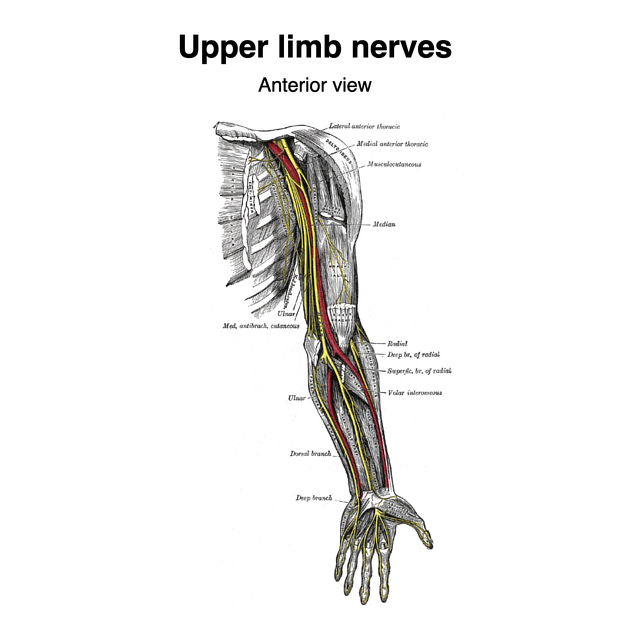
The ulnar nerve is one of the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and has a motor and sensory supply to the forearm and hand.
On this page:
Summary
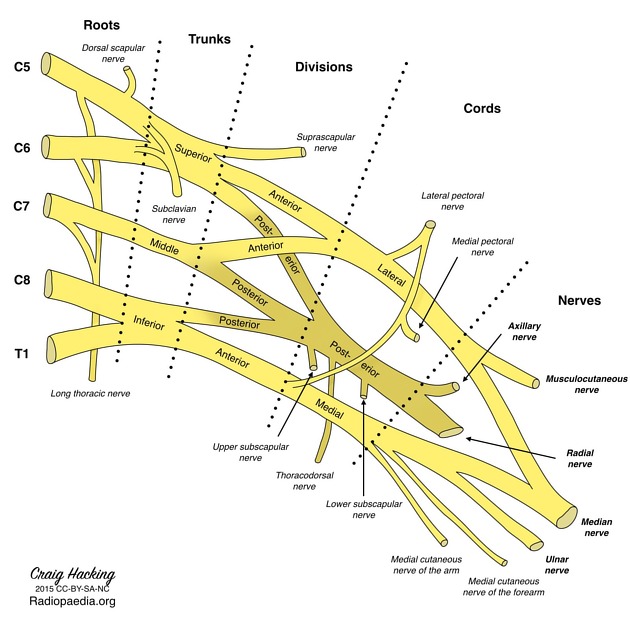
origin: medial cord from roots C8-T1
course: medial to the axillary artery to descend downwards and pass posterior to the medial epicondyle of the humerus, continues down the forearm and dives into Guyon's canal as it approaches the wrist
major branches: dorsal cutaneous branch, palmar cutaneous branch, branch to palmaris brevis, superficial terminal branch, deep terminal branch
motor supply: innervates all the muscles of the hand, except for the first and second lumbricals, abductor pollicis brevis and opponens pollicis
sensory supply: medial aspect of the palm, the palmar and dorsal aspects of the fifth digit, and the adjacent half of the fourth digit
Gross anatomy
Origin
The ulnar nerve originates as a terminal branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus with nerve root fibers from the ventral rami of C8-T1.
Course
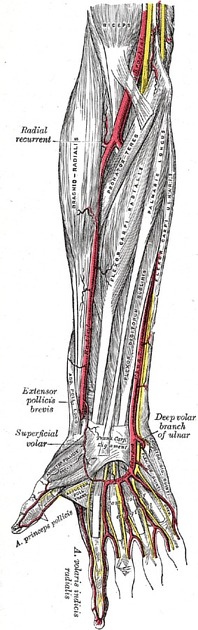
Arm
In the arm, the ulnar nerve runs medial to the axillary artery and subsequently the brachial artery on the coracobrachialis muscle in the anterior compartment of the arm. The nerve passes into the posterior compartment through the medial intermuscular septum, piercing the arcade of Struthers running distally with the superior ulnar collateral artery. Further on, it runs between the medial head of the triceps brachii muscle and the medial intermuscular septum to pass posterior to the medial humeral epicondyle in the superficial condylar groove (cubital tunnel).
Forearm
The ulnar nerve enters the forearm from the arm in between the two heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) muscle. It subsequently lies superficial to flexor digitorum profundus, deep to FCU and medial to the ulnar artery. It courses distally along the ulnar aspect of the forearm and at the wrist, the ulnar nerve runs lateral to the tendon of FCU.
