Persistent median artery of the forearm
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Henry Knipe had no recorded disclosures.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Yoshi Yu had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Yoshi Yu's current disclosures- Persistent median artery
- Persistent median artery (PMA)
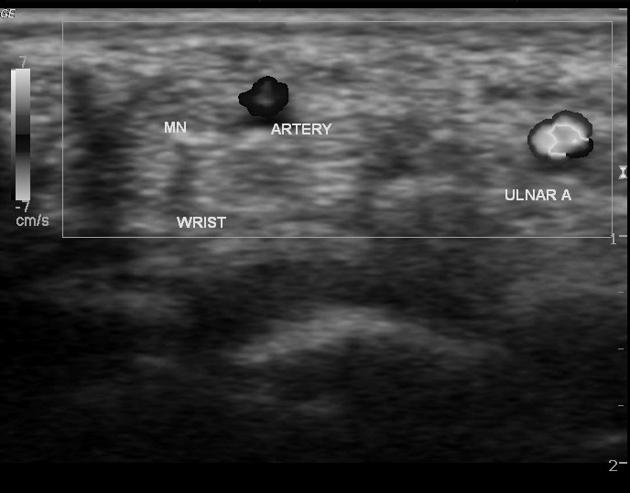
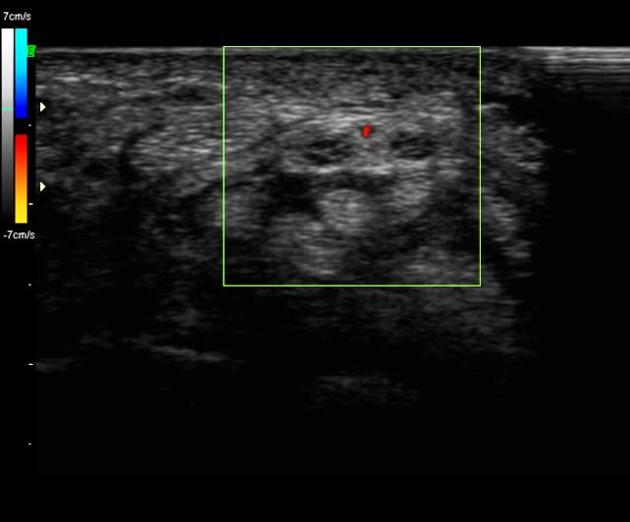
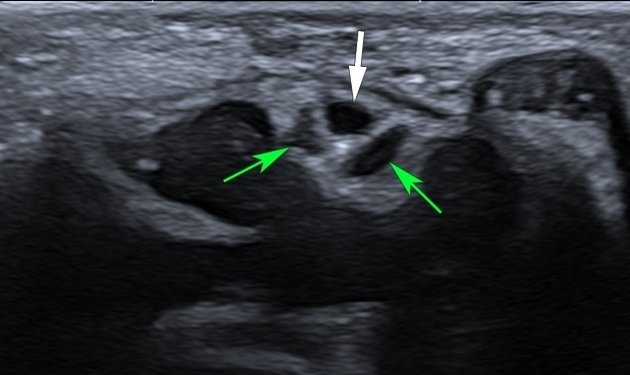
The persistent median artery of the forearm is an accessory artery that arises from the ulnar artery in the proximal forearm and is a persistent embryological remnant of the axial artery that usually regresses by eight weeks gestation 4.
On this page:
Epidemiology
It is present in ~10% (range 2.2-23%) of the population.
