Pulmonary hydatid infection is a common manifestation of hydatid disease.
For a general discussion, and for links to other system specific manifestations, please refer to the article on hydatid disease.
On this page:
Epidemiology
The lung is the second most common site of involvement with Echinococcus granulosus in adults after the liver (10-30% of cases), and the most common site in children 1. The coexistence of liver and lung disease is present in only 6% of patients 2.
Clinical presentation
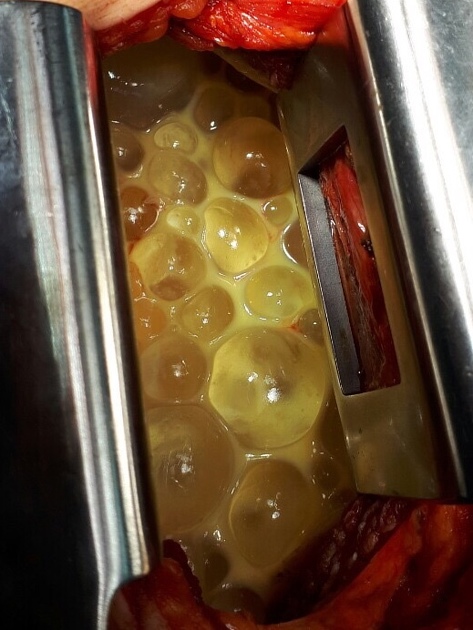