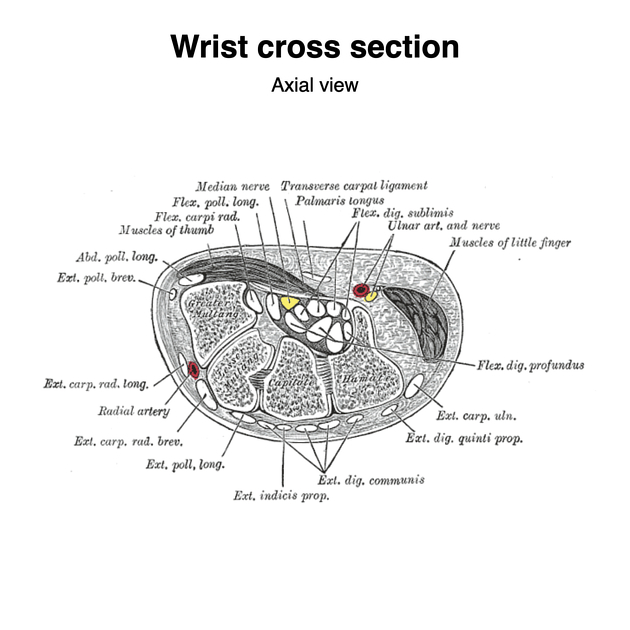
Hand
Prior to passing the flexor retinaculum at the wrist, the ulnar nerve gives off the dorsal cutaneous branch.
The ulnar nerve enters the hand superficial to the flexor retinaculum and inside Guyon's canal traveling with the ulnar artery and vein. Then it divides into its terminal branches at the level of the hook of hamate and the branches are separated by a fibrous arch of flexor digiti minimi that runs between the pisiform and the hook of hamate 8.
Branches
Terminal branches
dorsal cutaneous branch of the ulnar nerve
palmar cutaneous branch of the ulnar nerve
-
superficial branch of the ulnar nerve
branch to palmaris brevis
deep branch of the ulnar nerve
Supply
The ulnar nerve has both sensory and motor supply:
-
motor
flexor digitorum profundus (medial half)
hypothenar muscles (abductor digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi brevis, opponens digiti minimi)
3rd and 4th lumbricals
palmar and dorsal interossei muscles
flexor pollicis brevis (deep head)
-
sensory
articular innervation to elbow, wrist, carpal and phalangeal joints
cutaneous innervation to ulnar aspect of the hand, specifically the 5th digit and the medial half of the 4th digit
Size
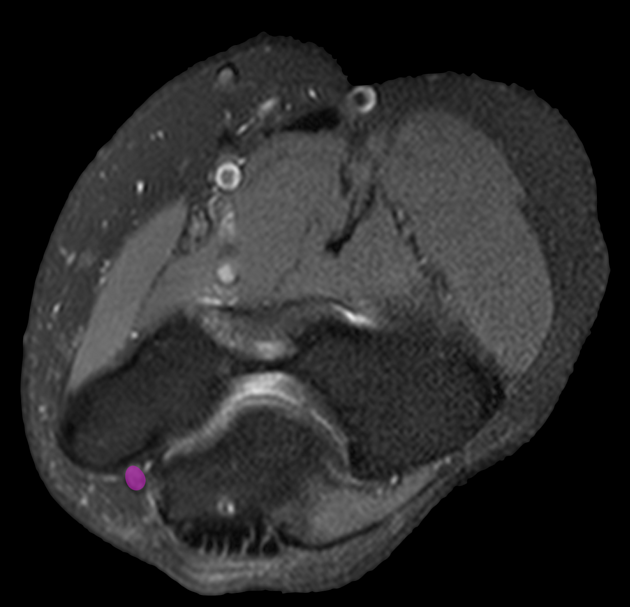
Cross-sectional diameters vary dependent on where the ulnar is measured but the upper limit of normal when measured on ultrasound is approximately 10 mm2 10,11.
Variant anatomy
may arise from the 7th and/or 8th cervical nerve roots only
prefixed or postfixed formations involving C7 or T2, respectively
may pass in front of the medial epicondyle of the distal humerus
branch to the dorsum may be absent
-
anastomoses between ulnar and median nerves which may complicate clinical examination or nerve conduction studies 9
Martin-Gruber anastomosis: between median nerve or anterior interosseous branch and ulnar nerve, in the forearm
Riche-Cannieu anastomosis: between the recurrent branch of median nerve and deep branch of ulnar nerve, in the hand
Marinacci anastomosis: a reverse Martin-Gruber anastomosis, between the ulnar nerve and median nerve
Berrettini anastomosis: between digital sensory nerve of ulnar and median nerves
Related pathology
-
ulnar nerve impingement










 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.