Haematocrit effect
Last revised by Avni K P Skandhan
on 16 Nov 2021
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Niknejad M, Skandhan A, St-Amant M, et al. Haematocrit effect. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 19 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-21492
rID:
21492
Article created:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created Mohammad Taghi Niknejad had no recorded disclosures.
View Mohammad Taghi Niknejad's current disclosures
Last revised:
16 Nov 2021,
Avni K P Skandhan
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Avni K P Skandhan had no recorded disclosures.
View Avni K P Skandhan's current disclosures
Revisions:
11 times, by
7 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Systems:
Sections:
Synonyms:
- Hematocrit effect
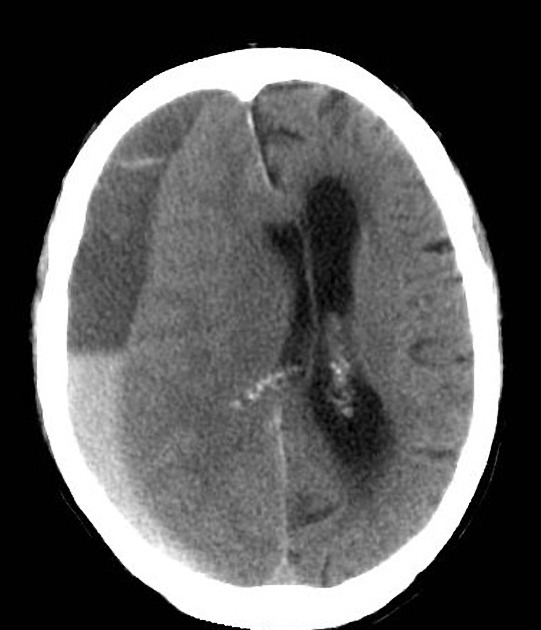
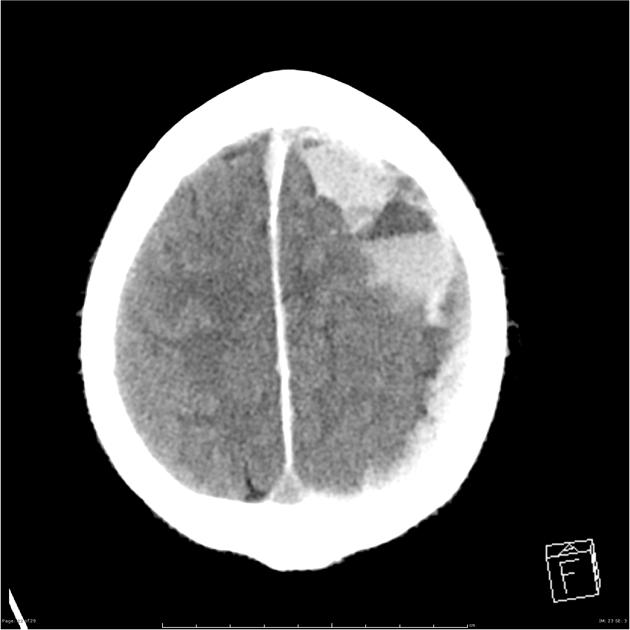
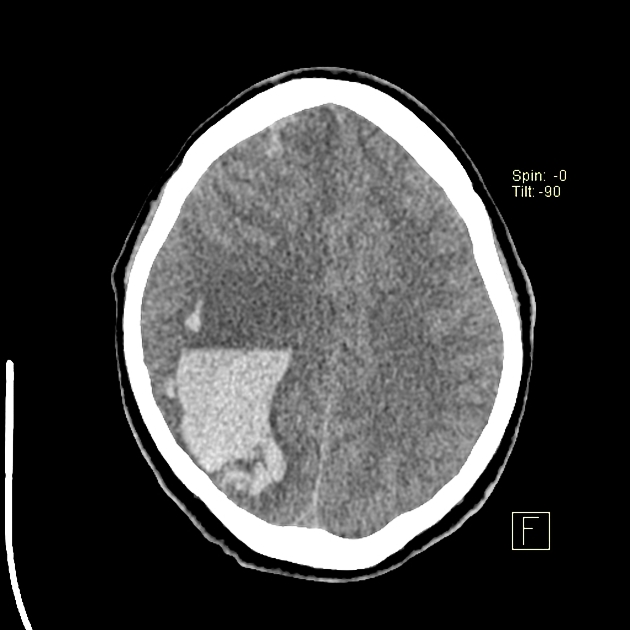
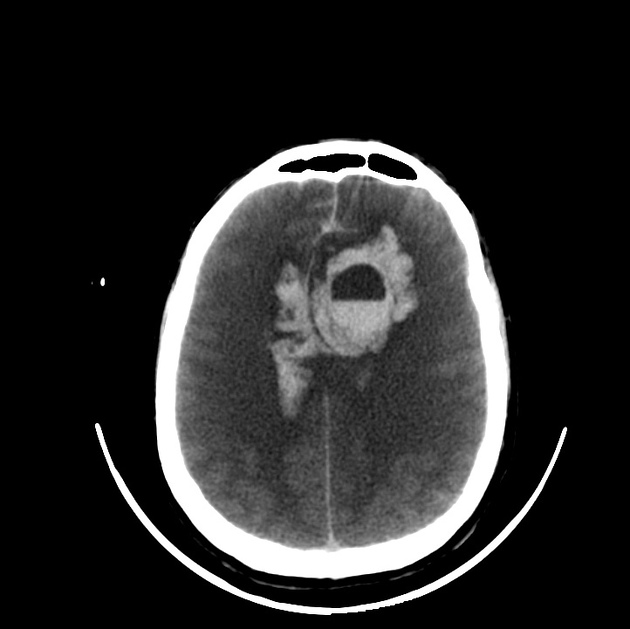
The haematocrit effect with fluid-fluid levels is a result of the layering of heavier cellular elements of blood located dependent on a liquid supernatant. It can be seen on CT or MRI. It is most frequently seen in the setting of anticoagulation therapy or coagulopathy.
On reversal of the coagulopathy; the bleeding will eventually stabilise, the fluid levels disappear and the haematoma gradually resorb.
See also
References
- 1. Haaga JR, Boll D. CT and MRI of the whole body. Mosby. (2009) ISBN:0323053750. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Emergencies in Radiology (Emergencies In Series). Oxford University Press. ISBN:019923843X. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 3. Negus S, Sidhu PS. MRI of retroperitoneal collections: a comparison with CT. Br J Radiol. 2000;73 (872): 907-12. doi:10.1259/bjr.73.872.11026872 - Pubmed citation
- 4. Cox M, Bisangwa S, Herpich F, Crudele A, Pineda C. Fluid Levels in the Bleeding Brain: A Marker for Coagulopathy and Hematoma Expansion. Intern Emerg Med. 2017;12(7):1071-3. doi:10.1007/s11739-017-1604-1 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Articles:
Cases:
- Lipohemarthrosis of the shoulder
- Bilateral subdural haematomas
- Rectus sheath hematoma
- Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumour (MPNST)
- Rectus sheath haematoma with active extravasation
- Intracranial haemorrhage with fluid-fluid level
- Intracranial haemorrhage with fluid-fluid level
- Bilateral acute-on-chronic subdural haematomas
- Bilateral acute-on-chronic subdural haematoma
- Haematocrit effect
- Lipohaemarthrosis




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.