When pulmonary hydatid cysts rupture and communicate with bronchioles, patients expectorate what is described as 'grape skin'-like material 7.
Pathology
Thoracic involvement may occur via 1:
transdiaphragmatic route (0.6-16% of cases of hepatic disease)
haematogenous spread
Although Echinococcus granulosus presents commonly with unilocular cysts, Echinococcus multilocularis and Echinococcus vogeli may cause alveolar and polycystic echinococcosis.
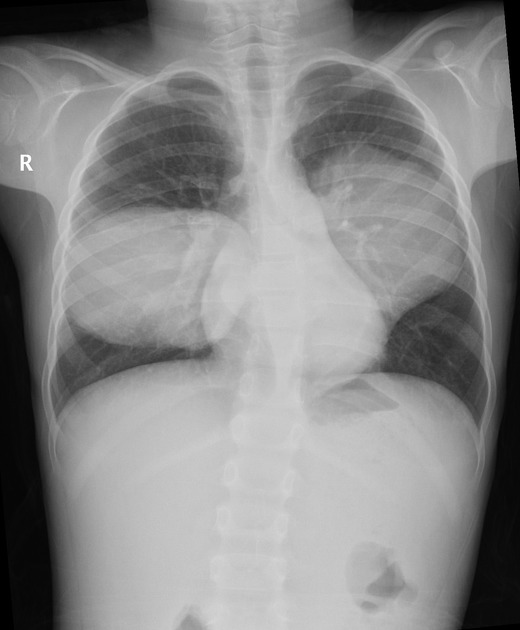
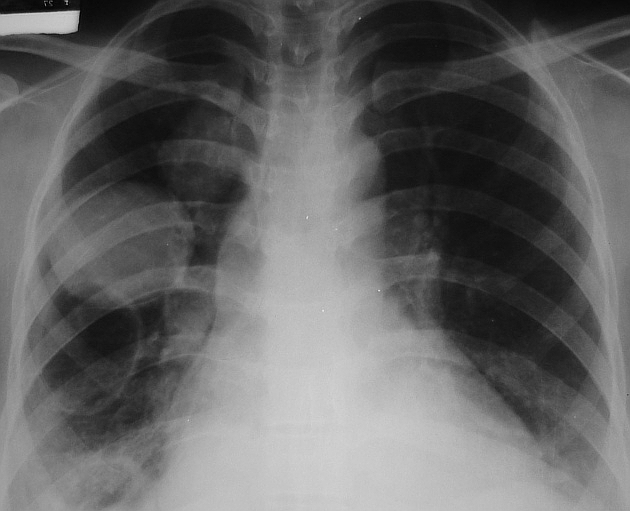
Radiographic features
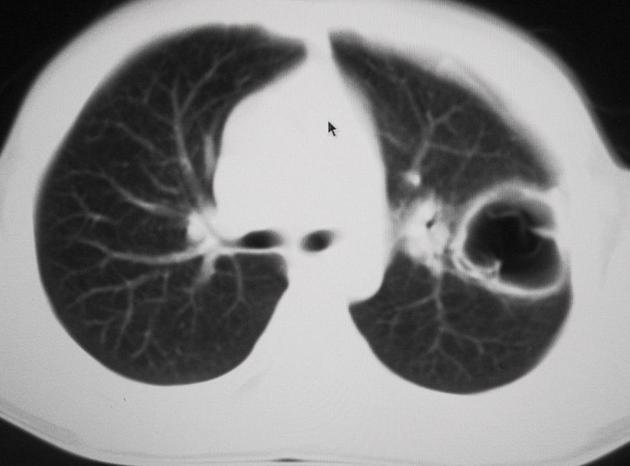
