Refraction
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Patricia O'Gorman had no recorded disclosures.
View Patricia O'Gorman's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Henry Knipe had the following disclosures:
- Micro-X Ltd, Shareholder (past)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosures- Snell's law
- Snell law
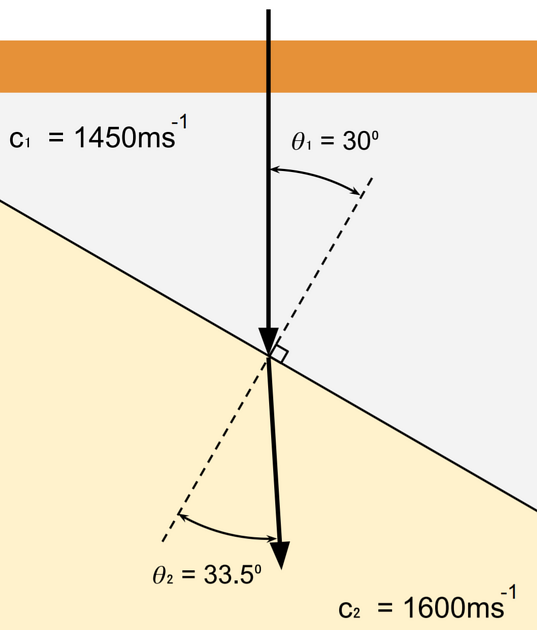
Refraction of a sound wave occurs if it travels between tissues with different propagation speeds. As the incident pulse or returning echo strikes an interface of different density or elasticity and therefore a different propagation speed, the direction of the wave changes according to Snell’s law 1 :
- sin θ1/sinθ2 = c1/c2
Where:
- sin θ1 = incident angle of the sound wave at the interface
- sin θ2 = refraction angle of the sound wave in the new medium
- c1 = propagation speed in the initial medium
- c2 = propagation speed in the new medium
Ultrasound machines assume all pulsed waves and returning echoes travel along a direct path, therefore refraction can cause refraction artifact 2 .
References
- 1. Carol M. Rumack. Diagnostic Ultrasound. (2011) ISBN: 9780323053976 - Google Books
- 2. Feldman M, Katyal S, Blackwood M. US Artifacts. Radiographics. 2009;29(4):1179-89. doi:10.1148/rg.294085199 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Imaging physics
- imaging physics
- imaging in practice
- imaging technology
-
x-ray physics
- ionising radiation
- interaction with matter
- x-ray spectrum
- radiation units
- effective dose
- entrance skin dose
- radiation safety
- radiation damage (biomolecular)
- radiation damage (skin injury)
- stochastic effect
- CT physics
-
MRI physics
- B0
- chemical shift
- dependence of magnetisation (proton density, field strength and temperature)
- echo time
- eddy currents
- electromagnetic induction
- Ernst angle
- flip angle
- Larmor frequency
- magnetic dipole
- magnetic field gradient
- magnetic susceptibility
- magnetism
- molecular tumbling rate effects on T1 and T2
- net magnetisation vector (NMV)
- relaxation
- repetition time
- resonance and radiofrequency (RF)
- units of magnetism
- ultrasound physics
- nuclear medicine physics





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.