True vocal cords
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Dan Youssef had no recorded disclosures.
View Dan Youssef's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had the following disclosures:
- Philips Australia, Paid speaker at Philips Spectral CT events (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosures- vocal cord
- vocal folds
- vocal fold
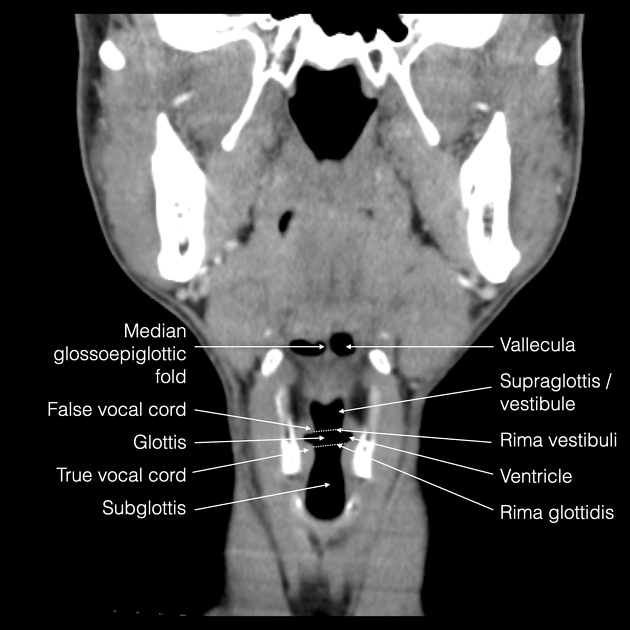
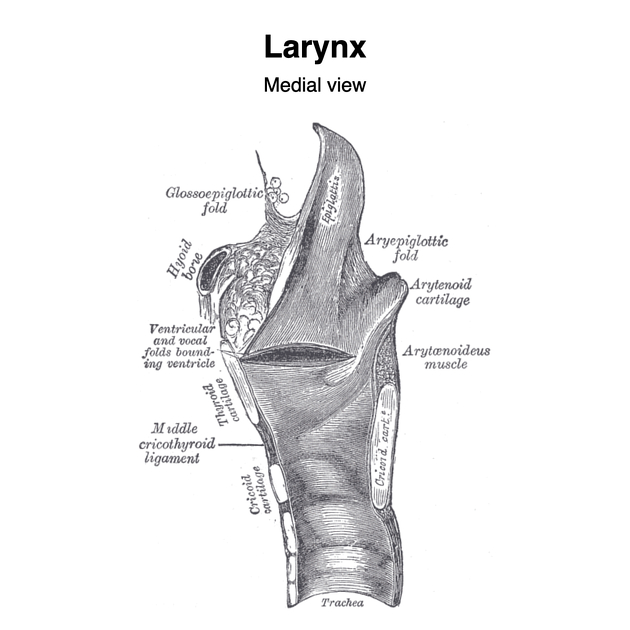
The true vocal cords are the thickened, free edge of the cricovocal membrane/ligament also known as cricothyroid ligament, lined by mucous membrane 1. Together, they constitute the glottis and form the rima glottidis, which is the V-shaped aperture through which air passes. Their primary role is in phonation where vibration of the adducted vocal cords gives rise to sound waves with a certain pitch.
The cricovocal membrane, also known as conus elasticus, extends upwards from a semicircular base following the contours of the cricoid cartilage to form a horizontal upper free border attached anteriorly in the midline to thyroid cartilage and posteriorly to the vocal process of the arytenoid cartilage 1. This free edge between the thyroid laminae and the arytenoid cartilage is thickened as the cricovocal ligament 1.
Stratified squamous epithelium lines the vocal folds. The lamina propria is very firmly attached over the vocal cords.
The body of the true vocal cord contains the muscles that release tension in the cord: vocalis and thyroarytenoid muscles.