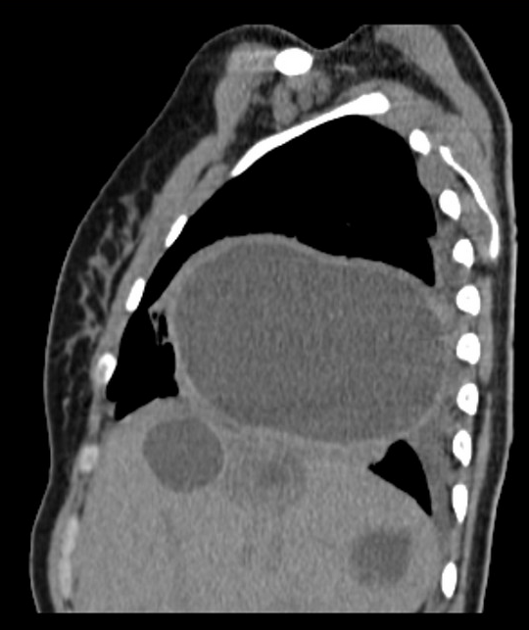
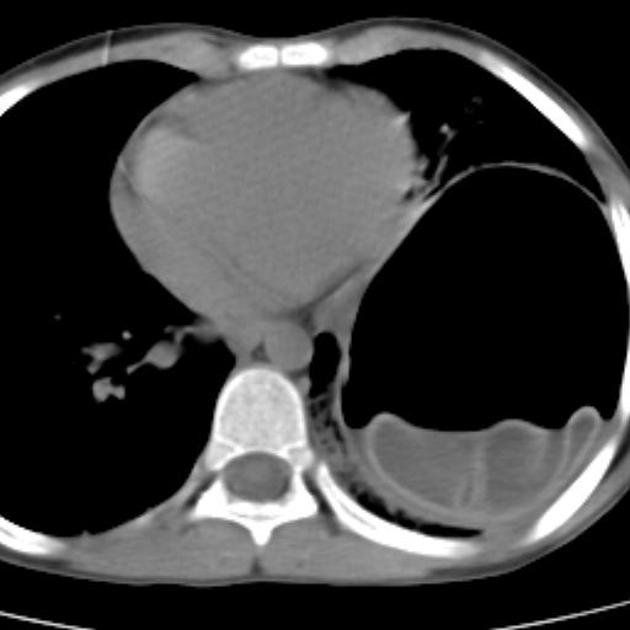
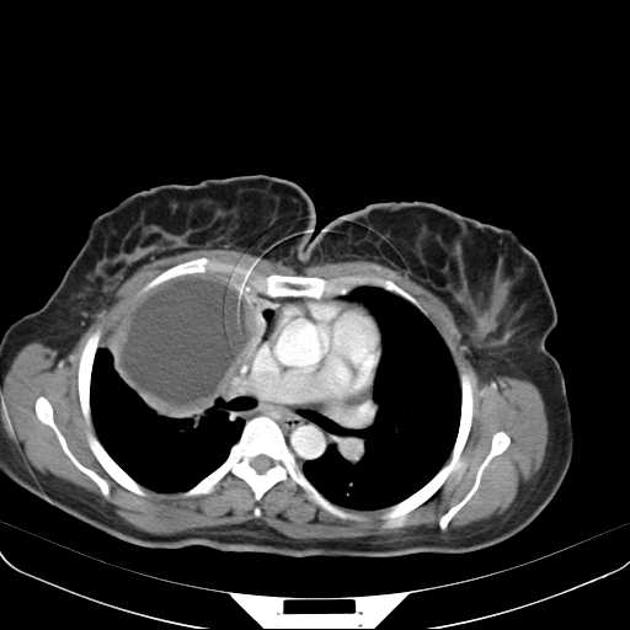
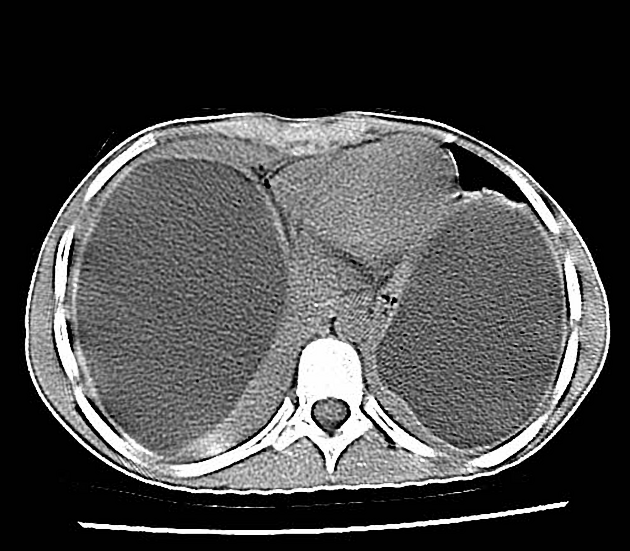
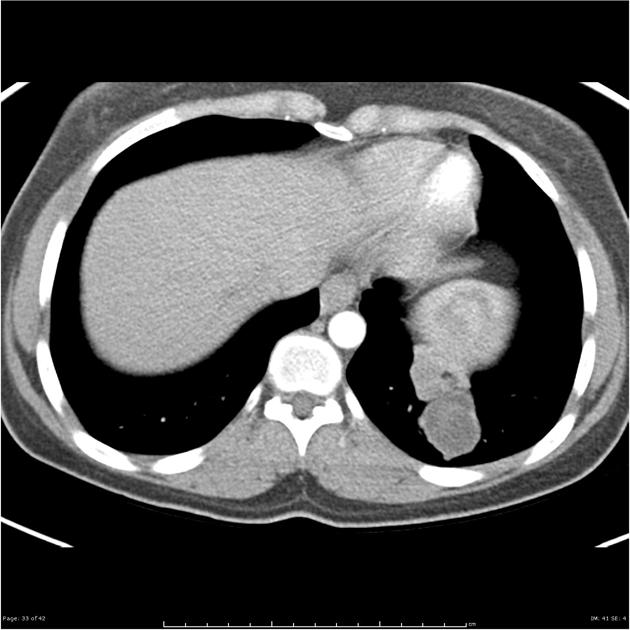
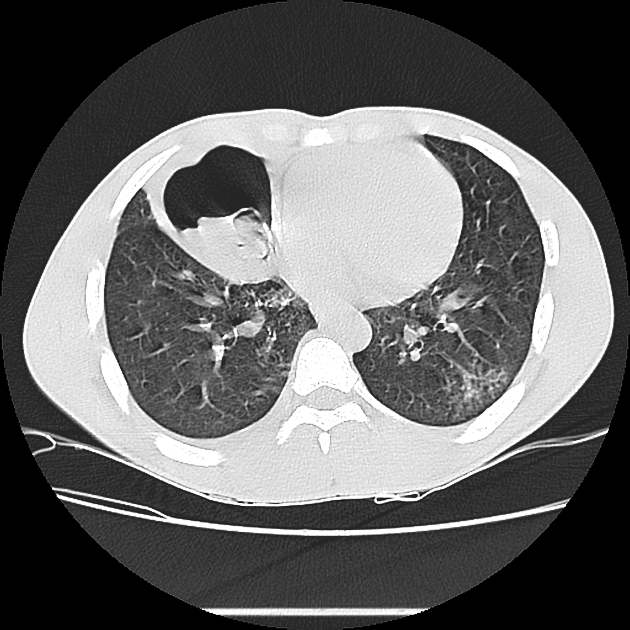
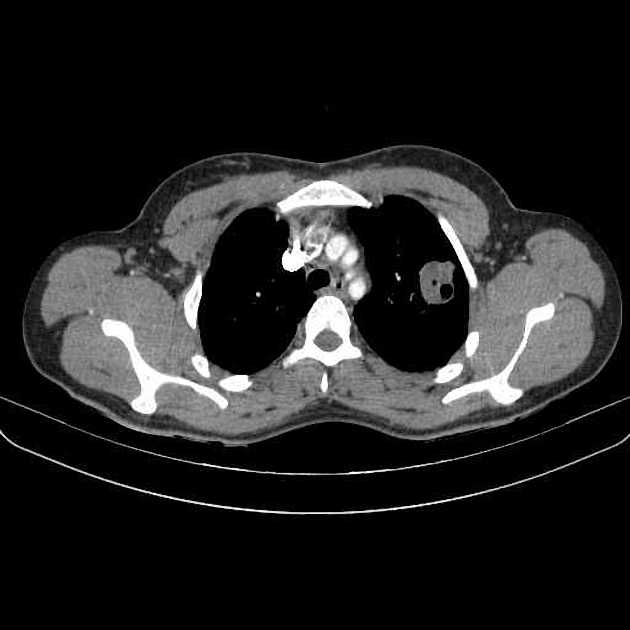
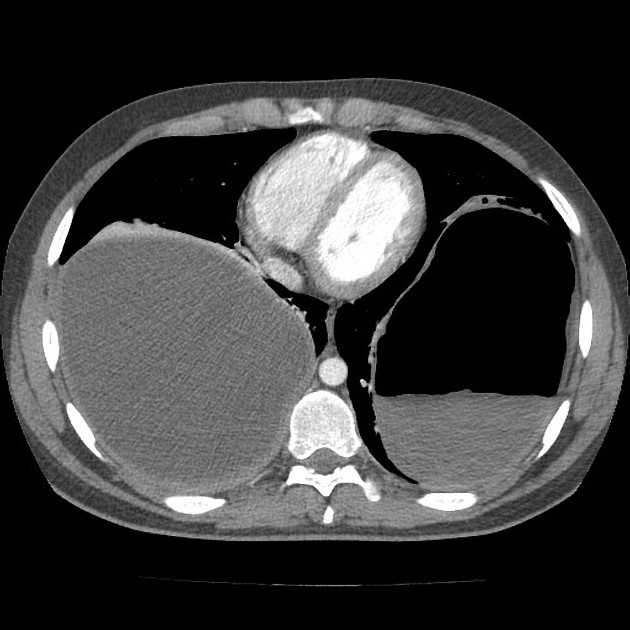
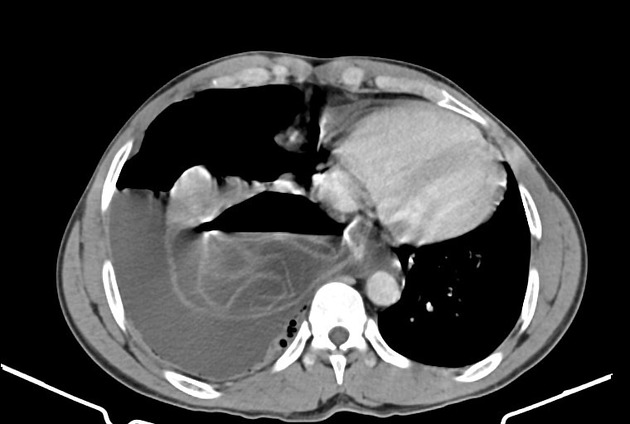
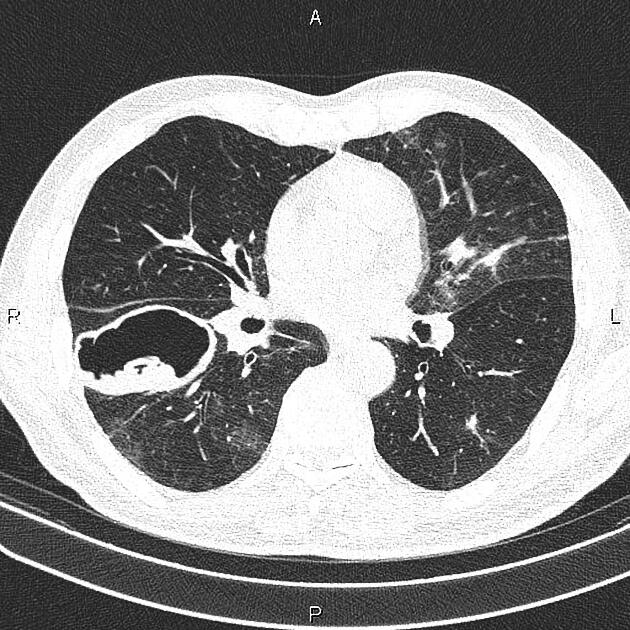
CT
Generally, chest CT scan features include 2:
solitary cystic lesion up to 20 cms in diameter
multiple cystic lesions, unilateral or bilateral
