Tracheostomy tube
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Amanda Er had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Amanda Er's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Arlene Campos had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Arlene Campos's current disclosures- Tracheotomy tube
- Tracheotomy tubes
- Tracheostomy tubes
- Armoured tracheostomy tubes
- Armoured tracheostomy tube
- Armored tracheostomy tubes
- Armored tracheostomy tube
Tracheostomy tubes, a.k.a. tracheotomy tubes, are inserted through a stoma post-tracheostomy to help patients unable to breathe normally. It may be temporary or permanent depending on the patient's condition, with its insertion where clinically indicated showing a lowered in-hospital mortality rate 1. To enable verbal communication, variations of the tube include:
electrolarynx
fenestrated tracheostomy tube
talking tracheostomy tube
speaking valve (e.g. Passy Muir valve)
armoured tracheostomy tube
On this page:
Indications
-
abnormalities in the upper airway
congenital
traumatic
inability to clear mucus from the lungs
laryngeal injury
obstructive sleep apnoea
Contraindications
active cellulitis over anterior neck 2
Radiographic features
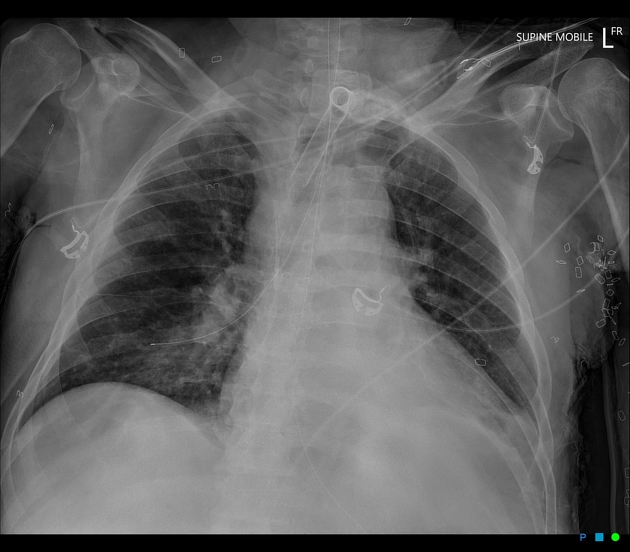
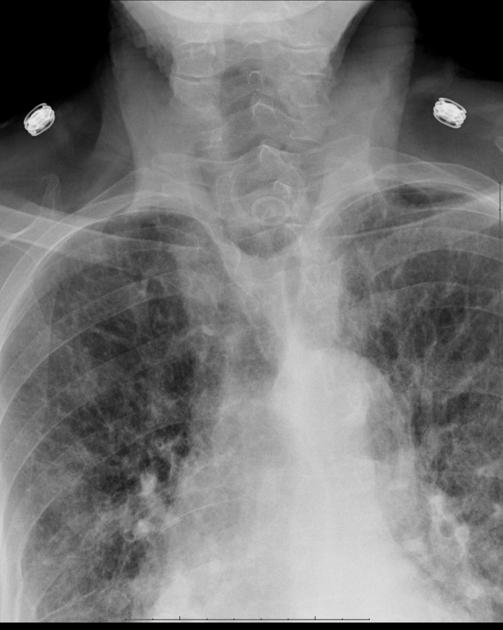
Plain radiograph
Unlike endotracheal tubes, there are no universally accepted imaging guidelines on determining the correct tracheostomy tube placement for adult patients. Some suggestions have included the tube tip being located at:
the midpoint between the upper end of the tube (i.e. insertion point) and the carina
the level of the clavicles
NB: Clinical decisions regarding tracheostomy tube size and position should not be based on a chest x-ray 3,4; direct tracheoscopy measurement is still recommended 3.
