Truncation artifact (CT)
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Botz B, Murphy A, Knipe H, Truncation artifact (CT). Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 26 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-70537
rID:
70537
Article created:
25 Aug 2019,
Bálint Botz
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created Bálint Botz had no recorded disclosures.
View Bálint Botz's current disclosures
Last revised:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Andrew Murphy had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Andrew Murphy's current disclosures
Revisions:
3 times, by
3 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Sections:
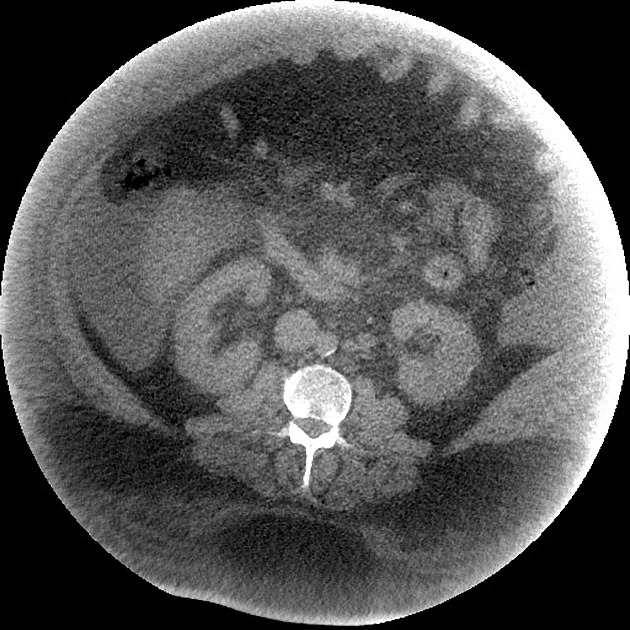
Truncation artifact in CT is an apparently increased curvilinear band of attenuation along the edge of the image.
This artifact is encountered when parts of the imaged body part remain outside the field of view (e.g. due to patient body habitus), which results in inaccurate measurement of attenuation along the edge of the image. The artifact can be reduced - if possible - by using an extended FOV reconstruction of the affected region 1.
References
- 1. Benjamin L. Triche, John T. Nelson Jr, Noah S. McGill, Kristin K. Porter, Rupan Sanyal, Franklin N. Tessler, Jonathan E. McConathy, David M. Gauntt, Michael V. Yester, Satinder P. Singh. Recognizing and Minimizing Artifacts at CT, MRI, US, and Molecular Imaging. (2019) RadioGraphics. 39 (4): 1017-1018. doi:10.1148/rg.2019180022 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Articles:
Related articles: Computed tomography
- computed tomography in practice
-
computed tomography overview
- iodinated contrast media
- CT IV contrast media administration
-
CT artifacts
- patient-based artifacts
- physics-based artifacts
- hardware-based artifacts
- ring artifact
- tube arcing
- out of field artifact
- air bubble artifact
- helical and multichannel artifacts
- CT technology
-
generations of CT scanners
- helical CT scanning
- step and shoot scanning
- ultra-high-resolution CT (UHRCT)
- CT x-ray tube
- CT fluoroscopy
- cone-beam CT
-
generations of CT scanners
- dual-energy CT
- CT image reconstruction
- CT image quality
- CT dose
-
CT protocols
- composite
- head & neck
- chest
- abdomen and pelvis
- CT abdomen-pelvis (protocol)
- CT abdominal aorta
- CT adrenals (protocol)
- CT cholangiography (protocol)
- CT colonography (protocol)
- CT enteroclysis (protocol)
- CT enterography (protocol)
- CT gastrography (protocol)
- CT kidneys, ureters and bladder (protocol)
- CT urography (protocol)
- CT Renal mass (protocol)
- CT angiography of the splanchnic vessels (protocol)
- CT renal split bolus
- CT pancreas (protocol)
- liver




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.