Fascicular sign
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
St-Amant M, Feger J, Abdeldjalil B, et al. Fascicular sign. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 21 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-19091
rID:
19091
Article created:
5 Aug 2012,
Maxime St-Amant ◉
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created Maxime St-Amant had no recorded disclosures.
View Maxime St-Amant's current disclosures
Last revised:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Joachim Feger had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Joachim Feger's current disclosures
Revisions:
12 times, by
10 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Systems:
Sections:
Synonyms:
- Fascicle sign
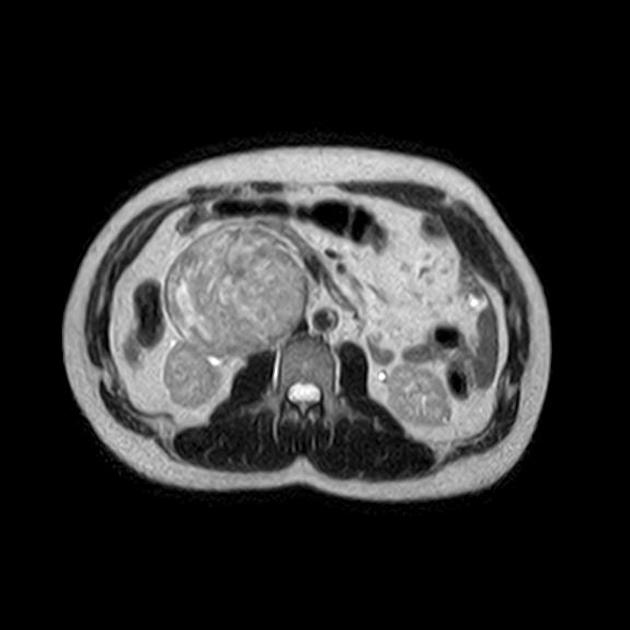
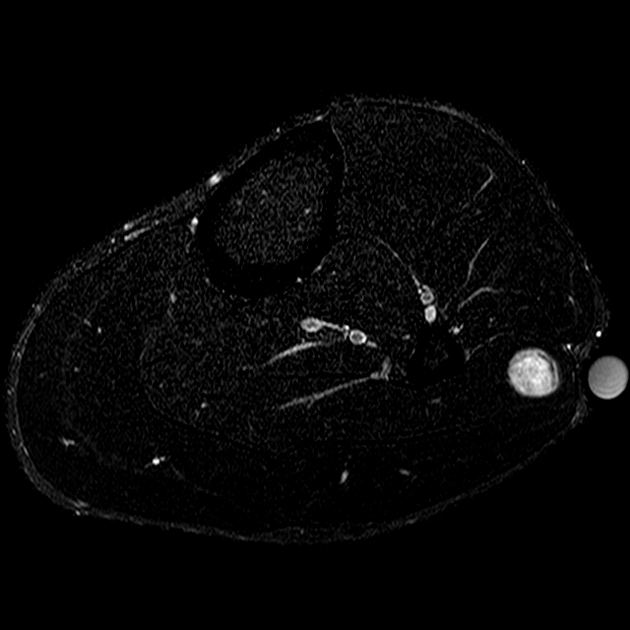
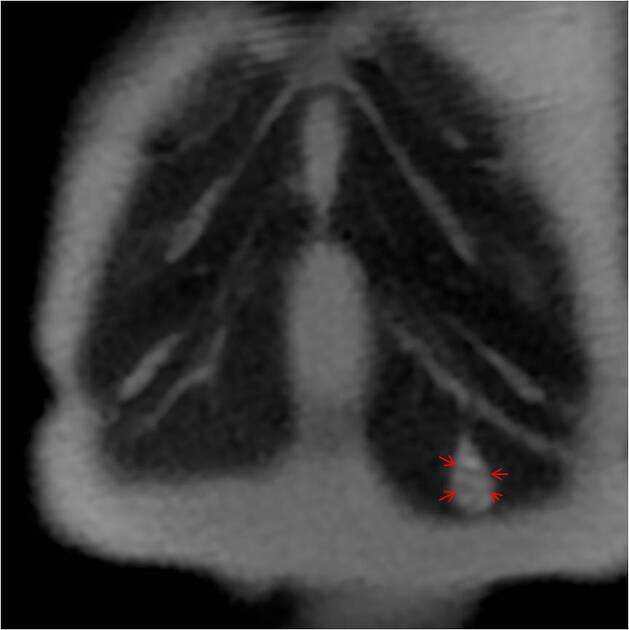
The fascicular sign is a finding on T2-weighted MRI images that suggests a lesion of neurogenic origin. It is characterised by multiple small ring-like structures with peripheral hyperintensity representing the fascicular bundles within the nerves.
It is found in various neurogenic tumours, including:
schwannoma/neurilemoma
malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumour (PNST): a spindle cell carcinoma arising from a nerve or a neurofibroma
References
- 1. Murphey M, Smith W, Smith S, Kransdorf M, Temple H. From the Archives of the AFIP. Imaging of Musculoskeletal Neurogenic Tumors: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation. Radiographics. 1999;19(5):1253-80. doi:10.1148/radiographics.19.5.g99se101253 - Pubmed
- 2. Teh J & Whiteley G. MRI of Soft Tissue Masses of the Hand and Wrist. Br J Radiol. 2007;80(949):47-63. doi:10.1259/bjr/53596176 - Pubmed
- 3. Beaman F, Kransdorf M, Menke D. Schwannoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation. Radiographics. 2004;24(5):1477-81. doi:10.1148/rg.245045001 - Pubmed




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.