Complications
Insertion
bleeding
damage to oesophagus
mucus and fluid build-up, leading to breathing difficulties and infection
References
- 1. Combes A, Luyt C, Nieszkowska A, Trouillet J, Gibert C, Chastre J. Is Tracheostomy Associated with Better Outcomes for Patients Requiring Long-Term Mechanical Ventilation?*. Crit Care Med. 2007;35(3):802-7. doi:10.1097/01.ccm.0000256721.60517.b1
- 2. Raimonde AJ, Westhoven N, Winters R. Tracheostomy. [Updated 2021 Dec 29]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan. NCBI
- 3. Keane A, Saadi R, Slonimsky E, Wilson M, May J. Comparison of Tracheoscopy and Portable Chest X-Ray in the Evaluation of Infant Tracheostomy Tube Position. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2021;141:110566. doi:10.1016/j.ijporl.2020.110566 - Pubmed
- 4. Tobler W, Mella J, Ng J, Selvam A, Burke P, Agarwal S. Chest X-Ray After Tracheostomy is Not Necessary Unless Clinically Indicated. World J Surg. 2012;36(2):266-9. doi:10.1007/s00268-011-1380-4 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Chest
- imaging techniques
-
chest radiograph
- radiography
-
approach
- ABCDE
- ABCDEFGHI
- congenital heart disease
- medical devices in the thorax
- common lines and tubes
- nasogastric tubes
- endotracheal tubes
- central venous catheters
- oesophageal temperature probe
- tracheostomy tube
- pleural catheters
- cardiac conduction devices
- prosthetic heart valve
- review areas
-
airspace opacification
- differential diagnoses of airspace opacification
- lobar consolidation
-
atelectasis
- mechanism-based
- morphology-based
- lobar lung collapse
- chest x-ray in the exam setting
- cardiomediastinal contour
- chest radiograph zones
- tracheal air column
- fissures
- normal chest x-ray appearance of the diaphragm
- nipple shadow
-
lines and stripes
- anterior junction line
- posterior junction line
- right paratracheal stripe
- left paratracheal stripe
- posterior tracheal stripe/tracheo-oesophageal stripe
- posterior wall of bronchus intermedius
- right paraspinal line
- left paraspinal line
- aortic-pulmonary stripe
- aortopulmonary window
- azygo-oesophageal recess
- spaces
- signs
- air bronchogram
- big rib sign
- Chang sign
- Chen sign
- coin lesion
- continuous diaphragm sign
- dense hilum sign
- double contour sign
- egg-on-a-string sign
- extrapleural sign
- finger in glove sign
- flat waist sign
- Fleischner sign
- ginkgo leaf sign
- Golden S sign
- Hampton hump
- haystack sign
- hilum convergence sign
- hilum overlay sign
- Hoffman-Rigler sign
- holly leaf sign
- incomplete border sign
- juxtaphrenic peak sign
- Kirklin sign
- medial stripe sign
- melting ice cube sign
- more black sign
- Naclerio V sign
- Palla sign
- pericardial fat tag sign
- Shmoo sign
- silhouette sign
- snowman sign
- spinnaker sign
- steeple sign
- straight left heart border sign
- third mogul sign
- tram-track sign
- walking man sign
- water bottle sign
- wave sign
- Westermark sign
- HRCT
-
chest radiograph
- airways
- bronchitis
- small airways disease
-
bronchiectasis
- broncho-arterial ratio
- related conditions
- differentials by distribution
- narrowing
-
tracheal stenosis
- diffuse tracheal narrowing (differential)
-
bronchial stenosis
- diffuse airway narrowing (differential)
-
tracheal stenosis
- diverticula
- pulmonary oedema
-
interstitial lung disease (ILD)
- Anti-Jo-1 antibody-positive interstitial lung disease
- drug-induced interstitial lung disease
-
hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- acute hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- subacute hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- aetiology
- bird fancier's lung: pigeon fancier's lung
- farmer's lung
- cheese workers' lung
- bagassosis
- mushroom worker’s lung
- malt worker’s lung
- maple bark disease
- hot tub lung
- wine maker’s lung
- woodsman’s disease
- thatched roof lung
- tobacco grower’s lung
- potato riddler’s lung
- summer-type pneumonitis
- dry rot lung
- machine operator’s lung
- humidifier lung
- shower curtain disease
- furrier’s lung
- miller’s lung
- lycoperdonosis
- saxophone lung
-
idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (mnemonic)
- acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP)
- cryptogenic organising pneumonia (COP)
- desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP)
- non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP)
- idiopathic pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis
- lymphoid interstitial pneumonia (LIP)
- respiratory bronchiolitis–associated interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD)
- usual interstitial pneumonia / idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (UIP/IPF)
-
pneumoconioses
- fibrotic
- non-fibrotic
-
lung cancer
-
non-small-cell lung cancer
-
adenocarcinoma
- pre-invasive tumours
- minimally invasive tumours
- invasive tumours
- variants of invasive carcinoma
- described imaging features
- adenosquamous carcinoma
- large cell carcinoma
- primary sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung
- squamous cell carcinoma
- salivary gland-type tumours
-
adenocarcinoma
- pulmonary neuroendocrine tumours
- preinvasive lesions
-
lung cancer invasion patterns
- tumour spread through air spaces (STAS)
- presence of non-lepidic patterns such as acinar, papillary, solid, or micropapillary
- myofibroblastic stroma associated with invasive tumour cells
- pleural invasion
- vascular invasion
- tumours by location
- benign neoplasms
- pulmonary metastases
- lung cancer screening
- lung cancer staging
-
non-small-cell lung cancer






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.