Infraspinatus tendon tears are rotator cuff injuries affecting the infraspinatus tendon generally associated with other rotator cuff tears and are usually due to degenerative processes, trauma, or constant overhead motion strain 1.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Isolated full-thickness infraspinatus tendon tears are very uncommon 2. They are usually associated with supraspinatus tendon tears.
Clinical presentation
Patients will present with shoulder pain and tenderness along the infraspinatus tendon. They might present with a weakness in the affected arm and a limited range of motion.
Associations
Associated conditions include:
Pathology
Classification
A modification of the original Codman classification may be used to categorise tears:
-
-
rim rent tear: articular surface tear of the footprint
tendon delamination or interstitial tear
cleavage tear: tendon delamination with fluid signal intensity filling the gap
critical zone tear: partial or full-thickness
Radiographic features
Plain radiograph
Calcific tendonitis around the greater tubercle may be seen.
Joint effusion and loss of the acromiohumeral interval could be seen in massive rotator cuff tears.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound can be considered for initial assesement of the infraspinatus tendon. Although it is sufficient for the diagnosis of full thickness tears, some partial tears may be underdiagnosed.
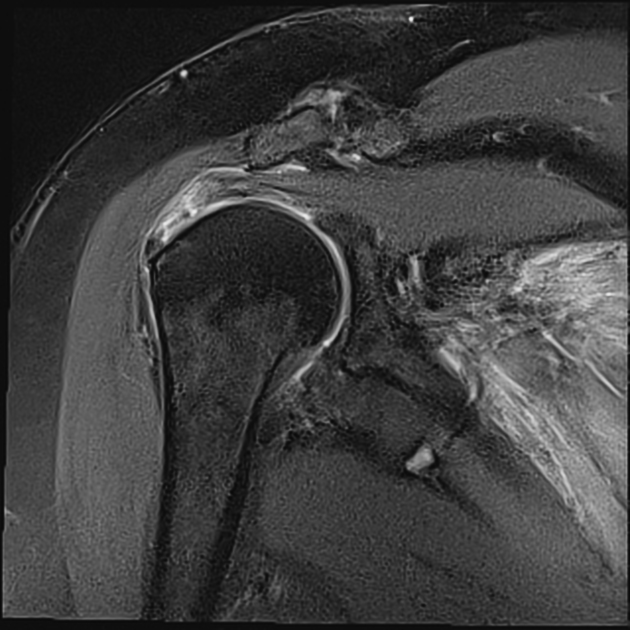
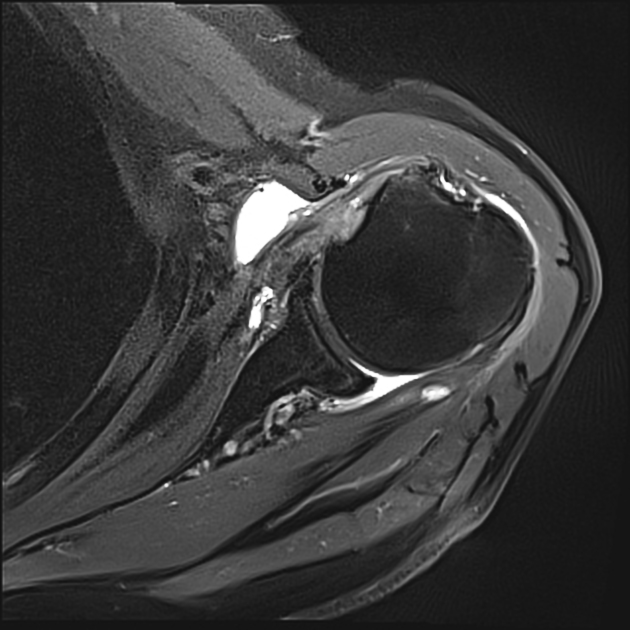
MRI
MRI is the modality of choice in the diagnosis and the pre-operative planning of infraspinatus tendon tears as it demonstrates the tear, it's location, size and all associated lesions.
Radiology report
The radiological report should include a description of the following 3:
location and size of the tear
tear pattern and extent
tendon retraction
rotator cuff associated tears
level of muscle fatty degeneration
acromioclavicular joint osteoarthritis
Treatment and prognosis
Infraspinatus tendon tears could be managed conservatively or surgically, based on the patient age, size of tear, activity level, and mechanism of tear 4.
Differential diagnosis
Possible considerations on low resolution modalities include
supraspinatus tendon tear (inferior margin)






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.