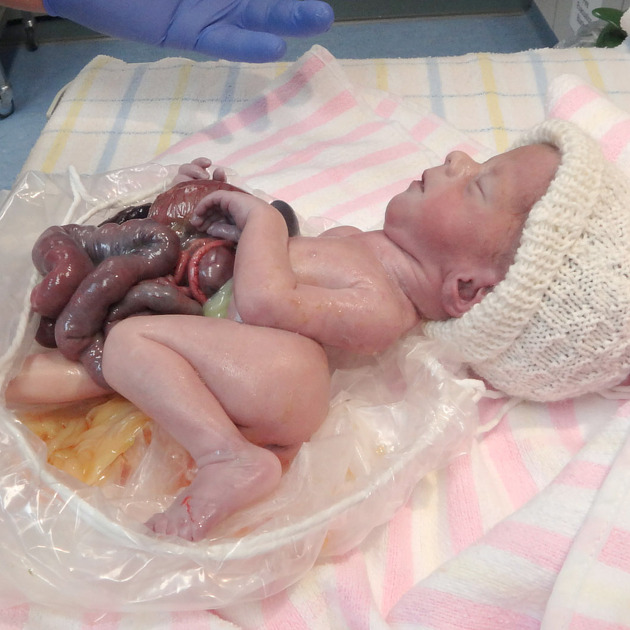
The limb-body wall complex (LBWC) is a rare variable group of congenital limb and body wall defects (involving mainly the chest and abdomen). They can include:
abdominoschisis: usually large and left-sided 4, and almost always present
-
anomalies of the lower limbs:
scoliosis (often profound)
On this page:
Epidemiology
The estimated incidence is at around 1 in 10-14,000 live births.
Pathology
The etiology is controversial; proposed mechanisms include:
early amnion rupture
early vascular disruption
embryologic malformation with abnormal development of the body folds
Internal organs are frequently affected with a high incidence of cardiac and diaphragmatic defects, bowel atresia, renal agenesis, and hydronephrosis.
Risk factors
maternal cocaine abuse (probable) 8-9
Associations
Radiographic features
Ultrasound
May show a large abdominal wall defect with the fetus being adherent to the placenta. The umbilical cord insertion site is challenging to find or is absent, and there is direct apposition of the membranous sac to the amniochorionic membrane. An accompanying kyphoscoliosis/scoliosis may also be detected on ultrasound. Early first-trimester scanning may also show an increased nuchal translucency 10.
Treatment and prognosis
The condition carries an extremely poor prognosis and is invariably fatal 3,4. Management is often supportive. Future pregnancies are however not thought to carry an increased risk of redeveloping the condition.
Differential diagnosis
General imaging considerations include:
amniotic band syndrome (some characterize LBWC to fall under the spectrum of the amniotic band syndrome)




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.