
-
MIBG scans
- I-123 MIBG
- I-131 MIBG
-
I-123
- indium agents
- In-111 Octreoscan
- In-111 OncoScint
- In-111 Prostascint
- In-111 oxine labeled WBC
- krypton-81m
- nitrogen-13
- oxygen-15
- phosphorus-32
- selenium-75
-
technetium agents
- Tc-99m DMSA
- Tc-99m DTPA
- Tc-99m DTPA aerosol
- Tc-99m HMPAO
- Tc-99m HMPAO labeled WBC
- Tc-99m MAA
- Tc-99m MAG3
- Tc-99m MDP
- Tc-99m mercaptoacetyltriglycine
- Tc-99m pertechnetate
- Tc-99m labeled RBC
- Tc-99m sestamibi
- Tc-99m sulfur colloid
- Tc-99m sulfur colloid (oral)
- thallium-201 chloride
- xenon agents
- in vivo therapeutic agents
- pharmaceuticals used in nuclear medicine
-
emerging methods in medical imaging
- radiography
- phase-contrast imaging
- CT
- deep-learning reconstruction
- photon counting CT
- virtual non-contrast imaging
- ultrasound
- magnetomotive ultrasound (MMUS)
- superb microvascular imaging
- ultrafast Doppler imaging
- ultrasound localization microscopy
- MRI
- nuclear medicine
- total body PET system
- immuno-PET
- miscellaneous
- radiography




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.