Ochronosis, or alkaptonuria (AKU), is a rare multisystem autosomal recessive metabolic disorder.
On imaging, the most particular presentation is on the spine, with osteoporotic bones and dense disc calcifications.
On this page:
Terminology
The term ochronosis usually refers to the bluish-black discolouration of certain tissues, such as the ear cartilage and the ocular tissue, seen with alkaptonuria. Some authorities, however, refer to musculoskeletal manifestations of alkaptonuria as ochronosis 3. The term ochronosis originates from ‘Ocher / ώχρα’ in Greek meaning a dark yellow color, but can progress to bluish grey and black.
Epidemiology
The estimated incidence is around 1:250,000-1,000,000 3,5.
Clinical presentation
Patients often have pigmentation of auricular cartilages and sclera. Urine color tends to be dark (at birth sometimes diagnosed by discolouration of diapers). Up to 25% of patients with alkaptonuria do not have the characteristic dark urine staining; many patients remain undiagnosed until adulthood.
Pathology
The condition results due to excessive build-up of homogentisic acid (HGA) from a lack of homogentisic oxidase (a defect in the biochemical pathway for the degradation of amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine). The excess HGA binds to collagen in connective tissue. The affected connective tissues become weak and brittle with time, leading to chronic inflammation, degeneration, and osteoarthrosis (progressive arthropathy).
Genetics
A defective gene has been mapped to chromosome 3q21–q23 5.
Radiographic features
Plain radiograph
The most well-described features are those involving the skeletal system.
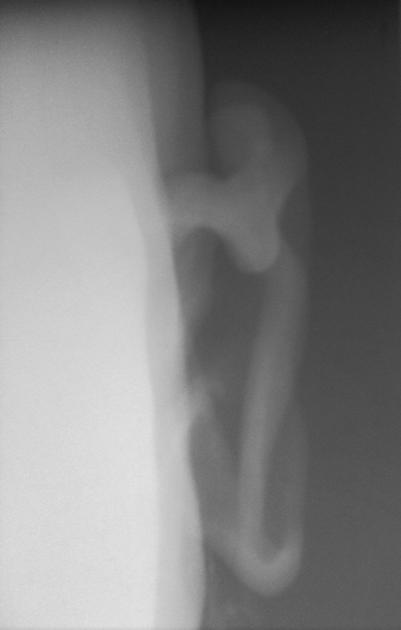
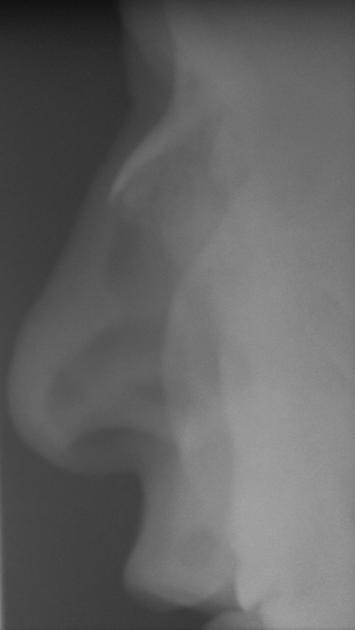
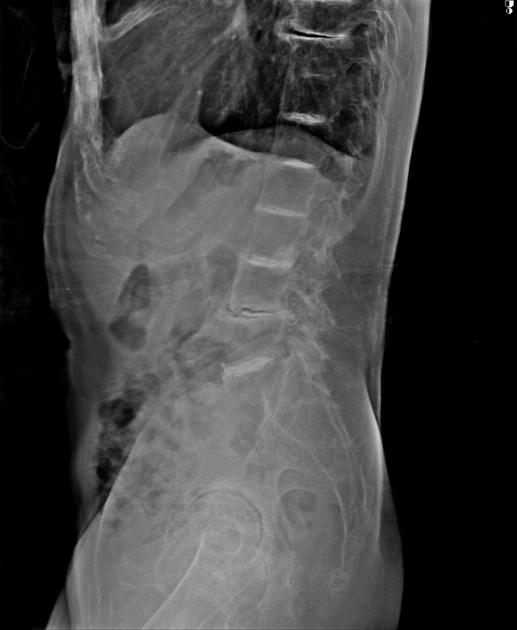
Vertebral
severe osteoporosis
multilevel intervertebral disc calcification: tends to be widespread (and involves nucleus pulposus)
multilevel vacuum phenomenon
syndesmophyte formation
multilevel disc space narrowing
Joints
symmetrical or asymmetrical joint space loss: early osteoarthritis
most commonly in the knee joint; however, the shoulder, the hip and other joints can also be involved
Treatment and prognosis
As of April 2023, there is no effective treatment for alkaptonuria. A low-protein diet is recommended, thus minimizing phenylalanine and tyrosine intake. Vitamin C has been shown to slow down conversion of homogentisate to polymer deposits in the skin. Finally, nitisinone has been shown to halt ochronosis in mice 7.
Complications
spontaneous tendon ruptures have been reported 3
deposition in heart and kidneys can lead to cardiac and renal failure
History and etymology
Ochronosis was defined by Virchow, who histologically described the connective tissue in alkaptonuria, given the cartilage's ocher (yellow) hue under the microscope.
Differential diagnosis
For skeletal radiographic manifestations consider:
calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD): mainly extravertebral
There is a broad differential for intervertebral disc calcification.






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.