Lines and tubes are important components in chest radiographic evaluation.
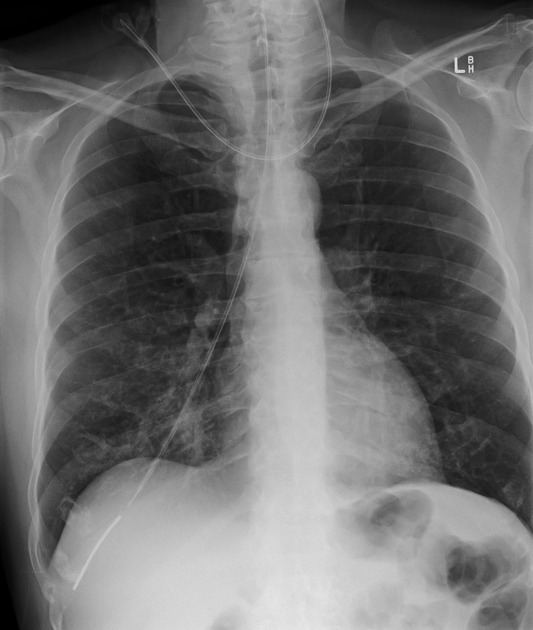
Nasogastric tube (NGT)
See: nasogastric tube positioning.
Correct position
-
NG tube tip ≥10 cm distal to the gastro-oesophageal junction
i.e. below the left hemidiaphragm
Complications
insertion into trachea or bronchus (pneumonia/pulmonary contusion/pulmonary laceration)
pharyngeal or oesophageal perforation
Nasopharyngeal airway tube (NPAT)
See: nasopharyngeal airway tube
Correct position
Tip immediately above the epiglottis
Complications
risk of intracranial positioning in patients with basal skull fracture
Endotracheal tube (ETT)
See: evaluation of endotracheal tube position.
Correct position
Complications
selective intubation (contralateral lung collapse/hyperinflation of ipsilateral lung/pneumothorax)
tooth aspiration
Central venous line/catheter (CVL/CVC)
Correct position
-
CV line tip in the superior vena cava or at the superior cavoatrial junction
i.e. at level of 1st anterior intercostal space above the carina
Complications
insertion into right atrium or ventricle (non-bacterial thrombotic endocarditis / dysrhythmias / myocardial perforation)
mediastinal haematoma secondary to vessel perforation
line fracture +/- embolisation
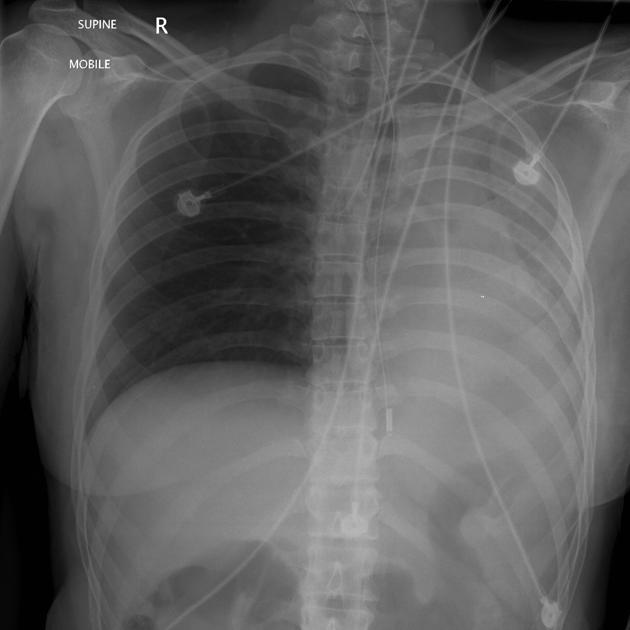
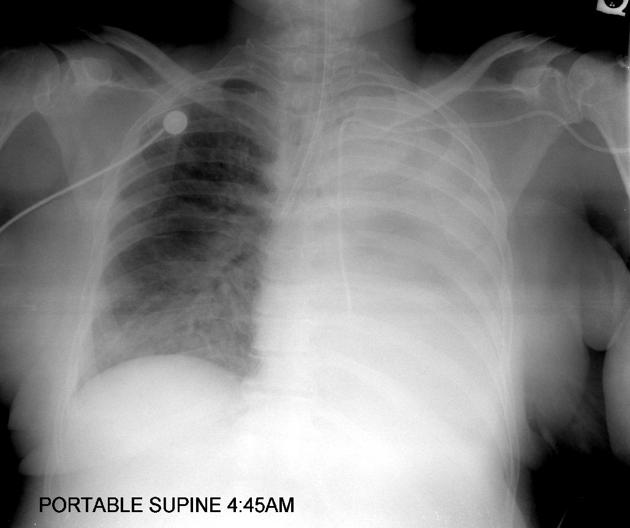
Intercostal tube/catheter (ICC)
See: intercostal catheter
Correct position
-
