Paraduodenal hernias are internal hernias due to failure of the descending or ascending colonic mesentery to fuse with the posterior parietal peritoneum. Left paraduodenal hernia is more common and can cause closed-loop bowel obstruction and infarction.
On this page:
Clinical presentation
The patient may have a history of recurrent positional post-prandial pain and can present acutely with pain and vomiting due to small bowel obstruction.
Pathology
Left paraduodenal hernia
the more common of the two paraduodenal hernias (75%)
small bowel herniates through a single layer of distal colonic mesentery into a retroperitoneal fossa of Landzert (2% incidence at autopsy) that accompanies this abnormality
there is congenital failure of fusion of the descending colon mesentery to the parietal peritoneum in the left upper quadrant
Right paraduodenal hernia
the less common of the two paraduodenal hernias (25%)
small bowel herniates through a layer of the ascending colon mesentery into the associated retroperitoneal fossa of Waldeyer
there is congenital failure of fusion of the ascending colon mesentery to the parietal peritoneum in the right lower quadrant
associated with small bowel malrotation
Radiographic features
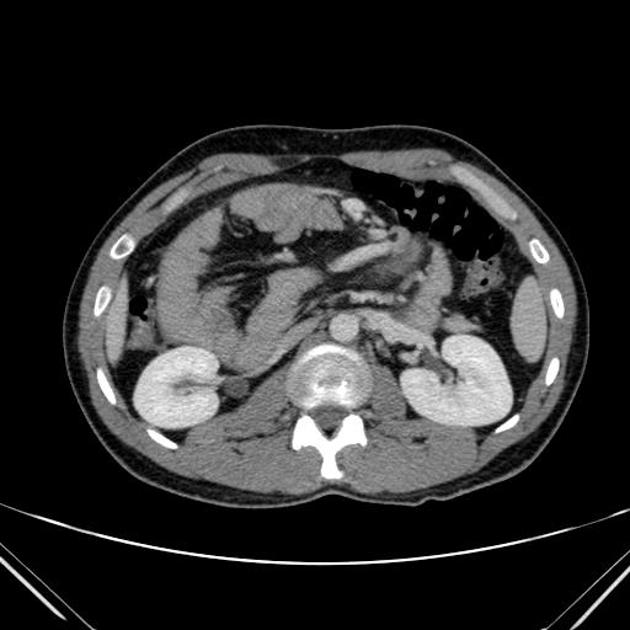
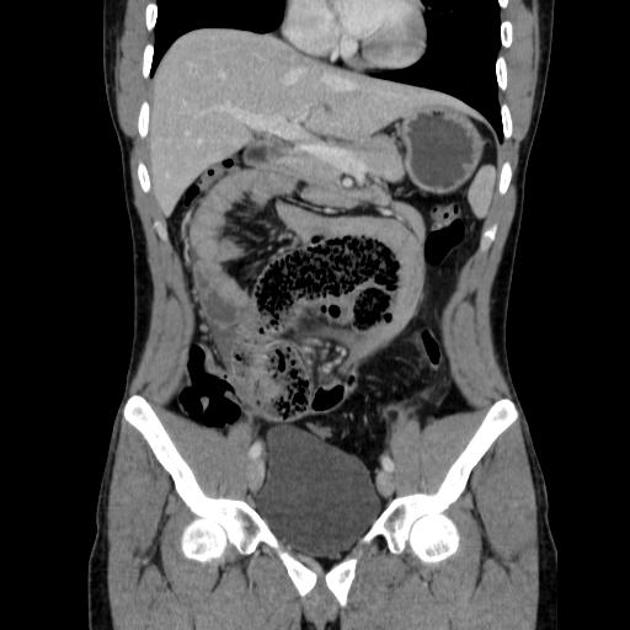
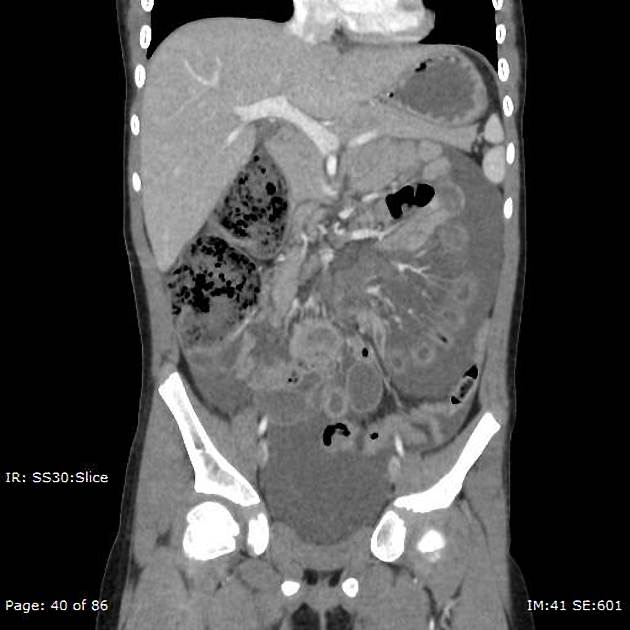
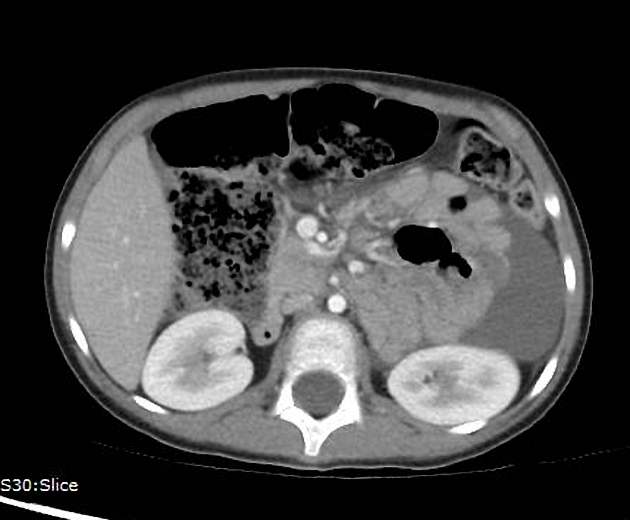
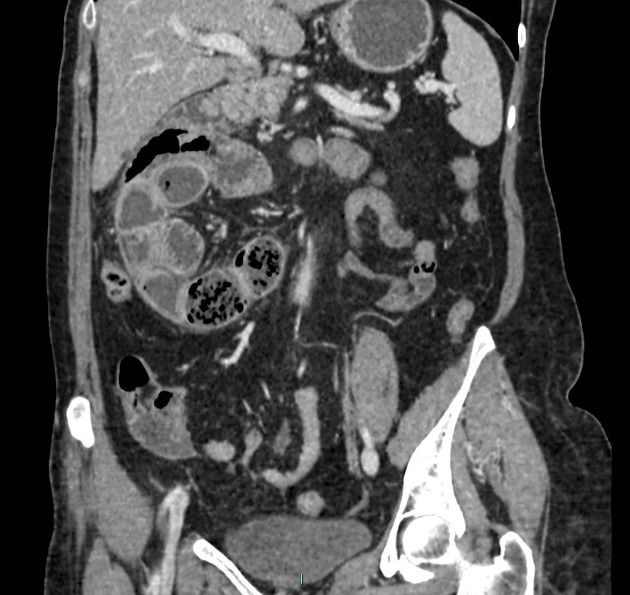
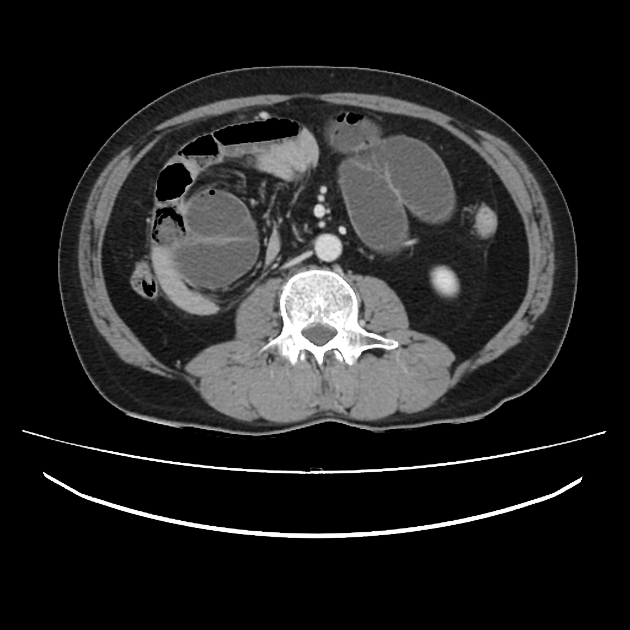
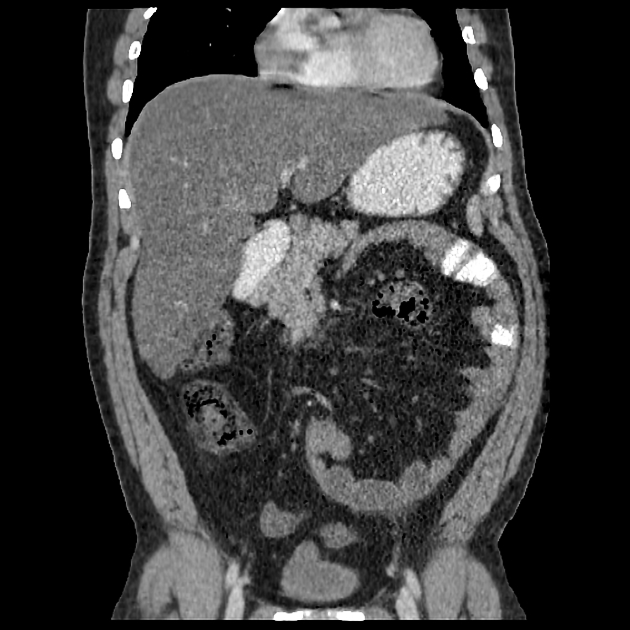
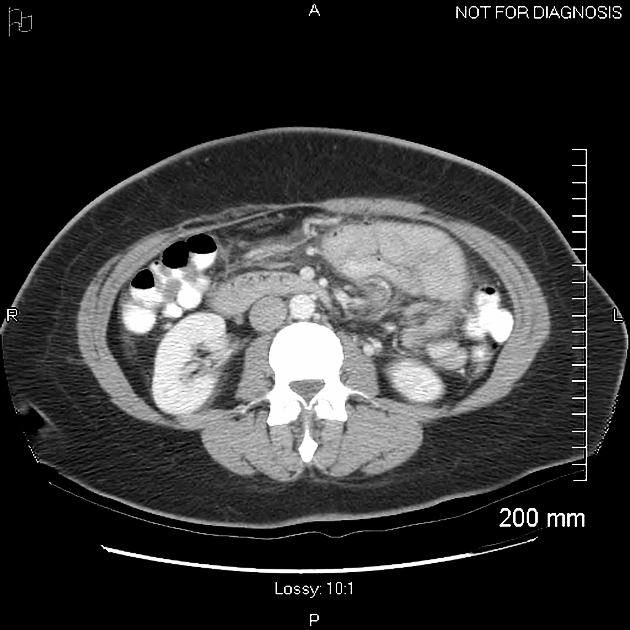
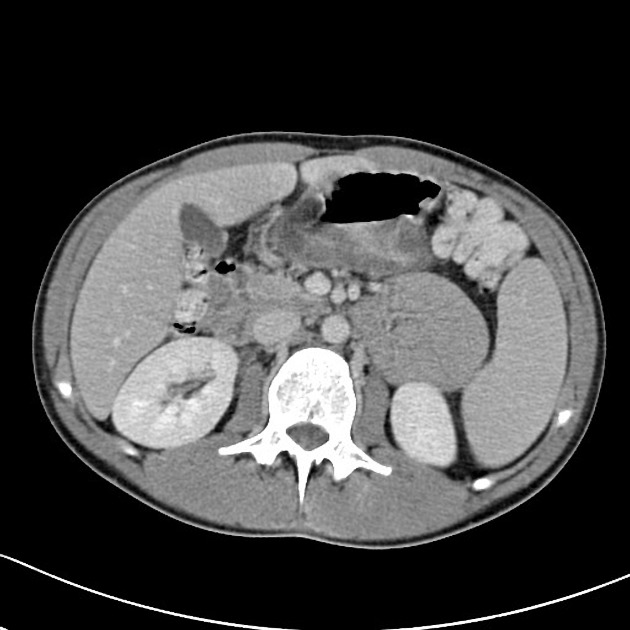
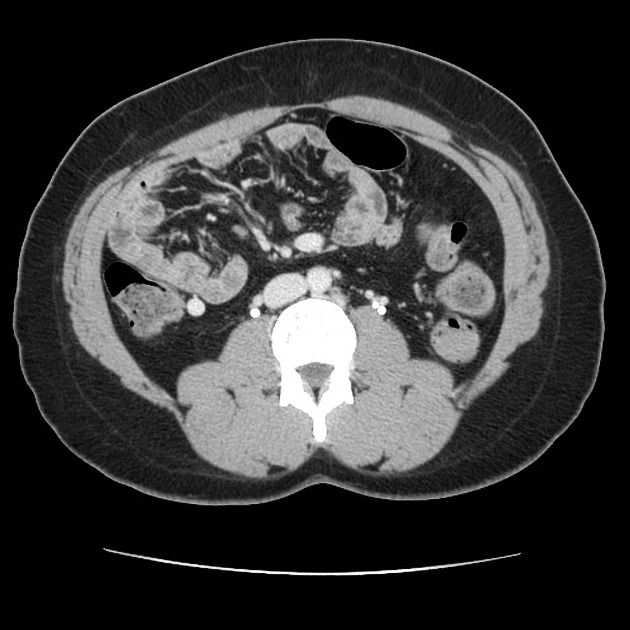
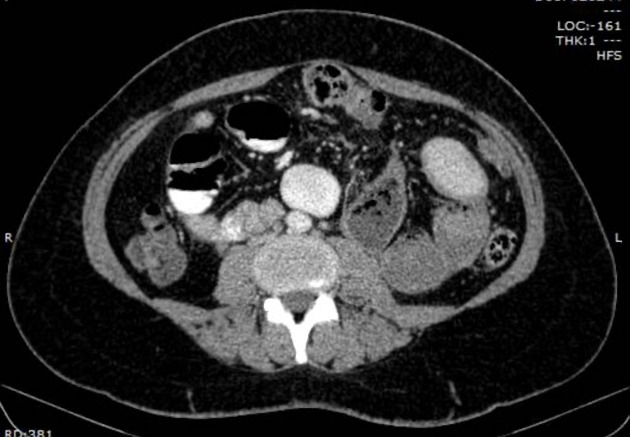
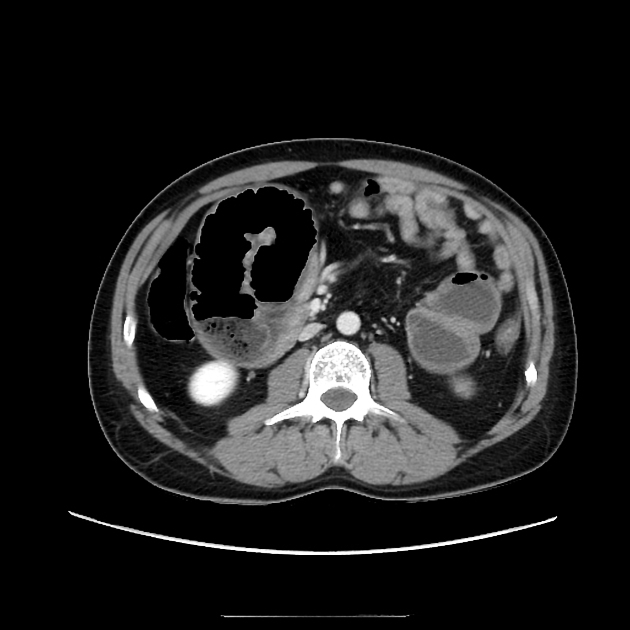
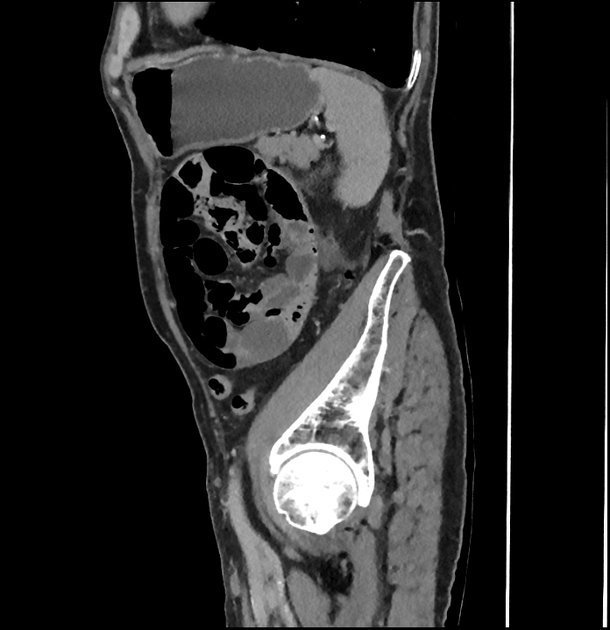
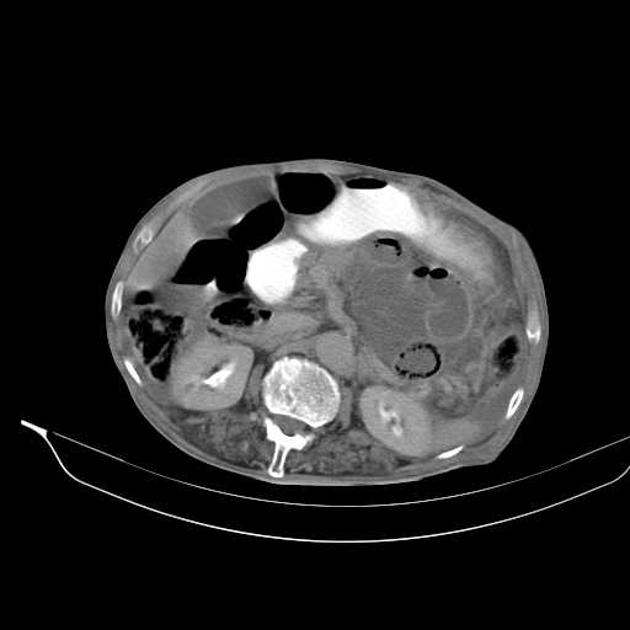
