Embryonal tumors with multilayered rosettes (ETMR) are rare small round blue cell tumor of the central nervous system. They are one of the most aggressive brain tumors usually encountered in children and are WHO grade 4 tumors.
On this page:
Terminology
Previously embryonal tumors with multilayered rosettes (ETMR) were known as embryonal tumor with abundant neuropil and true rosettes (ETANTR). This term was, however, removed from the 2016 update to WHO classification of CNS tumors in favor of embryonal tumors with multilayered rosettes (ETMR) which incorporates not only ETANTR but also ependymoblastoma and primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the central nervous system (CNS PNET), which have also been removed 6.
The terminological changes have resulted from the presence of amplification of the C19MC microRNA cluster on chromosome 19 in both CNS PNET and ETANTR, suggesting that these are the one entity with variable growth pattern 6. Similarly, medulloepithelioma no longer appears as a distinct entity in the 5th Edition (2021) of WHO classification of CNS tumors, and is stated to be "not recommended" terminology 7.
Epidemiology
Embryonal tumor with multilayered rosettes occurs in children aged 4 years and under, mostly in children under 2 years, and is more common in girls, unlike the other CNS embryonal tumors, in which boys are equally or more commonly affected 7.
Clinical presentation
The clinical features are determined by the location and extent of the tumor. Most are supratentorial in location, a few are infratentorial, and they are very rarely encountered in the spinal cord.
Increased intracranial pressure, seizures, hemiparesis, cerebellar signs, cranial nerve palsies, and other neurologic deficits have all been reported.
Pathology
Microscopic appearance
Embryonal tumors with multilayered rosettes demonstrate one of three histological patterns:
embryonal tumor with abundant neuropil and true rosettes
ependymoblastoma
Typically these tumors are characterized by undifferentiated neuroepithelial cells resembling those of classic CNS PNET (historical), abundant well-differentiated neuropil, and ependymoblastic rosettes scattered throughout paucicellular regions of neoplastic neuropil. It has very characteristic ependymoblastic rosettes in both highly cellular as well as acellular areas.