Related pathology
References
- 1. Mcminn. Last's Anatomy. Elsevier Australia. (2003) ISBN:0729537528. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Hamdan A, Hamdan KE, Hamdan JH, Hamdan GA, Hamdan RS, Hamdan EHA, Hamdan. Prevalence of Dysphagia in Patients With Non-neoplastic Vocal Fold Pathology. (2019) Journal of voice : official journal of the Voice Foundation. doi:10.1016/j.jvoice.2018.05.003 - Pubmed
- 3. Braun J, Braun DC, Braun CA, Braun SP, Braun dBF, Braun. [Vocal cord dyskinesia and/or asthma]. (2018) Revue des maladies respiratoires. doi:10.1016/j.rmr.2017.11.001 - Pubmed
- 4. Lyu D, Lyu CY, Lyu YH, Lyu RJ, Lyu ZY, Lyu. [Research status and challenges of vocal cord leukoplakia]. (2018) Zhonghua er bi yan hou tou jing wai ke za zhi = Chinese journal of otorhinolaryngology head and neck surgery. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2018.08.016 - Pubmed
- 5. Andrew Benner, Piyush Sharma, Sandeep Sharma. Anatomy, Head and Neck: Cervical, Respiratory, Larynx, and Cricoarytenoid. StatPearls Publishing. 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538307/ - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Subglottis
- Ligaments of the larynx
- Laryngeal vestibule
- Glottic web
- Paraglottic space
- Supraglottis
- False vocal cords
- Point-of-care ultrasound (curriculum)
- Internal laryngeal nerve
- Rima glottidis
- Synechiae
- Laryngeal carcinoma (staging)
- Recurrent laryngeal nerve
- Arytenoid cartilage
- Vocal cord paralysis
- Glottis
- Larynx
- Anterior commissure of the larynx
- Rima vestibuli
- Thyroid cartilage
- Vocal cords (Gray's illustration)
- Larynx (Gray's illustrations)
- Laryngeal muscles (Gray's illustration)
- Larynx - coronal CT labelled anatomy
- Vocal cord paralysis
- Normal vocal cords (ultrasound)
- Laryngeal supraglottic cancer
- Pharyngolaryngeal metallic foreign body
- Glottic cancer - Glottic cancer - stage cT1b
- Vocal cord paralysis
Related articles: Anatomy: Head and neck
- skeleton of the head and neck
-
cranial vault
- scalp (mnemonic)
- fontanelle
-
sutures
- calvarial
- facial
- frontozygomatic suture
- frontomaxillary suture
- frontolacrimal suture
- frontonasal suture
- temporozygomatic suture
- zygomaticomaxillary suture
- parietotemporal suture (parietomastoid suture)
- occipitotemporal suture (occipitomastoid suture)
- sphenofrontal suture
- sphenozygomatic suture
- spheno-occipital suture (not a true suture)
- lacrimomaxillary suture
- nasomaxillary suture
- internasal suture
- basal/internal
- skull landmarks
- frontal bone
- temporal bone
- parietal bone
- occipital bone
- skull base (foramina)
-
facial bones
- midline single bones
- paired bilateral bones
- cervical spine
- hyoid bone
- laryngeal cartilages
-
cranial vault
- muscles of the head and neck
- muscles of the tongue (mnemonic)
- muscles of mastication
-
facial muscles
- epicranius muscle
- circumorbital and palpebral muscles
- nasal muscles
-
buccolabial muscles
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- levator labii superioris alaeque nasalis muscle
- levator labii superioris muscle
- zygomaticus major muscle
- zygomaticus minor muscle
- levator anguli oris muscle
- malaris muscle
- risorius muscle
- depressors, retractors and evertors of the lower lip
- depressor labii inferioris muscle
- depressor anguli oris muscle
- mentalis muscle
- compound sphincter
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- incisivus labii superioris muscle
- incisivus labii inferioris muscle
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- muscle of mastication
- modiolus
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- muscles of the middle ear
- orbital muscles
- muscles of the soft palate
- pharyngeal muscles
- suprahyoid muscles
- infrahyoid muscles
- intrinsic muscles of the larynx
- muscles of the neck
- platysma muscle
- longus colli muscle
- longus capitis muscle
- scalenus anterior muscle
- scalenus medius muscle
- scalenus posterior muscle
- scalenus pleuralis muscle
- sternocleidomastoid muscle
-
suboccipital muscles
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- accessory muscles of the neck
- deep cervical fascia
-
deep spaces of the neck
- anterior cervical space
- buccal space
- carotid space
- danger space
- deep cervical fascia
- infratemporal fossa
- masticator space
- parapharyngeal space
- stylomandibular tunnel
- parotid space
- pharyngeal (superficial) mucosal space
- perivertebral space
- posterior cervical space
- pterygopalatine fossa
- retropharyngeal space
- suprasternal space (of Burns)
- visceral space
- surgical triangles of the neck
- orbit
- ear
- paranasal sinuses
- upper respiratory tract
- viscera of the neck
- blood supply of the head and neck
-
arterial supply
-
common carotid artery
- carotid body
- carotid bifurcation
- subclavian artery
- variants
-
common carotid artery
- venous drainage
-
arterial supply
- innervation of the head and neck
-
cranial nerves
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
-
trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- trigeminal ganglion
- ophthalmic division
- maxillary division
- mandibular division
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- (spinal) accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck
- cervical sympathetic ganglia
- greater occipital nerve
- third occipital nerve
-
cervical plexus
- muscular branches
- longus capitis
- longus colli
- scalenes
- geniohyoid
- thyrohyoid
-
ansa cervicalis
- omohyoid (superior and inferior bellies separately)
- sternothyroid
- sternohyoid
- phrenic nerve
- contribution to the accessory nerve (CN XI)
- cutaneous branches
- muscular branches
- brachial plexus
- pharyngeal plexus
-
cranial nerves
- lymphatic drainage of the head and neck
- embryological development of the head and neck










 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.