These hernias usually appear as an encapsulated mass-like cluster of small bowel loops. A closed-loop obstruction may develop and strangulation may occur with engorged vessels, mesenteric edema and free fluid. This can progress to infarction.
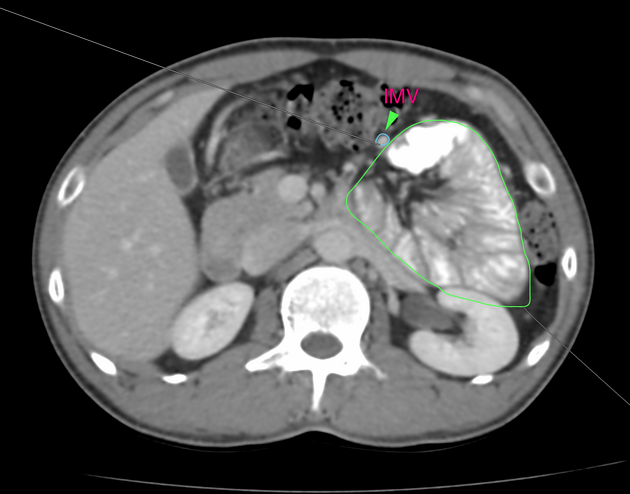
Vascular landmarks around the neck of the internal hernia help to make a confident diagnosis:
-
left paraduodenal hernia
cluster of small bowel loops in the left anterior pararenal space
the inferior mesenteric vein (IMV) and ascending branch of the left colic artery are within the anterior neck of the hernial orifice
-
right paraduodenal hernia
cluster of small bowel loops inferior to the third portion of the duodenum
the superior mesenteric vein (SMV), the superior mesenteric artery (SMA), and the right colic vein are within the anterior neck of the hernial orifice
Differential diagnosis
Small bowel loops may form a cluster in normal patients. Thin patients may be especially challenging since it may be difficult to follow the course of the collapsed loops of small bowel.
Roux-en-Y loops (e.g. bariatric surgery or liver transplant) can be complicated by internal hernias.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.