Paratendinopathy or paratenonitis 5,6 describes the inflammation of the paratenon, a membrane-like structure in tendons without synovial sheath 1,2.
On this page:
Terminology
Paratenonitis has sometimes also been referred to as "peritendinitis" 2 or "paratendonitis" 3.
Epidemiology
Paratenonitis is common, but its frequency depends on the tendon involved. It is commonly found in athletes as a result of overuse injury 1.
Risk factors
dancers
long-distance runners
Diagnosis
A combination of typical clinical and typical imaging findings can establish the diagnosis.
Clinical presentation
Local pain and swelling, tenderness on palpation along the anatomic course of the tendon 4 and movement restriction in the chronic stage 1.
Pathology
Aetiology
Paratenonitis can develop as a result of overuse or repetitive microtrauma 1.
Location
Paratenonitis affects tendons with a paratenon and thus without a synovial sheath 1:
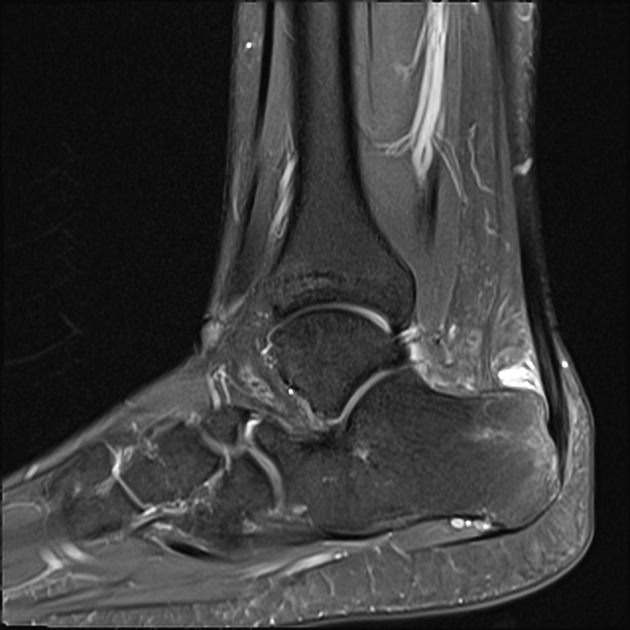
Achilles tendon: most common
gluteal tendons
Radiographic features
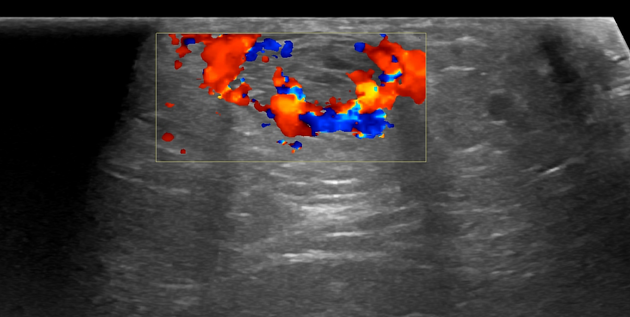
Ultrasound
On ultrasound, paratenonitis might appear as a linear hypoechoic lining around the tendon with associated hyperaemia on colour Doppler in chronic inflammation 2.
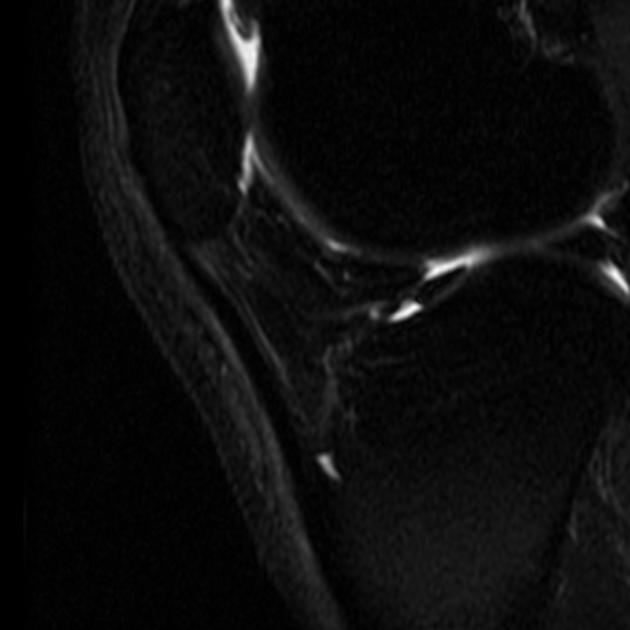
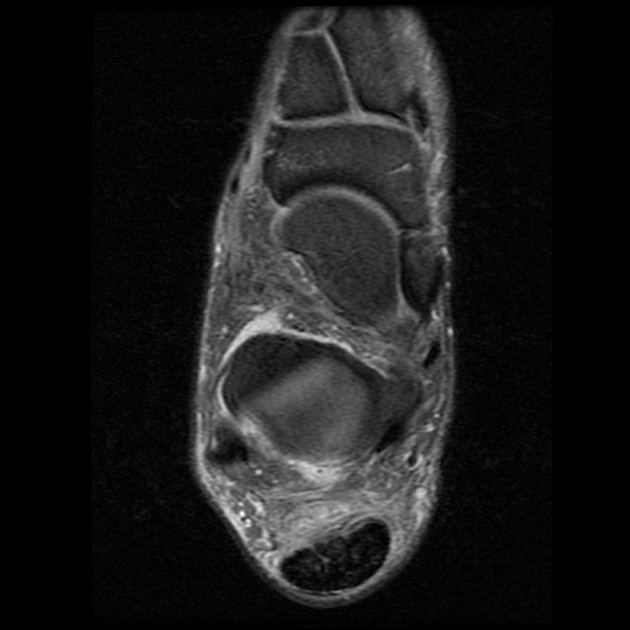
MRI
In the acute phase, a linear fluid intensity structure can be seen around the tendon. In the chronic phase, soft tissue scar-like structures can be seen extending into the peritendinous fatty tissue 1,2.
T1: hypointense
T2/PD: hyperintense
STIR/PDFS: hyperintense
T1 C+ (Gd): enhancement
Radiology report
A description of the following features should be in the radiology report:
inflammatory changes of the paratenon
presence or absence of tendinopathy
presence or absence of tendon tears or rupture
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment is usually conservative with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, activity modification, physical therapy 4. If conservative management fails, paratenon stripping can be performed.
Complications
Chronic paratenonitis can further progress into tendinopathy and tendon tears.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.