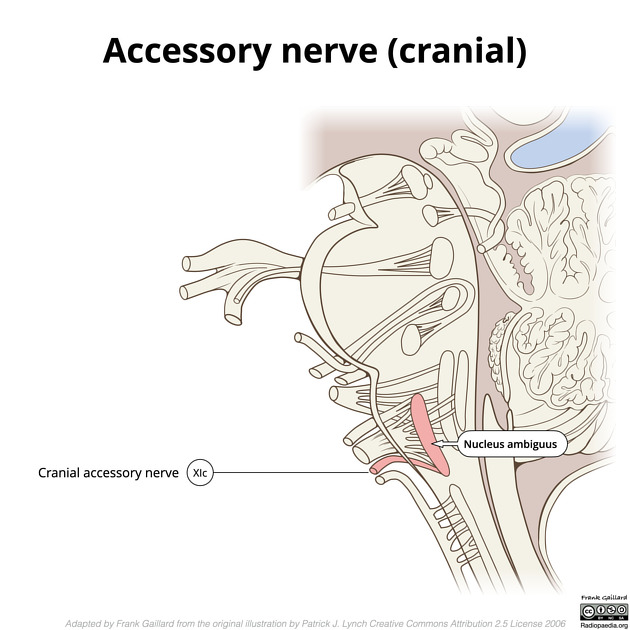
Nucleus ambiguus
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Chris Rothe had no recorded disclosures.
View Chris Rothe's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had the following disclosures:
- Philips Australia, Paid speaker at Philips Spectral CT events (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosuresThe nucleus ambiguus is a large longitudinal nucleus within the medulla oblongata that provides motor innervation to muscles of the pharynx, larynx and soft palate in addition to housing preganglionic nuclei involved in the parasympathetic nervous system augmentation of heart rate 1,2.
Gross anatomy
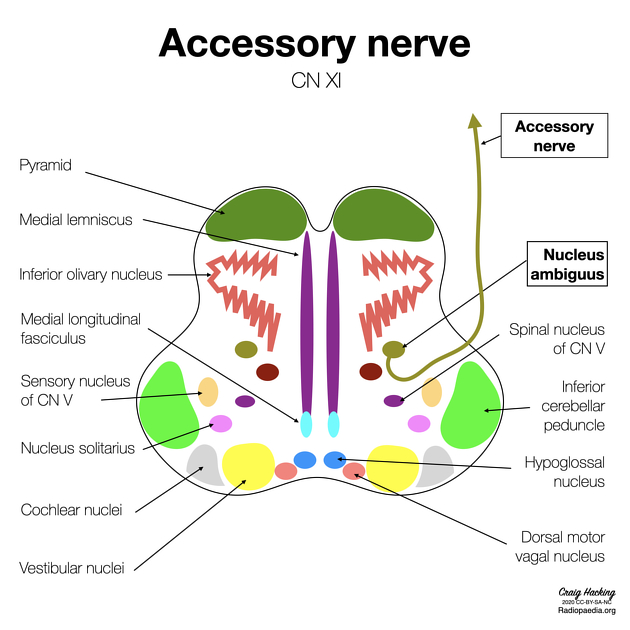
The nucleus ambiguus is a paired nucleus located in the lateral aspect of the rostral medulla.
It lies dorsal to the inferior olivary nucleus and ventromedial to the spinal nucleus and tract of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It is located medial to the lateral spinothalamic tract.
The dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve (CN X) and the solitary tract nucleus both lie dorsal to the nucleus ambiguus, and their respective fibers course around the dorsolateral aspect of the nucleus ambiguus.
Innervation
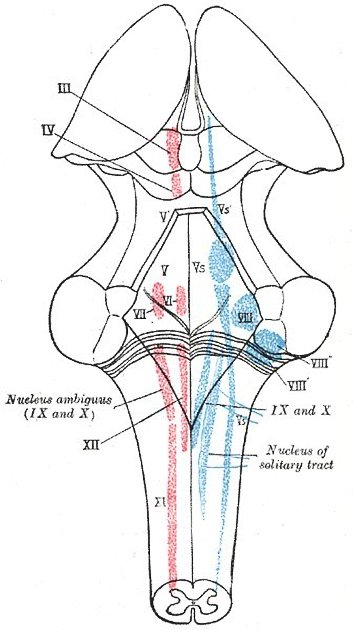
The nucleus ambiguus houses cell bodies which provide motor fibers to the glossopharyngeal (CN IX), vagus (CN X) and spinal accessory nerves (CN XI), which pass laterally from the nucleus ambiguus to exit the medulla in the postolivary sulcus.
The nucleus ambiguus provides motor innervation to the stylopharyngeus muscle with the efferent fibers traveling within the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX).
The nucleus ambiguus also provides motor innervation to the superior, middle and inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscles in addition to the muscles of the soft palate (palatopharyngeus, salpingopharyngeus, levator veli palatini, palatoglossus and the muscles of the uvula). These efferent fibers arising from the nucleus ambiguus travel through pharyngeal branches of the vagus nerve (CN X) which arise from the inferior (nodose) vagal ganglion.
The external laryngeal nerve supplies the cricothyroid muscle (the only intrinsic muscle of the larynx not supplied by the recurrent laryngeal nerve).
The recurrent laryngeal nerve provides motor innervation to all of the intrinsic laryngeal muscles except the cricothyroid muscle.
The nucleus ambiguus also houses preganglionic neurons which contribute to vagal parasympathetic control of heart rate.
References
- 1. BOGDANA PETKO, PRASANNA TADI. Neuroanatomy, Nucleus Ambiguus. (2019) Pubmed
- 2. JIJIANG WANG, MUSTAPHA IRNATEN, ROBERT A. NEFF, PRIYA VENKATESAN, CORY EVANS, ARTHUR D. LOEWY, THOMAS C. METTENLEITER, DAVID MENDELOWITZ. Synaptic and Neurotransmitter Activation of Cardiac Vagal Neurons in the Nucleus Ambiguus. (2001) Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 940 (1): 237. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03680.x - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.