Rectus abdominis muscle schwannoma - with fat split sign and fascicular sign
Presentation
left abdominal parietal mass with intermittent localized pain.
Patient Data
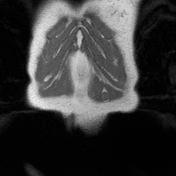

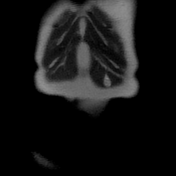

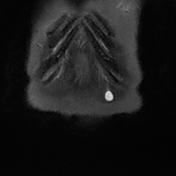





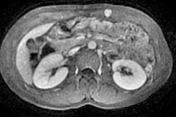

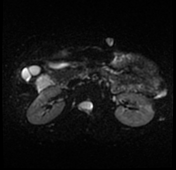

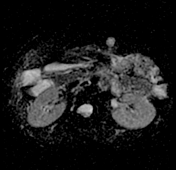

A well-defined oval-shaped mass is seen in the left rectus abdominis muscle showing isosignal to the muscle on T1, hypersignal on T2, STIR and DWI with no restriction on the ADC map. After gadolinium administration the mass is vividly enhancing.
Multiple small ring-like structures are seen throughout the lesion leading to the fascicular sign (best seen on coronal T2 and STIR images). The mass is surrounded by a thin margin of fat in its proximal and distal ends leading to the classic split fat sign (seen on coronal T1 images).
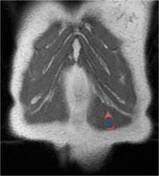

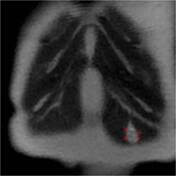
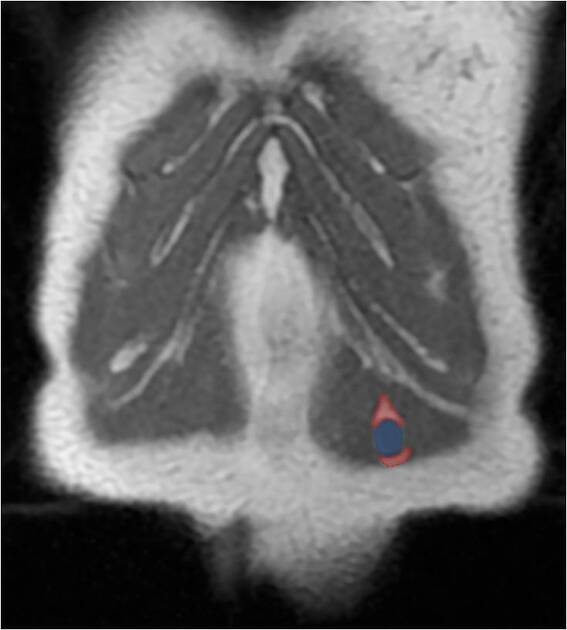
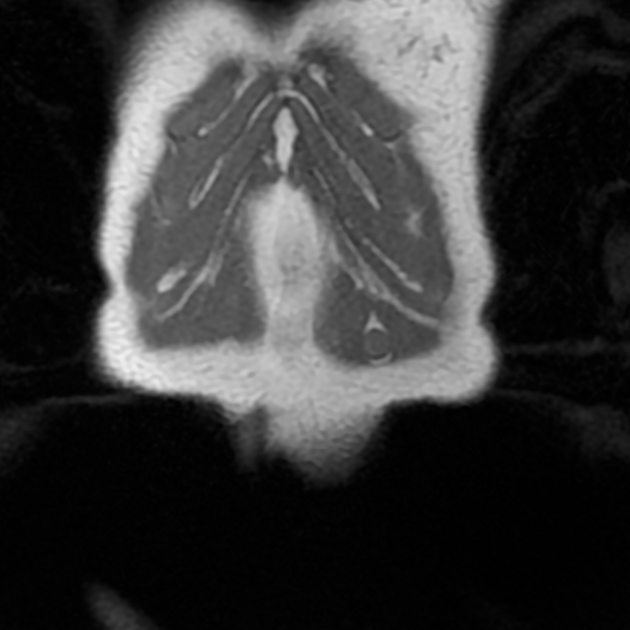
Annotated images:
The first image illustrates the split fat sign seen as a fine rind of fat (red) surrounding the proximal and distal ends of the well-defined schwannoma (blue).
The second image illustrastes the fascicular sign with multiple T2 hypointense ring-like structures within the lesion (red arrows).

Conclusion of the pathology report: histological and immunohistochemical findings in favor of remodeled schwannoma with safe surgical margins.
Case Discussion
The patient underwent surgical resection with histopathology confirming the diagnosis of left rectus abdominis muscle schwannoma (see above).
The fascicular sign and split fat sign are described typically on MRI images with peripheral nerve sheath tumors.
The fascicular appearance seems to be more commonly associated with schwannoma than neurofibroma.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.