Gross anatomy
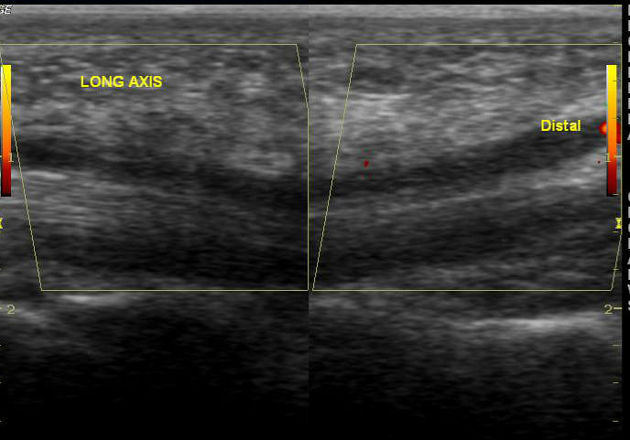
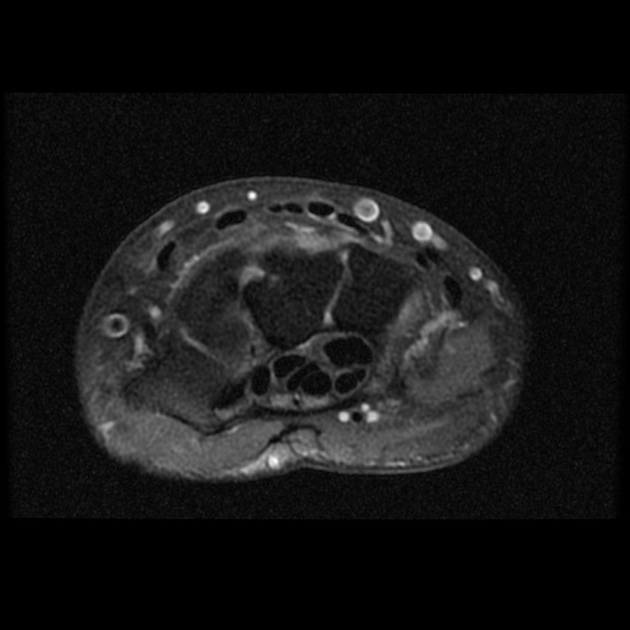
The persistent median artery of the forearm is a continuation of the common or anterior interosseous artery and accompanies the median nerve as it passes through the forearm and carpal tunnel.
It is unilateral ~67% of the time and is associated with anomalous median nerves ~70% (range 63-80%) of the time - most commonly bifid median nerves followed by high division of the median nerve. The persistent median artery is contained within the epineurium of the normal or bifid median nerve.
The persistent median artery is located on the ulnar aspect of the normal median nerve but if the median nerve is bifid the persistent median artery is located between the two nerve bundles.
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Development
In early embryonic development, the median artery is the major supply to the forearm and hand. As the radial and ulnar arteries develop, the median artery usually regresses, only remaining as a tiny vessel accompanying the median nerve within the carpal tunnel, which is not normally visible on imaging. Occasionally, the median artery fails to regress and remains as a large vessel into maturity 6.
Related pathology
The persistent median artery can be a cause of carpal tunnel syndrome and is important to recognize if imaging is performed pre-operatively as it may be damaged during surgery. If it is not recognized intra-operatively due to tourniquet use subsequent damage may be a cause of post-operative bleeding.
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Gassner E, Schocke M, Peer S, Schwabegger A, Jaschke W, Bodner G. Persistent Median Artery in the Carpal Tunnel: Color Doppler Ultrasonographic Findings. J Ultrasound Med. 2002;21(4):455-61. doi:10.7863/jum.2002.21.4.455 - Pubmed
- 2. Rodríguez-Niedenführ M, Sañudo J, Vázquez T, Nearn L, Logan B, Parkin I. Median Artery Revisited. J Anat. 1999;195 ( Pt 1)(1):57-63. doi:10.1046/j.1469-7580.1999.19510057.x - Pubmed
- 3. Haładaj R, Wysiadecki G, Dudkiewicz Z, Polguj M, Topol M. Persistent Median Artery as an Unusual Finding in the Carpal Tunnel: Its Contribution to the Blood Supply of the Hand and Clinical Significance. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:32-9. doi:10.12659/MSM.912269 - Pubmed
- 4. Natsis K, Iordache G, Gigis I et al. Persistent Median Artery in the Carpal Tunnel: Anatomy, Embryology, Clinical Significance, and Review of the Literature. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2009;68(4):193-200. - Pubmed
- 5. Osiak K, Elnazir P, Mazurek A, Pasternak A. Prevalence of the Persistent Median Artery in Patients Undergoing Surgical Open Carpal Tunnel Release: A Case Series. Translational Research in Anatomy. 2021;23:100113. doi:10.1016/j.tria.2021.100113
- 6. Eyer B. Persistent Median Artery - Radsource. Radsource. Radsource
Incoming Links
- Thrombosis of persistent median artery
- Persistent median artery of the forearm with bifid median nerve - bilateral
- Bifid median nerve and persistent median artery of the forearm
- Bifid median nerve and persistant median artery
- Thrombosis of persistent median artery
- Thrombosis of persistent median artery
- Thrombosis of persistent median artery of the forearm
- Thrombosis of persistent median artery of upper limb