intercostal tube tip lies between visceral and parietal pleura
anterosuperiorly to drain pneumothorax
posteroinferiorly to drain pleural effusion or haemothorax
Complications
placement into lung parenchyma, interlobar fissure or subcutaneous tissue
mediastinal or abdominal visceral trauma
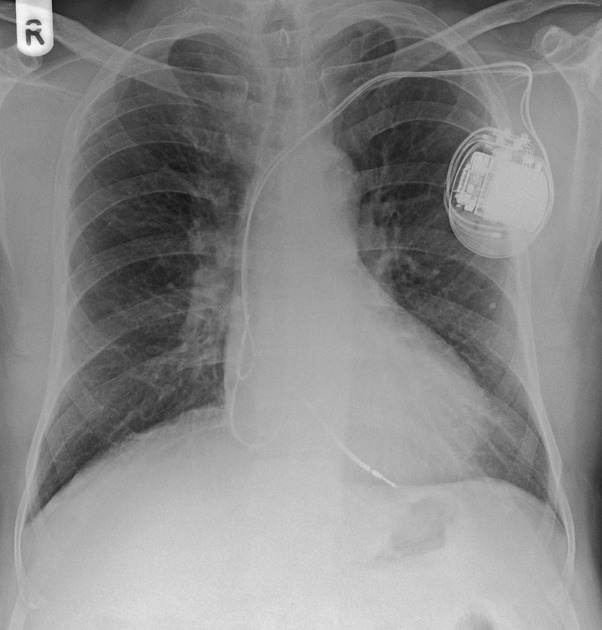
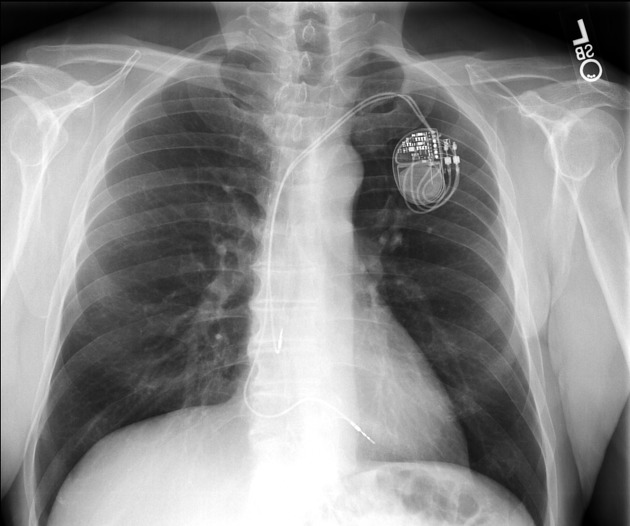
Permanent pacemaker (PPM)
Correct position
single chamber: electrode tip in right atrial appendage (atrial pacing) or right ventricular apex (ventricular pacing)
dual chamber: electrode tips in right atrium and right ventricular apex
biventricular: electrode tips in right atrium, right ventricle and coronary sinus
implantable converter defibrillator: electrode tip in apex of right ventricle
Complications
lead malposition (dysrhythmias)
pneumothorax
Temperature probe
See: temperature probe
Correct position
in the upper to mid thoracic oesophagus
Complications
placement into trachea or bronchus
pneumomediastinum
pneumothorax
Pericardial drain
Correct position
usually inserted on the left of midline into the pericardial space
Intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP)
See: intra-aortic balloon pump
Correct position
tip at the level of the AP window
Complications
aortic dissection
obstruction of the left subclavian artery (too high)
obstruction of the splanchnic arteries (too low)














 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.