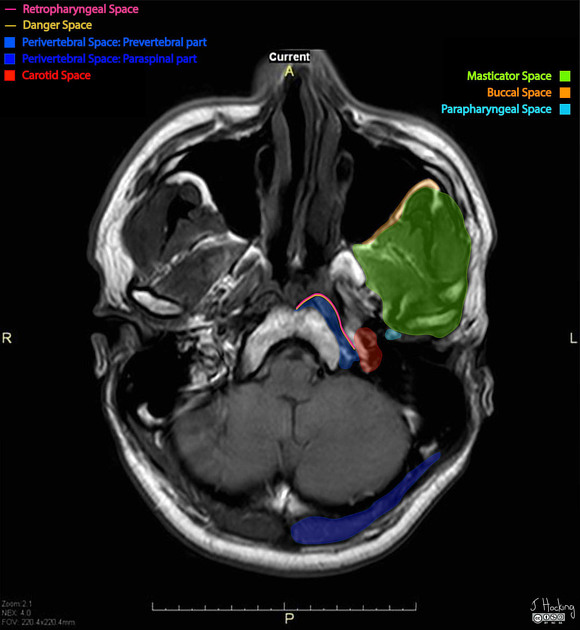
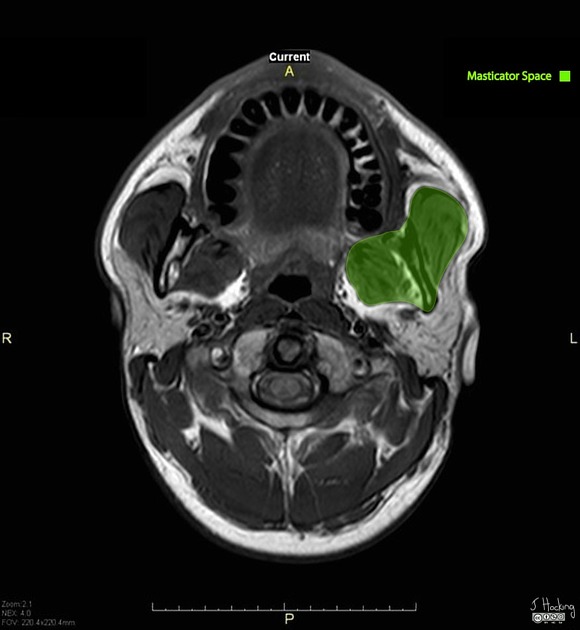
Masticator space
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Sonam Vadera had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Sonam Vadera's current disclosures- Masticatory space
- Masticator spaces
The masticator space is the deep compartment of the head and neck that contains the muscles of mastication.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
The masticator spaces are paired suprahyoid cervical spaces on each side of the face. Each space is enveloped by the superficial (investing) layer of the deep cervical fascia. The superficial layer of the deep cervical fascia splits into two at the lower border of the mandible. The inner layer runs deep to the medial pterygoid muscle and attaches to the skull base medial to foramen ovale. The outer layer covers the masseter and temporalis muscles and attaches to the parietal calvaria superiorly.
Contents
ramus and body of mandible
-
mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (Vc)
enters the masticator space via the foramen ovale 1
inferior alveolar artery and vein
The masticator space contains fibroadipose tissue of potential spaces between the muscles and bones that can be described by the following subcompartments 9:
Boundaries and relations
anteriorly: buccal space
posterolaterally: parotid space
medially: parapharyngeal space
inferomedially: submandibular space
Communications
Masticator space malignancy or infection can spread perineurally via the foramen ovale and along the course of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve into the middle cranial fossa.