- Thrombosis of persistent median artery of upper limb
- Carpal tunnel syndrome - with inverted notch sign
- Bilateral persistent median artery of the forearm with unilateral bifid median nerve
- Bifid median nerve and persistent median artery of the forearm
Related articles: Anatomy: Upper limb
-
skeleton of the upper limb
- clavicle
- scapula
- humerus
- radius
- ulna
- hand
- accessory ossicles of the upper limb
- accessory ossicles of the shoulder
- accessory ossicles of the elbow
-
accessory ossicles of the wrist (mnemonic)
- os centrale carpi
- os epilunate
- os epitriquetrum
- os styloideum
- os hamuli proprium
- lunula
- os triangulare
- trapezium secondarium
- os paratrapezium
- os radiostyloideum (persistent radial styloid)
- joints of the upper limb
-
pectoral girdle
-
shoulder joint
- articulations
- associated structures
- joint capsule
- bursae
- ligaments
- movements
- scapulothoracic joint
-
glenohumeral joint
- arm flexion
- arm extension
- arm abduction
- arm adduction
- arm internal rotation (medial rotation)
- arm external rotation (lateral rotation)
- circumduction
- arterial supply - scapular anastomosis
- ossification centers
-
shoulder joint
-
elbow joint
- proximal radioulnar joint
- ligaments
- associated structures
- movements
- alignment
- arterial supply - elbow anastomosis
- development
-
wrist joint
- articulations
-
ligaments
- intrinsic ligaments
- extrinsic ligaments
- radioscaphoid ligament
- dorsal intercarpal ligament
- dorsal radiotriquetral ligament
- dorsal radioulnar ligament
- volar radioulnar ligament
- radioscaphocapitate ligament
- long radiolunate ligament
- Vickers ligament
- short radiolunate ligament
- ulnolunate ligament
- ulnotriquetral ligament
- ulnocapitate ligament
- ulnar collateral ligament
- associated structures
- extensor retinaculum
- flexor retinaculum
- joint capsule
- movements
- alignment
- ossification centers
-
hand joints
- articulations
- carpometacarpal joint
-
metacarpophalangeal joints
- palmar ligament (plate)
- collateral ligament
-
interphalangeal joints
- palmar ligament (plate)
- collateral ligament
- movements
- ossification centers
- articulations
-
pectoral girdle
- spaces of the upper limb
- muscles of the upper limb
- shoulder girdle
- anterior compartment of the arm
- posterior compartment of the arm
-
anterior compartment of the forearm
- superficial
- intermediate
- deep
-
posterior compartment of the forearm (extensors)
- superficial
- deep
- muscles of the hand
-
accessory muscles
- elbow
- volar wrist midline
- palmaris longus profundus
- aberrant palmaris longus
- volar wrist radial-side
- accessory flexor digitorum superficialis indicis
- flexor indicis profundus
- flexor carpi radialis vel profundus
- accessory head of the flexor pollicis longus (Gantzer muscle, common)
- volar wrist ulnar-side
- dorsal wrist
- blood supply to the upper limb
-
arteries
- subclavian artery (mnemonic)
- axillary artery
- brachial artery (proximal portion)
- ulnar artery
- radial artery
- veins
-
arteries
- innervation of the upper limb
- intercostobrachial nerve
-
brachial plexus (mnemonic)
- branches from the roots
- branches from the trunks
- branches from the cords
- lateral cord
- posterior cord
- medial cord
- terminal branches
- lymphatic drainage of the upper limb





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.