Trabecular patterns of the proximal femur refer to the five groups of trabeculae that are demonstrable within the femoral head and neck.
On this page:
Images:
Gross anatomy
Trabeculae are a supportive and connective tissue element that forms in cancellous bone. Trabeculae develop in normal and healing bones. The trabecular pattern of growth follows the course of stress lines along the bone, and maximum trabeculae develop along the lines of maximum stress.
To understand the progress of trabecular patterns, it is imperative that we understand the concept put forth by Julius Wolff, known as Wolff’s Law 3.
Wolff's law
Wolff's law suggests that there are dynamic internal forces as well as static and dynamic external forces acting on the bone. These static forces are imposed by gravity and the dynamic forces by weight bearing. Wolff's Law implies a reaction of a living bone to the mechanical forces on a bone segment 3.
If the loading on a particular bone increases, then the bone will remodel itself over time to become stronger and resist the loading in that particular bone segment and for that particular force of loading.
The proximal femur is an apt example to show the trabecular pattern based on Wolf’s law. Both tensile and compressive forces are present and correspond to the lines of forces.
Types of trabeculae
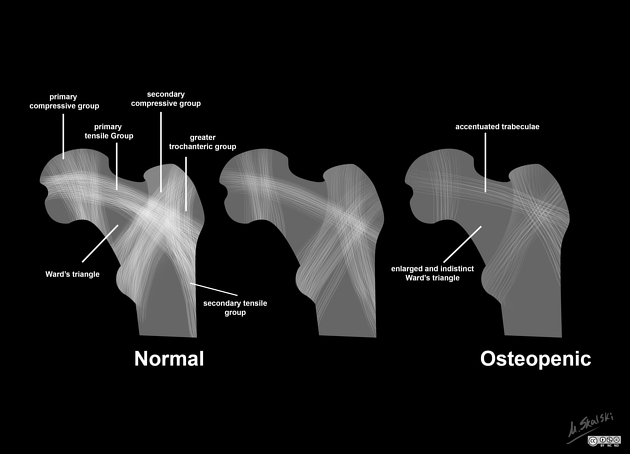
principal tensile trabeculae
principal compressive/medial compressive trabeculae
secondary compressive/lateral compressive trabeculae
secondary tensile trabeculae
greater trochanteric trabeculae
Principal tensile trabeculae
it is in the form of an arc
extends from the lateral margin of the greater trochanter to the inferior aspect below the fovea
the arc traverses through the superior cortex of the neck and the femoral head
Principal compressive /medial compressive trabeculae
it is vertically oriented and has a triangular configuration
extends from the medial cortex of the head into the femoral neck
Secondary compressive/lateral compressive trabeculae
it has a fan-like configuration
extends from the calcar and lesser trochanter to the greater trochanter
A central area bounded by the three trabecular patterns is referred to as the Ward triangle 4.
History and etymology
Trabecula is derived from Latin word trabs meaning beam or bar.
Clinical importance
As per the Garden classification of subcapital femoral fractures, the displacement is graded as per the position of the medial compressive trabecular 4.
stage I: medial trabeculae form an angle greater than 180°
stage II: medial trabeculae of head form an angle of approximately 160° with femoral neck
stage III: medial trabeculae are out of alignment with those of pelvis
stage IV: medial trabeculae are in alignment with those of pelvis
As osteoporosis begins, the small bridging trabeculae are resorbed and lead to accentuation of trabecular groups. It is during this stage that Ward triangle begins to become large and ill-defined. In late stages even the principal trabecular groups are weakened. This concept is utilized in a grading of osteoporosis by Singh et al 6.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.