When they have an ependymoblastoma pattern, they lack ganglion cells and a neuropil-like matrix.
Occasionally a distinct histological pattern is encountered that mimics a primitive neural tumor; this is known as a medulloepithelioma pattern.
Genetics
Amplification of the C19MC region on chromosome 19 (19q13.42) has been identified as characteristic of these tumors, present in approximately 90% of cases. 7.
If C19MC amplification is absent, then these tumors are known as ETMR-NOS even if other mutations (e.g. DICER1) are identified 6,7.
Radiographic features
MRI
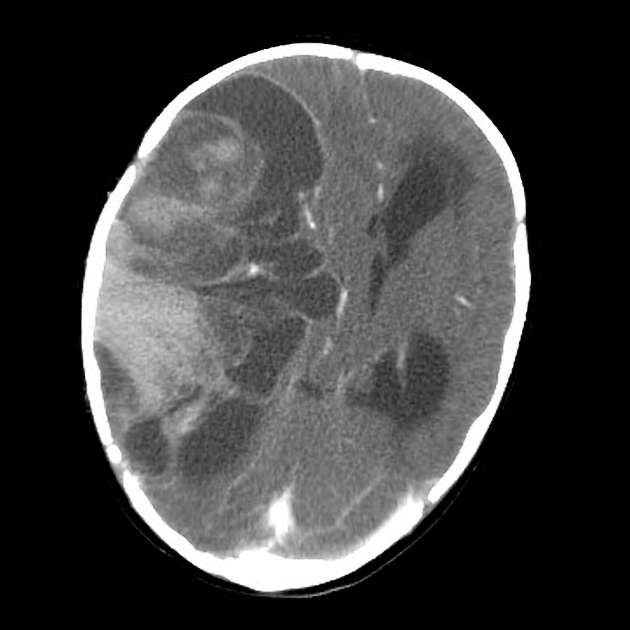
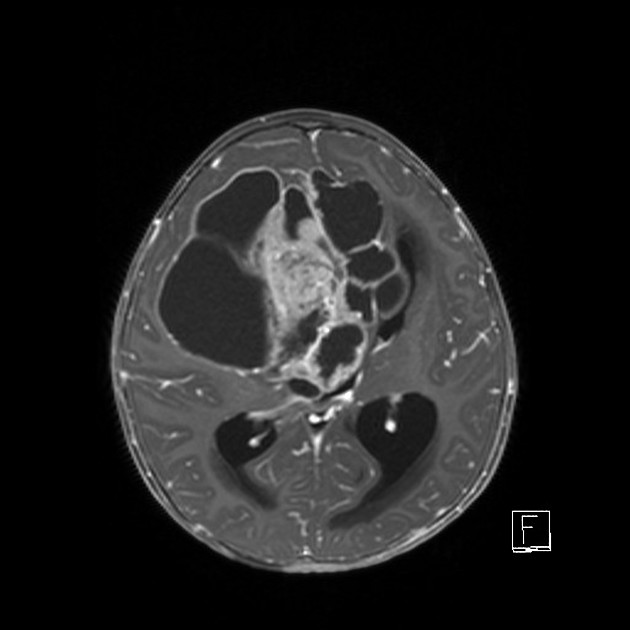
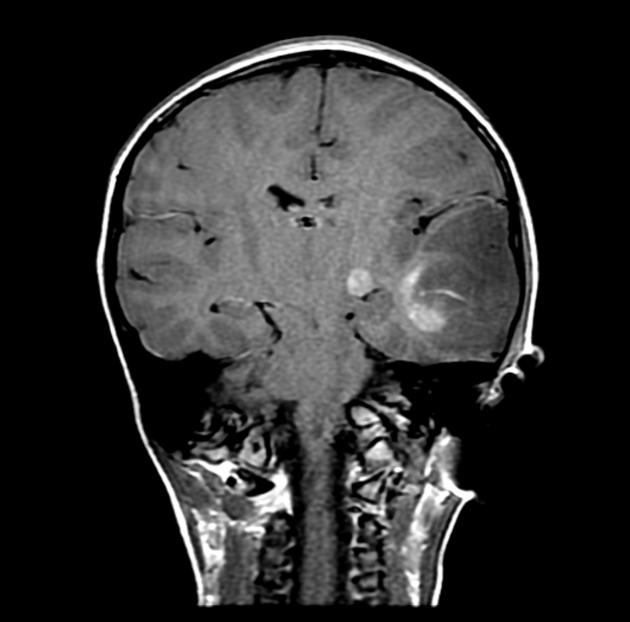
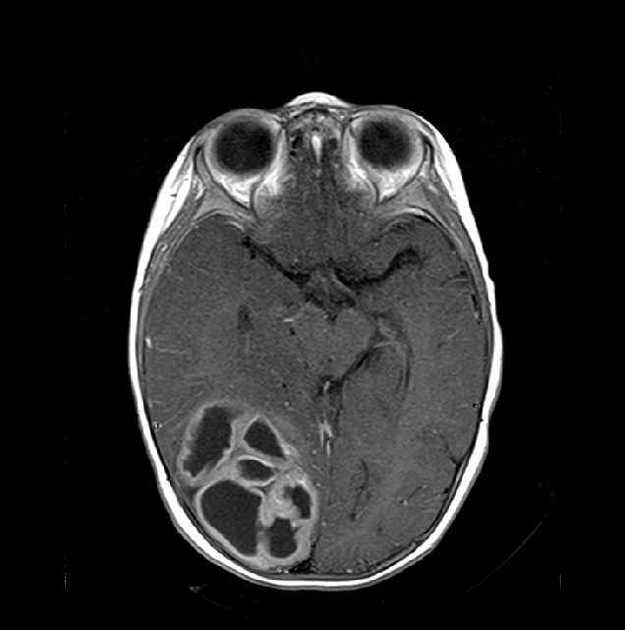
The tumor appears as a large, demarcated, solid mass featuring patchy or no contrast enhancement, with surrounding edema, often with significant mass effect. A minority of the reported cases have shown cystic components and microcalcifications.
T1: decreased intensity
T2: increased intensity
T1 C+ (Gd): patchy or no contrast enhancement
MR spectroscopy shows choline peak and a high ratio of choline/aspartate suggesting hypercellularity of the tumor.
Staging
Following maximal surgical resection, patients can be staged according to the extent of spread within and outside of the central nervous system 7,8.
M0: no evidence of subarachnoid or hematogenous metastasis
M1: microscopic tumor cells found in the cerebrospinal fluid
M2: gross nodular seeding demonstrated in the cerebellar/cerebral subarachnoid space or in the third or lateral ventricles
M3: gross nodular seeding in the spinal subarachnoid space
M4: metastasis outside the central nervous system
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment options for ETMR include surgical resection, systemic chemotherapy and craniospinal radiation (when appropriate).
Unfortunately, the prognosis is dismal, with articles reporting ~75% of cases have died within the median survival of 9 months.
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis varies according to the location of the tumor. The general imaging differential for the brainstem and infratentorial embryonal tumors with multilayered rosettes include:





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.