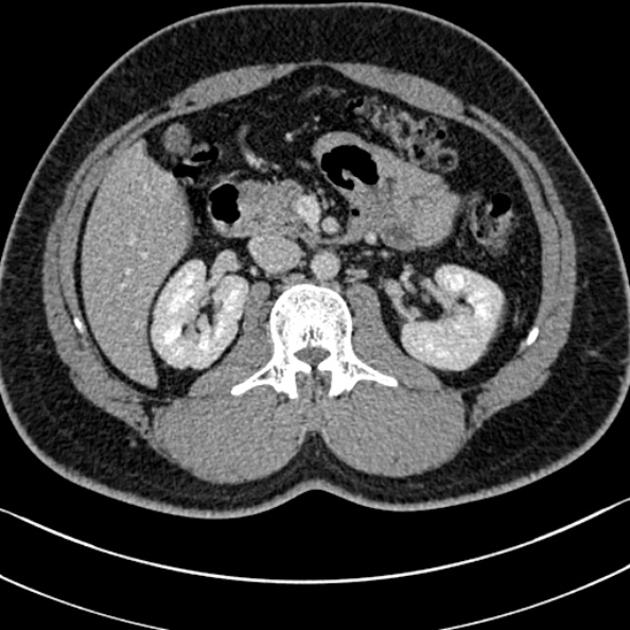
The nephrogenic phase, also known as the nephrographic phase or the renal parenchymal phase, is a postcontrast injection time range in which there is an optimal enhancement of the renal parenchyma including the medulla.
On this page:
Technique
The acquisition time depends on the intravenous device (central or peripheral), the concentration of the contrast medium, and the injection rate.
-
time from injection through an upper extremity vein: 85-120 seconds with a mean of:
100 seconds at an injection rate of 2 ml/s 1,2
88 seconds at a rate of 3 ml/s 2
time from bolus tracking: 80 seconds
Physiology
During this phase, the contrast agent filters through the glomeruli and enters the loop of Henle and the collecting ducts 3.
Clinical use
Nephrogenic phase imaging allows the detection of renal lesions and is required for both renal CT and MRI.
Related pathology
The nephrogenic phase may be delayed in patients with abnormal renal or cardiac function. Read more on the delayed nephrogenic phase.
This phase may occur earlier when the injection is performed at rapid rates 2.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.