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Radiographic appearance
Ultrasound
limited use when imaging the masticator space
masseter muscles, zygomatic arch, outer cortex of the ramus of mandible and suprazygomatic segment of temporal muscle can all be visualised
-
limited visualisation of a number of important structures 3:
pterygoid muscles
pterygoid venous plexus
mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve
Related pathology
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Fernandes T, Lobo JC, Castro R et-al. Anatomy and pathology of the masticator space. Insights Imaging. 2013;4 (5): 605-16. doi:10.1007/s13244-013-0266-4 - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 2. Abdel Razek AA. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of lesions at masticator space. Jpn J Radiol. . doi:10.1007/s11604-014-0289-x - Pubmed citation
- 3. Gervasio A, D'Orta G, Mujahed I et-al. Sonographic anatomy of the neck: The suprahyoid region. J Ultrasound. 2011;14 (3): 130-5. doi:10.1016/j.jus.2011.06.001 - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
Incoming Links
- Infratemporal fossa
- Dental abscess
- Mucosal melanoma of the head and neck (staging)
- Tonsillitis
- Oral cavity carcinoma (staging)
- Pterygopalatine fossa
- Deep spaces of the head and neck
- Submasseteric space
- Superficial layer of the deep cervical fascia
- Pharyngobasilar fascia
- Carotid space
- Pterygomandibular space
- Inferior alveolar nerve
- Necrotizing otitis externa
- Head and neck anatomy
- Parapharyngeal space
- Blue rubber bleb naevus syndrome
- Parotid space
- Masticatory muscle hypertrophy
- Acute submandibular abscess and unpaired anterior jugular vein
- Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
- Sinonasal nonkeratinizing squamous cell carcinoma
- Odontogenic epidural abscess
- Mandibular fractures with temporomandibular joint dislocation and masticator space blow-out fracture
- Trigeminal schwannoma
- Sinonasal lymphoma
- Masticator space abscess - dental origin
- Masticator space abscess
- Masticator space infection
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the maxilla
- Masticator space: annotated MRI
- Masticator space abscess
Related articles: Anatomy: Head and neck
- skeleton of the head and neck
-
cranial vault
- scalp (mnemonic)
- fontanelle
-
sutures
- calvarial
- facial
- frontozygomatic suture
- frontomaxillary suture
- frontolacrimal suture
- frontonasal suture
- temporozygomatic suture
- zygomaticomaxillary suture
- parietotemporal suture (parietomastoid suture)
- occipitotemporal suture (occipitomastoid suture)
- sphenofrontal suture
- sphenozygomatic suture
- spheno-occipital suture (not a true suture)
- lacrimomaxillary suture
- nasomaxillary suture
- internasal suture
- basal/internal
- skull landmarks
- frontal bone
- temporal bone
- parietal bone
- occipital bone
- skull base (foramina)
-
facial bones
- midline single bones
- paired bilateral bones
- cervical spine
- hyoid bone
- laryngeal cartilages
-
cranial vault
- muscles of the head and neck
- muscles of the tongue (mnemonic)
- muscles of mastication
-
facial muscles
- epicranius muscle
- circumorbital and palpebral muscles
- nasal muscles
-
buccolabial muscles
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- levator labii superioris alaeque nasalis muscle
- levator labii superioris muscle
- zygomaticus major muscle
- zygomaticus minor muscle
- levator anguli oris muscle
- malaris muscle
- risorius muscle
- depressors, retractors and evertors of the lower lip
- depressor labii inferioris muscle
- depressor anguli oris muscle
- mentalis muscle
- compound sphincter
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- incisivus labii superioris muscle
- incisivus labii inferioris muscle
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- muscle of mastication
- modiolus
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- muscles of the middle ear
- orbital muscles
- muscles of the soft palate
- pharyngeal muscles
- suprahyoid muscles
- infrahyoid muscles
- intrinsic muscles of the larynx
- muscles of the neck
- platysma muscle
- longus colli muscle
- longus capitis muscle
- scalenus anterior muscle
- scalenus medius muscle
- scalenus posterior muscle
- scalenus pleuralis muscle
- sternocleidomastoid muscle
-
suboccipital muscles
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- accessory muscles of the neck
- deep cervical fascia
-
deep spaces of the neck
- anterior cervical space
- buccal space
- carotid space
- danger space
- deep cervical fascia
- infratemporal fossa
- masticator space
- parapharyngeal space
- stylomandibular tunnel
- parotid space
- pharyngeal (superficial) mucosal space
- perivertebral space
- posterior cervical space
- pterygopalatine fossa
- retropharyngeal space
- suprasternal space (of Burns)
- visceral space
- surgical triangles of the neck
- orbit
- ear
- paranasal sinuses
- upper respiratory tract
- viscera of the neck
- blood supply of the head and neck
-
arterial supply
-
common carotid artery
- carotid body
- carotid bifurcation
- subclavian artery
- variants
-
common carotid artery
- venous drainage
-
arterial supply
- innervation of the head and neck
-
cranial nerves
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
-
trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- trigeminal ganglion
- ophthalmic division
- maxillary division
- mandibular division
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- (spinal) accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck
- cervical sympathetic ganglia
- greater occipital nerve
- third occipital nerve
-
cervical plexus
- muscular branches
- longus capitis
- longus colli
- scalenes
- geniohyoid
- thyrohyoid
-
ansa cervicalis
- omohyoid (superior and inferior bellies separately)
- sternothyroid
- sternohyoid
- phrenic nerve
- contribution to the accessory nerve (CN XI)
- cutaneous branches
- muscular branches
- brachial plexus
- pharyngeal plexus
-
cranial nerves
- lymphatic drainage of the head and neck
- embryological development of the head and neck





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.