Precentral gyrus
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Chad Wong had no recorded disclosures.
View Chad Wong's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Daniel J Bell had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Daniel J Bell's current disclosures- Primary motor cortex
- Motor strip
- M1
- pre central gyrus
- pre-central gyrus
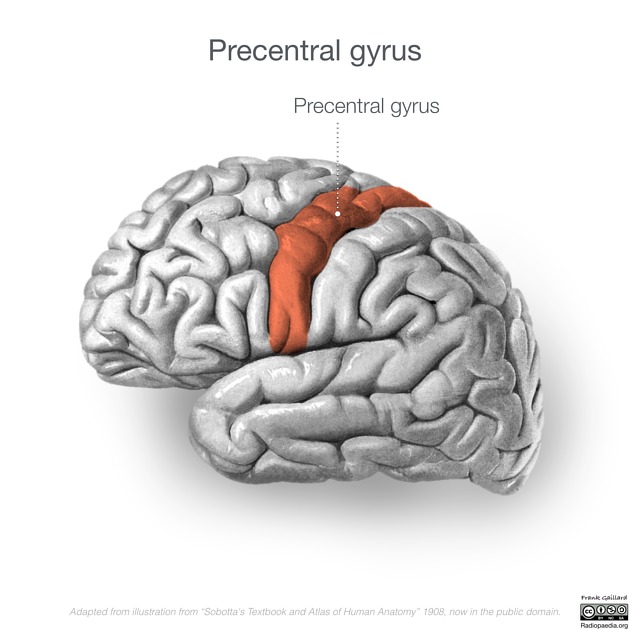
The precentral gyrus, also known as the primary motor cortex, is a very important structure involved in executing voluntary motor movements.
Gross anatomy
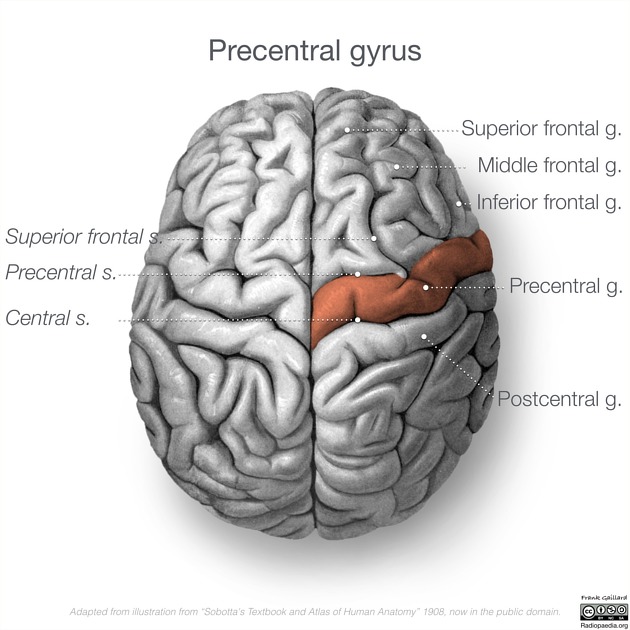
The precentral gyrus is a diagonally orientated cerebral convolution situated in the posterior portion of the frontal lobe. It is located immediately anterior to the central sulcus (fissure of Rolando), running parallel to it 1,2.
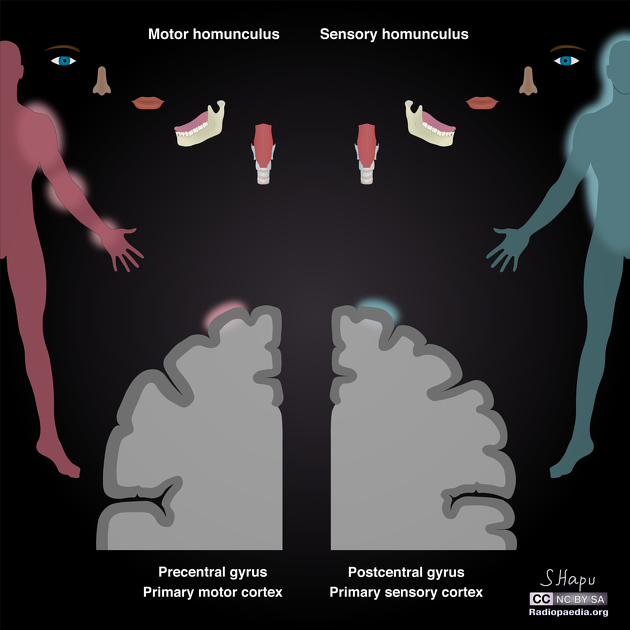
In the precentral gyrus, large neurones known as Betz cells send efferent axons that terminate on the contralateral motor cranial and spinal nuclei. The functional organisation of the precentral gyrus is such that clusters of Betz cells are somatotopically represented by an inverted homunculus. Therefore, head and face regions are innervated by the inferior portion of the precentral gyrus. Conversely, the lower limbs are innervated by the superior portion 4.
Relations
Anterior to the precentral gyrus, separated by the precentral sulcus, lie a set of areas composing the lateral premotor cortex and the supplemental motor area. Posteriorly, separated by the central sulcus, lies the primary somatosensory cortex.
Medially and inferiorly, it is bound by the cingulate gyrus. Laterally and inferiorly, it is bound by the Sylvian fissure 3.
The precentral gyrus is continuous with the postcentral gyrus on both the medial and superolateral aspects of each hemisphere. Medially, this occurs via the paracentral lobule, and superolaterally this connection is via the subcentral gyrus, which may be hidden within the operculum.
References
- 1. Encyclopedia of Clinical Neuropsychology. Springer. ISBN:0387799486. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Encyclopedia of Autism Spectrum Disorders:5 volume set. Springer. ISBN:1441916970. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 3. Parent A, Carpenter MB. Carpenter's Human neuroanatomy. Williams & Wilkins. ISBN:0683067524. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. Rivara CB, Sherwood CC, Bouras C et-al. Stereologic characterization and spatial distribution patterns of Betz cells in the human primary motor cortex. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol. 2003;270 (2): 137-51. doi:10.1002/ar.a.10015 - Pubmed citation
Incoming Links
- Central sulcus
- POLG-related disorders
- Broca's area
- Progressive supranuclear palsy
- Sigmoidal hook sign (brain)
- Upper T sign
- Motor band sign
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- Frontal lobe
- Homunculus
- Brodmann areas
- Wallerian degeneration
- Spetzler-Martin arteriovenous malformation grading system
- Precentral sulcus
- Eloquent cortex
- Lower T sign (central sulcus)
- Hemichorea-hemiballismus syndrome
- Corticospinal tract
- Middle frontal gyrus
- Omega sign (disambiguation)
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.