lower lobe predominant
no calcification, (low CO2 in lung inhibits calcium precipitation 10)
Uncomplicated cysts are characterised by:
round or oval masses with well-defined borders
enhancement after contrast injection
hypodense content relative to the capsule
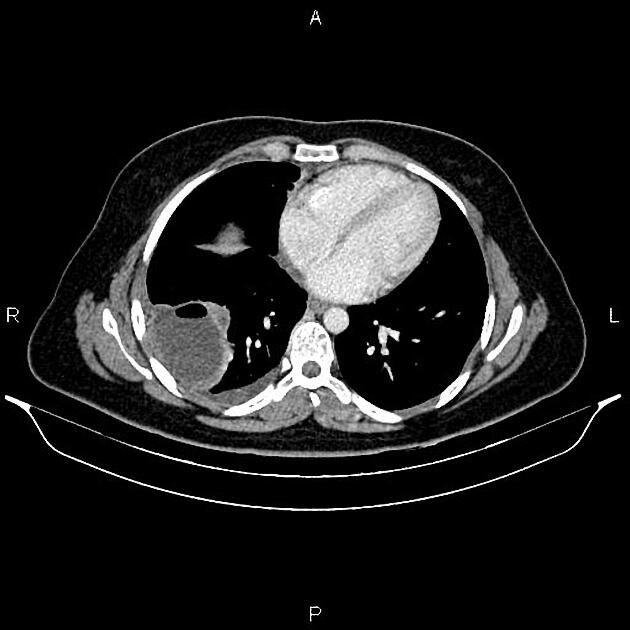
Complicated cysts may show:
meniscus sign or air crescent sign
cumbo sign or onion peel sign
consolidation adjacent to the cyst in case of a ruptured cyst
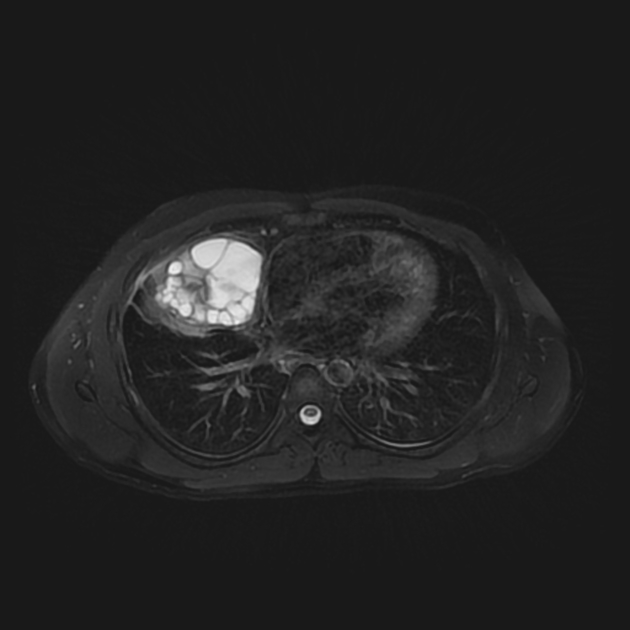
MRI
T1: hypointense
T2: hyperintense
The cyst capsule is hypointense on T2 weighted images (hypointense rim sign), isointense on T1 weighted images, and shows mild contrast enhancement. The folded membranes within cysts are T2-hypointense 8.
Ultrasound
Double-layered wall in univesicular cysts and a double-layered septum in cases of multivesicular cysts (wall sign) 9
Other less common thoracic hydatid manifestations include invasion of the mediastinum 4, pericardium, pleura, chest wall 5, cardiovascular system, or inferior vena cava 6.







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.