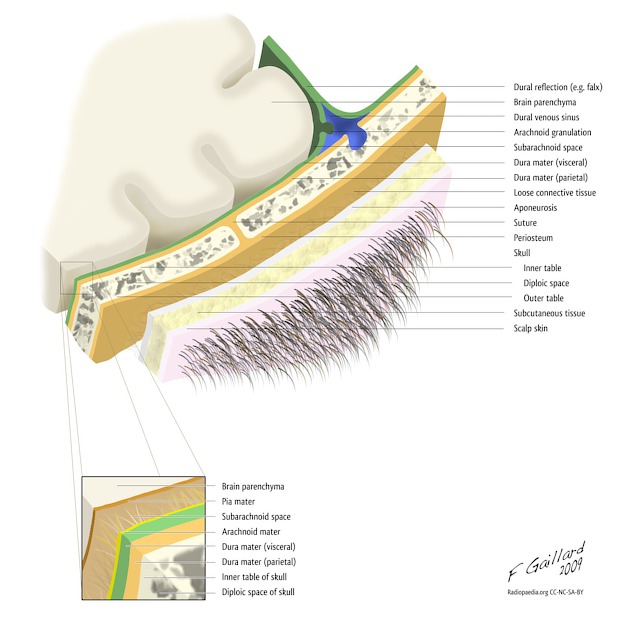
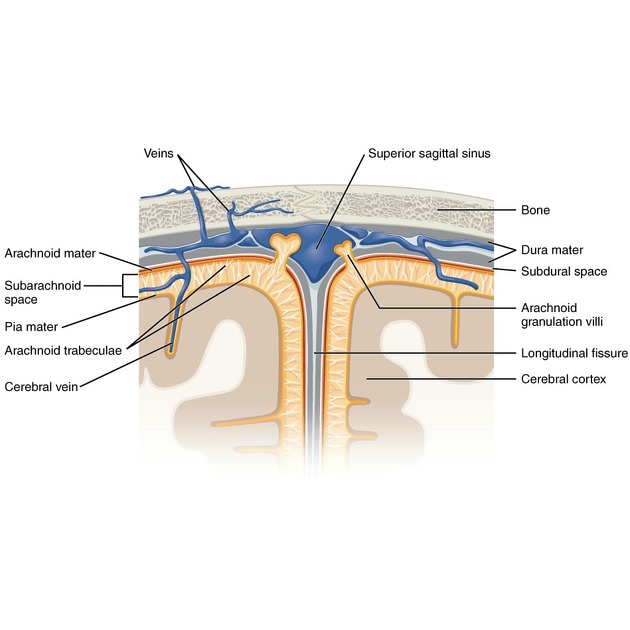
Cranial meninges
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Henry Knipe had no recorded disclosures.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Tariq Walizai had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Tariq Walizai's current disclosures- Cranial meninx
The cranial meninges (singular: meninx) surround the brain and are made up of four layers (from outermost to innermost):
On this page:
Terminology
The dura mater can also be known as the pachymeninx. The arachnoid mater and pia mater are collectively known as the leptomeninges 3. The spinal meninges are similar but have some important differences.
Anatomy
The meninges function to protect the brain but also provide a framework for blood vessels, nerves, lymphatics and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) 2.
There are two so-called potential spaces:
epidural (extradural) space: between the bone of the cranium and the outer layer of the dura mater
subdural space: between the inner layer of the dura mater and the arachnoid mater; this is not a true potential space as the two layers are fused, albeit closely, by the dural border zone and haematomas actually occur within this space 5
Traditionally, one CSF-containing space, subarachnoid space, is described located between the arachnoid and pia mater. However, a thin additional layer, the subarachnoid lymphatic-like membrane, has been found to divide this space into two compartments 6.
Arterial supply
There are several arteries that supply the dura with the middle meningeal artery being the main contributor.
Innervation
The sensory innervation of the meninges is primarily by meningeal branches of both the trigeminal and vagus nerves with a smaller contribution from the upper cervical spinal nerves.
History and etymology
The word meninges, is the plural of meninx, from the Classical Greek μηνιγξ (transliteration: meninx) and literally means membrane 7.
Quiz questions
References
- 1. J. Edward Bruni, Donald G. Montemurro. Human Neuroanatomy. (2009) ISBN: 9780195371420 - Google Books
- 2. William K. Ovalle, PhD, Patrick C. Nahirney, PhD. Netter's Essential Histology. (2013) ISBN: 9781455706310 - Google Books
- 3. Strominger NL, Demarest RJ, Laemle LB. Noback's Human Nervous System, Seventh Edition: Structure and Function (HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM (NOBACK)). Humana Press. ISBN:B00A9YGMYU. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. Peter Harris, Sue Nagy, Nicholas Vardaxis. Mosby's Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing and Health Professions - Australian & New Zealand Edition - EBook. (2014) ISBN: 9780729581387 - Google Books
- 5. Hasan D, Nikoubashman O, Pjontek R, Stockero A, Hamou H, Wiesmann M. MRI Appearance of Chronic Subdural Hematoma. Front Neurol. 2022;13:872664. doi:10.3389/fneur.2022.872664 - Pubmed
- 6. Møllgård K, Beinlich F, Kusk P et al. A Mesothelium Divides the Subarachnoid Space into Functional Compartments. Science. 2023;379(6627):84-8. doi:10.1126/science.adc8810 - Pubmed
- 7. James Diggle. The Cambridge Greek Lexicon. (2021) ISBN: 9781108836982 - Google Books
Incoming Links
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.