Sphenoid bone
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Aaron Wong had no recorded disclosures.
View Aaron Wong's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Joachim Feger had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Joachim Feger's current disclosures- Sphenoidal bone
- Os vespiforme
- Os sphexoideum
- Os sphecoides
- Os sphenoideum
- Sphenoid
- Os sphenoidale
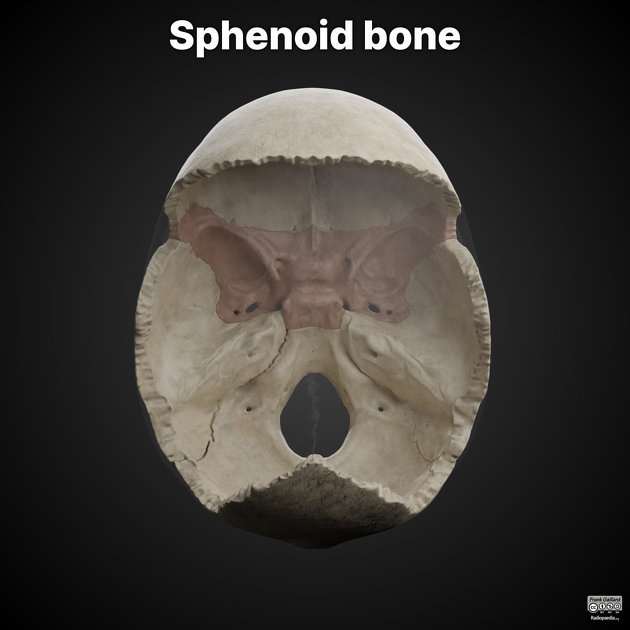
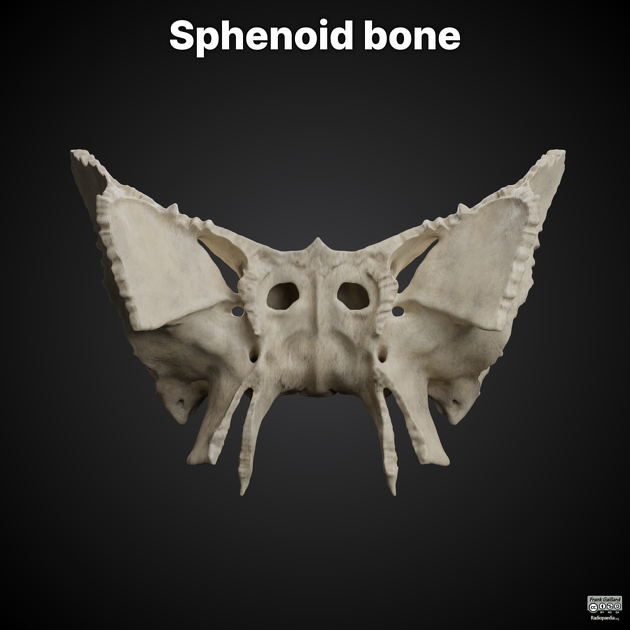
The sphenoid bone is a large, complex, unpaired bone forming the central parts of the anterior and central skull base.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
Parts of the sphenoid bone include:
-
contains the sphenoid sinus
Articulations
The sphenoid bone articulates with twelve bones:
unpaired bones include: frontal, ethmoid, vomer, and occipital
paired bones include: zygomatic, parietal, temporal, and palatine
Fissures, foramina, grooves and canals
The sphenoid bone includes:
Variant anatomy
The lateral craniopharyngeal canal, located in the lateral sphenoid recess, medial to foramen rotundum.
The persistent hypophyseal canal, also known as the craniopharyngeal canal when larger, communicates from the pituitary fossa to the nasopharynx.
Development
The sphenoid bone arises from multiple centres of ossification 5:
-
body
midline: presphenoid and postsphenoid, each with multiple centres of ossification
laterally: contribution from the medial crus of the orbitosphenoid
lesser wings: orbitosphenoids
greater wings: alisphenoids
History and etymology
Galen (129-199) first described the bone by this name. It is derived from the Greek σφήν (sphen) meaning wedge. Some sources claim that the intended name was sphecoid, derived from Greek σφηξ (sphex) meaning wasp, but was inaccurately copied or translated 3,4.
