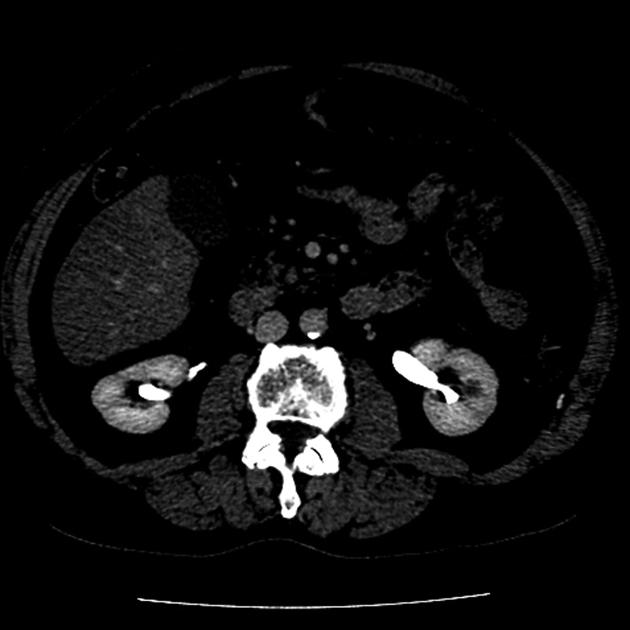
Excretory phase
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Andrew Murphy had no recorded disclosures.
View Andrew Murphy's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Andrew Murphy had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Andrew Murphy's current disclosures- Urographic phase
The excretory phase also known as the urographic phase is a postcontrast injection time range in which there is an optimal enhancement of the renal collecting systems.
On this page:
Images:
Technique
The acquisition time depends on the intravenous device (central or peripheral), the concentration of the contrast medium, and the injection rate 1.
- time from injection through an upper extremity vein
- 5-10 minutes
Physiology
Contrast is excreted into the calices and into the renal collecting systems 1.
Clinical use
Excretory phase imaging allows the detection of renal lesions, urothelial cancer parapelvic cysts, calyceal diverticula and urinary extravasation after renal trauma 2.
See also
References
- 1. Yuh BI, Cohan RH. Different phases of renal enhancement: role in detecting and characterizing renal masses during helical CT. (1999) AJR. American journal of roentgenology. 173 (3): 747-55. doi:10.2214/ajr.173.3.10470916 - Pubmed
- 2. Keihani S, Putbrese B, Rogers D et al. Optimal Timing of Delayed Excretory Phase Computed Tomography Scan for Diagnosis of Urinary Extravasation After High-Grade Renal Trauma. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2019;86(2):274-81. doi:10.1097/ta.0000000000002098 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Computed tomography
- computed tomography in practice
-
computed tomography overview
- iodinated contrast media[+][+]
- CT IV contrast media administration
-
CT artifacts[+][+]
- patient-based artifacts
- physics-based artifacts
- hardware-based artifacts
- ring artifact
- tube arcing
- out of field artifact
- air bubble artifact
- helical and multichannel artifacts
- CT technology[+][+]
-
generations of CT scanners
- helical CT scanning
- step and shoot scanning
- ultra-high-resolution CT (UHRCT)
- CT x-ray tube
- CT fluoroscopy
- cone-beam CT
-
generations of CT scanners
- dual-energy CT[+][+]
- CT image reconstruction[+][+]
- CT image quality[+][+]
- CT dose[+][+]
-
CT protocols[+][+]
- composite
- head & neck
- chest
- abdomen and pelvis
- CT abdomen-pelvis (protocol)
- CT abdominal aorta
- CT adrenals (protocol)
- CT cholangiography (protocol)
- CT colonography (protocol)
- CT enteroclysis (protocol)
- CT enterography (protocol)
- CT gastrography (protocol)
- CT kidneys, ureters and bladder (protocol)
- CT urography (protocol)
- CT Renal mass (protocol)
- CT angiography of the splanchnic vessels (protocol)
- CT renal split bolus
- CT pancreas (protocol)
- liver




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.