Lateral medullary syndrome
Updates to Article Attributes
Lateral medullary syndrome (or Wallenberg syndrome) is a clinical syndrome caused by an acute ischemic infarct of the lateral medulla oblongata. This is most commonly due to occlusion of the intracranial portion of the vertebral artery followed by PICA and its branches 1-3.
Epidemiology
20% of ischemic strokes occur in the posterior circulation 5.
Wallenberg syndrome is the most prevalent posterior ischemic stroke syndrome 5.
Clinical presentation
This syndrome is characterized by:
- vestibulocerebellar symptoms: vertigo, falling towards the side of lesion, diplopia, and multidirectional nystagmus (inferior cerebellar peduncle and vestibular nucleus) 1-3
- autonomic dysfunction: ipsilateral Horner syndrome, hiccups 1-3
- sensory symptoms: initially abnormal stabbing pain over the ipsilateral face then loss of pain and temperature sensation over the contralateral side of body (spinal trigeminal nucleus involvement) 1-3
- ipsilateral bulbar muscle weakness: hoarseness, dysphonia, dysphagia, and dysarthria, decreased gag reflex (nucleus ambiguus) 1-3
Pathology
Etiology
Hypertension is the commonest risk factor followed by smoking and diabetes 5.
Wallenberg syndrome is caused most commonly by:
- atherothrombotic occlusion of the vertebral artery, the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA), and the medullary arteries
- cerebral embolism
- vertebral artery dissection, the commonest cause in young patients
Radiographic features
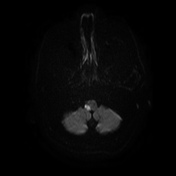
MRI
MRI with diffusion-weighted imaging is the best diagnostic test to confirm the infarct in the lateral medulla.The infarcted area is hyperintense on DWI and low signal on the ADC.
History and etymology
The syndrome was first described by Adolf Wallenberg (1862-1949), a German physician, in 1895 4.
-<p><strong>Lateral medullary syndrome</strong> (or <strong>Wallenberg syndrome</strong>) is a clinical syndrome caused by an acute ischemic infarct of the lateral <a href="/articles/medulla-oblongata">medulla oblongata</a>. This is most commonly due to occlusion of the intracranial portion of the <a href="/articles/vertebral-artery">vertebral artery</a> followed by <a href="/articles/posterior-inferior-cerebellar-artery">PICA</a> and its branches <sup>1-3</sup>. </p><h4>Clinical presentation</h4><p>This syndrome is characterized by:</p><ul>- +<p><strong>Lateral medullary syndrome</strong> (or <strong>Wallenberg syndrome</strong>) is a clinical syndrome caused by an acute ischemic infarct of the lateral <a href="/articles/medulla-oblongata">medulla oblongata</a>. This is most commonly due to occlusion of the intracranial portion of the <a href="/articles/vertebral-artery">vertebral artery</a> followed by <a href="/articles/posterior-inferior-cerebellar-artery">PICA</a> and its branches <sup>1-3</sup>. </p><h4>Epidemiology</h4><p>20% of ischemic strokes occur in the posterior circulation <sup>5</sup>.</p><p>Wallenberg syndrome is the most prevalent posterior ischemic stroke syndrome <sup>5</sup>. </p><h4>Clinical presentation</h4><p>This syndrome is characterized by:</p><ul>
-</ul><h4>History and etymology</h4><p>The syndrome was first described by <strong>Adolf Wallenberg</strong> (1862-1949), a German physician, in 1895 <sup>4</sup>.</p>- +</ul><h4>Pathology</h4><h5>Etiology</h5><p>Hypertension is the commonest risk factor followed by smoking and diabetes <sup>5</sup>.<sup> </sup></p><p>Wallenberg syndrome is caused most commonly by:</p><ul>
- +<li>atherothrombotic occlusion of the vertebral artery, the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA), and the medullary arteries</li>
- +<li>cerebral embolism</li>
- +<li>vertebral artery dissection, the commonest cause in young patients</li>
- +</ul><h4>Radiographic features</h4><h5>MRI</h5><p>MRI with diffusion-weighted imaging is the best diagnostic test to confirm the infarct in the lateral medulla.<sup> </sup>The infarcted area is hyperintense on DWI and low signal on the ADC.</p><h4>History and etymology</h4><p>The syndrome was first described by <strong>Adolf Wallenberg</strong> (1862-1949), a German physician, in 1895 <sup>4</sup>.</p>
References changed:
- 5. Lui F, Tadi P, Anilkumar AC. Wallenberg Syndrome. (2019) <a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29262144">Pubmed</a> <span class="ref_v4"></span>
Image 8 MRI (DWI) ( create )