Epistaxis (plural: epistaxes) is the medical term for a nosebleed, and is very common in clinical practice with a broad differential diagnosis. Anterior epistaxes mainly bleed from Kiesselbach's plexus and posterior epistaxes (5% of all epistaxis) from Woodruff's plexus.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Epistaxis is very common, with a lifetime incidence of ~60% 2.
Pathology
Aetiology
There is a broad range of causes, both local and systemic 2:
-
local
digital trauma (most common)
-
neoplasms (rare)
-
vascular malformations (rare)
hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome)
intracranial aneurysms (very rare)
chemical irritants
-
systemic
coagulopathy, congenital (e.g. von Willebrand disease) and acquired (e.g. alcohol use)
renal failure
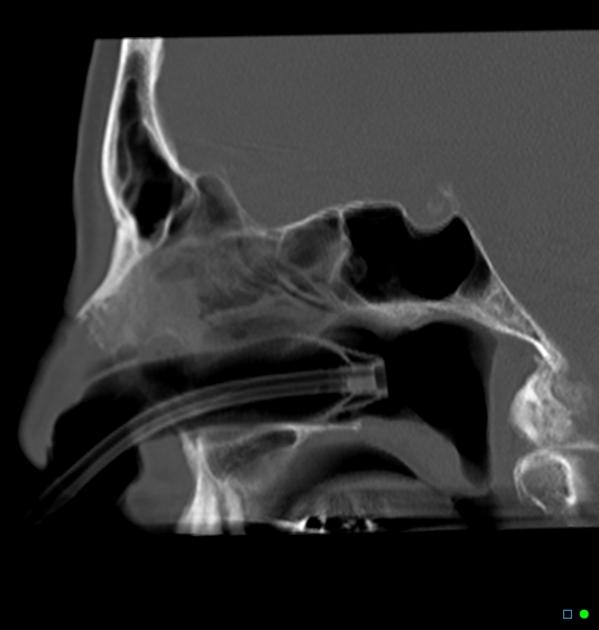
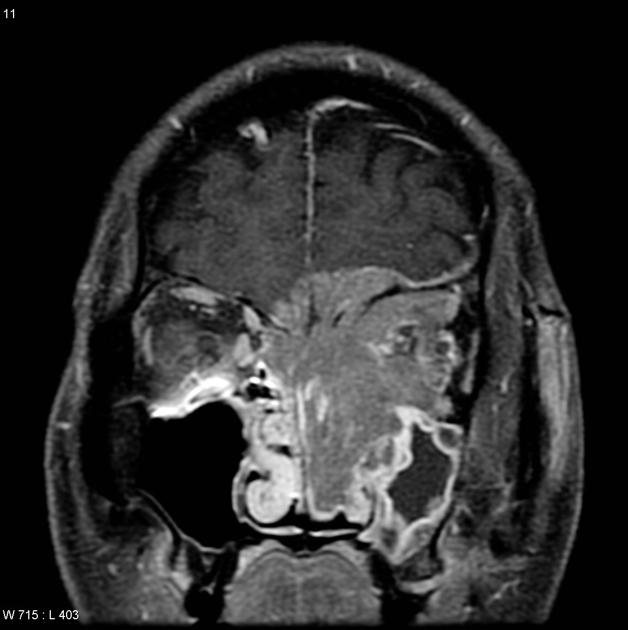
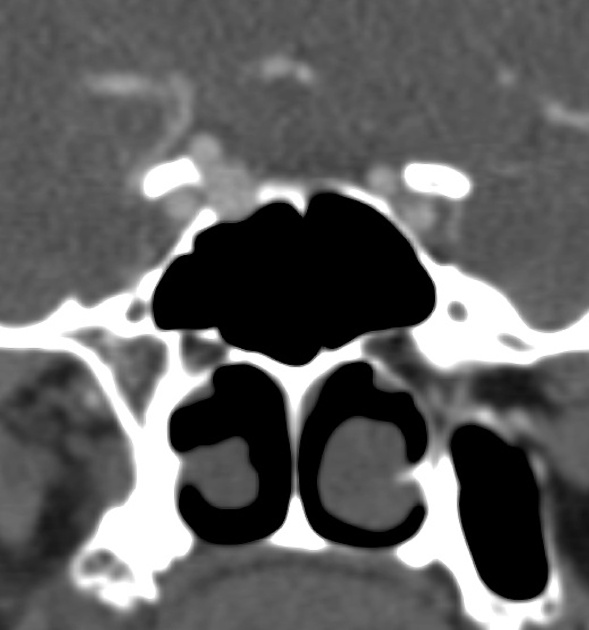
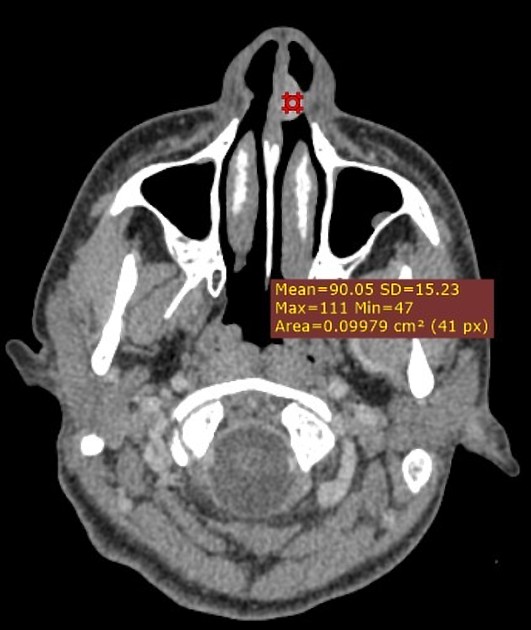
Radiographic features
They usually do not require imaging, unless they are very severe or recurrent. In rare instances, these can be evaluated in the interventional radiology suite for potential endovascular embolisation, especially if uncontrollable with nasal packing. Ideally, prior to embolisation, these cases should be imaged by head and neck CTA.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.