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Mcminn. Last's Anatomy. (2003) ISBN: 9780729537520 - Google Books
- 2. Susan Standring. Gray's Anatomy. (2008) ISBN: 9780443066849 - Google Books
- 3. Chmielewski P. New Terminologia Anatomica: Cranium and Extracranial Bones of the Head. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2021;80(3):477-86. doi:10.5603/FM.a2019.0129 - Pubmed
- 4. Er K, Schmieder K, Brenke C, Miller D, Parpaley Y, Gierthmuehlen M. Brainatomy: A Novel Way of Teaching Sphenoid Bone Anatomy With a Simplified 3-Dimensional Model. World Neurosurg. 2020;135:e50-70. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2019.10.128 - Pubmed
- 5. Nemzek W, Brodie H, Hecht S, Chong B, Babcook C, Seibert J. MR, CT, and Plain Film Imaging of the Developing Skull Base in Fetal Specimens. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000;21(9):1699-706. PMC8174876 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Diaphragma sellae
- Dorello canal
- Transalar herniation
- Ethmoid bone
- Pituitary fossa
- Foramen rotundum
- Infratemporal fossa
- Parietal bone
- Craniofacial fibrous dysplasia
- Squamous part of temporal bone
- Pterygopalatine fossa
- Tensor veli palatini muscle
- Sphenofrontal suture
- Deep temporal arteries
- Sphenoid wing dysplasia
- Base of the skull
- Temporal fossa
- Foramen Vesalii
- Palatovaginal canal
- Lingula (disambiguation)
- Fibrous dysplasia - sphenoid bone
- Fibrous dysplasia
- Spheno-orbital and calvarium intraosseous meningioma
- Sphenoid wing meningioma
- Clival fracture
- Spheno-occipital synchondrosis
- Sinonasal mucosal melanoma
- Sphenoid bone (Gray's illustrations)
- Sphenoid wing meningioma
- Nasal cavity (Gray's illustration)
- Sphenoid bone fibrous dysplasia
- En plaque meningioma with associated CPA / frontal convexity meningiomas
- Spheno-occipital synchondrosis
- Spheno-orbital meningioma
- Sphenoid bone fibrous dysplasia
- Sphenoid wing meningioma
- En plaque meningioma right sphenoid
- Sphenoid wing dysplasia
Related articles: Anatomy: Head and neck
- skeleton of the head and neck
-
cranial vault
- scalp (mnemonic)
- fontanelle
-
sutures
- calvarial
- facial
- frontozygomatic suture
- frontomaxillary suture
- frontolacrimal suture
- frontonasal suture
- temporozygomatic suture
- zygomaticomaxillary suture
- parietotemporal suture (parietomastoid suture)
- occipitotemporal suture (occipitomastoid suture)
- sphenofrontal suture
- sphenozygomatic suture
- spheno-occipital suture (not a true suture)
- lacrimomaxillary suture
- nasomaxillary suture
- internasal suture
- basal/internal
- skull landmarks
- frontal bone
- temporal bone
- parietal bone
- occipital bone
- skull base (foramina)
-
facial bones
- midline single bones
- paired bilateral bones
- cervical spine
- hyoid bone
- laryngeal cartilages
-
cranial vault
- muscles of the head and neck
- muscles of the tongue (mnemonic)
- muscles of mastication
-
facial muscles
- epicranius muscle
- circumorbital and palpebral muscles
- nasal muscles
-
buccolabial muscles
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- levator labii superioris alaeque nasalis muscle
- levator labii superioris muscle
- zygomaticus major muscle
- zygomaticus minor muscle
- levator anguli oris muscle
- malaris muscle
- risorius muscle
- depressors, retractors and evertors of the lower lip
- depressor labii inferioris muscle
- depressor anguli oris muscle
- mentalis muscle
- compound sphincter
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- incisivus labii superioris muscle
- incisivus labii inferioris muscle
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- muscle of mastication
- modiolus
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- muscles of the middle ear
- orbital muscles
- muscles of the soft palate
- pharyngeal muscles
- suprahyoid muscles
- infrahyoid muscles
- intrinsic muscles of the larynx
- muscles of the neck
- platysma muscle
- longus colli muscle
- longus capitis muscle
- scalenus anterior muscle
- scalenus medius muscle
- scalenus posterior muscle
- scalenus pleuralis muscle
- sternocleidomastoid muscle
-
suboccipital muscles
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- accessory muscles of the neck
- deep cervical fascia
-
deep spaces of the neck
- anterior cervical space
- buccal space
- carotid space
- danger space
- deep cervical fascia
- infratemporal fossa
- masticator space
- parapharyngeal space
- stylomandibular tunnel
- parotid space
- pharyngeal (superficial) mucosal space
- perivertebral space
- posterior cervical space
- pterygopalatine fossa
- retropharyngeal space
- suprasternal space (of Burns)
- visceral space
- surgical triangles of the neck
- orbit
- ear
- paranasal sinuses
- upper respiratory tract
- viscera of the neck
- blood supply of the head and neck
-
arterial supply
-
common carotid artery
- carotid body
- carotid bifurcation
- subclavian artery
- variants
-
common carotid artery
- venous drainage
-
arterial supply
- innervation of the head and neck
-
cranial nerves
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
-
trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- trigeminal ganglion
- ophthalmic division
- maxillary division
- mandibular division
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- (spinal) accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck
- cervical sympathetic ganglia
- greater occipital nerve
- third occipital nerve
-
cervical plexus
- muscular branches
- longus capitis
- longus colli
- scalenes
- geniohyoid
- thyrohyoid
-
ansa cervicalis
- omohyoid (superior and inferior bellies separately)
- sternothyroid
- sternohyoid
- phrenic nerve
- contribution to the accessory nerve (CN XI)
- cutaneous branches
- muscular branches
- brachial plexus
- pharyngeal plexus
-
cranial nerves
- lymphatic drainage of the head and neck
- embryological development of the head and neck










 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.