CT stair-step artifact
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created David Cuete had no recorded disclosures.
View David Cuete's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Mateusz Wilczek had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Mateusz Wilczek's current disclosures- CT stair-step artefact
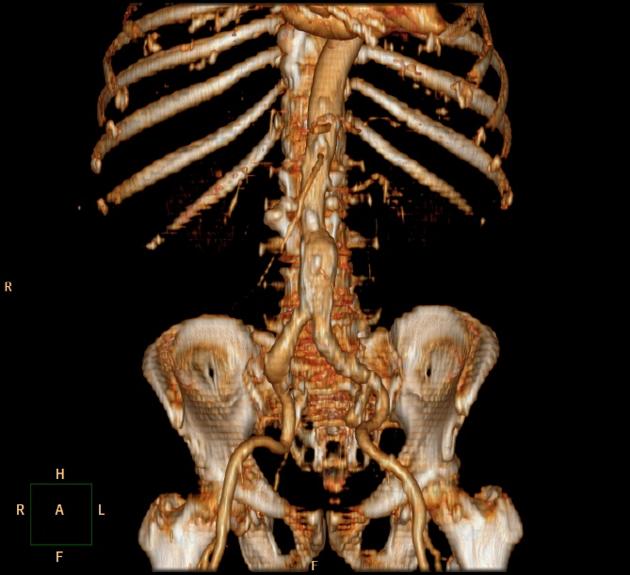
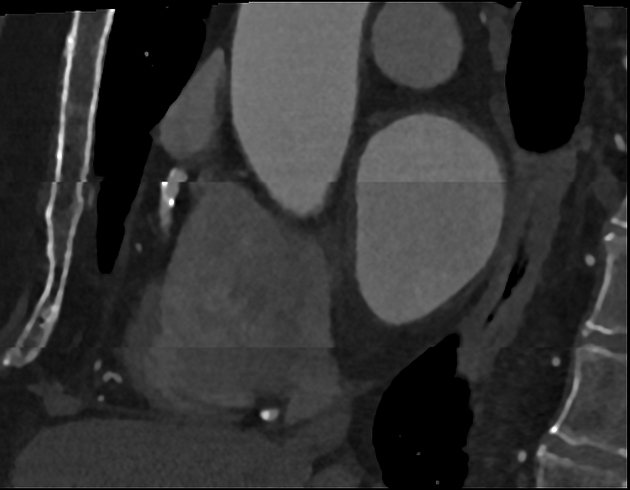
The CT stair-step artifact is found in straight structures which are orientated obliquely with respect to movement of the table and appear around the edges of sagittal and coronal reformatted images when wide collimations and non-overlapping reconstruction intervals are used.
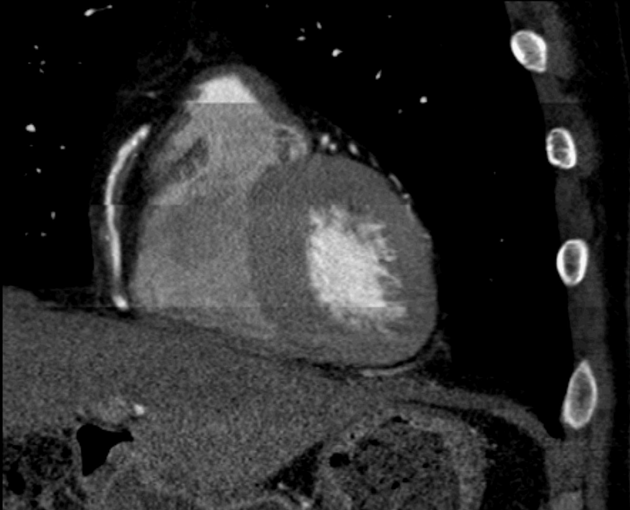
It is also seen in coronary CT angiography when step-wise reconstructions are from different cardiac phases. This is associated with heart rate variability and irregular heart rates.
Solution
This can be minimised by, using smaller collimation and overlapping reconstruction in helical imaging.
In coronary CT angiography, 256 and 320-detector CT scanners typically avoid this artifact. Some authors recommend beta-blockers to reduce stair-step artifact, others report limited results in achieving target heart rates with their use.
References
- 1. Barrett JF, Keat N. Artifacts in CT: recognition and avoidance. Radiographics. 2004;24 (6): 1679-91. doi:10.1148/rg.246045065 - Pubmed citation
- 2. Kalender WA. Computed Tomography. Publicis. (2011) ISBN:389578317X. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 3. Coronary CT Angiography: Practice Essentials, Overview, Clinical Applications: Coronary Artery Disease [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2018 Apr 2]. Available from: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1603072-overview#a9
- 4. Shapiro MD, Pena AJ, Nichols JH, Worrell S, Bamberg F, Dannemann N, et al. Efficacy of pre-scan beta-blockade and impact of heart rate on image quality in patients undergoing coronary multidetector computed tomography angiography. Eur J Radiol. 2008 Apr;66(1):37–41.
Incoming Links
Related articles: Computed tomography
- computed tomography in practice
-
computed tomography overview
- iodinated contrast media
- CT IV contrast media administration
-
CT artifacts
- patient-based artifacts
- physics-based artifacts
- hardware-based artifacts
- ring artifact
- tube arcing
- out of field artifact
- air bubble artifact
- helical and multichannel artifacts
- CT technology
-
generations of CT scanners
- helical CT scanning
- step and shoot scanning
- ultra-high-resolution CT (UHRCT)
- CT x-ray tube
- CT fluoroscopy
- cone-beam CT
-
generations of CT scanners
- dual-energy CT
- CT image reconstruction
- CT image quality
- CT dose
-
CT protocols
- composite
- head & neck
- chest
- abdomen and pelvis
- CT abdomen-pelvis (protocol)
- CT abdominal aorta
- CT adrenals (protocol)
- CT cholangiography (protocol)
- CT colonography (protocol)
- CT enteroclysis (protocol)
- CT enterography (protocol)
- CT gastrography (protocol)
- CT kidneys, ureters and bladder (protocol)
- CT urography (protocol)
- CT Renal mass (protocol)
- CT angiography of the splanchnic vessels (protocol)
- CT renal split bolus
- CT pancreas (protocol)
- liver




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.