Windmill artifact
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Bálint Botz had no recorded disclosures.
View Bálint Botz's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Andrew Murphy had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
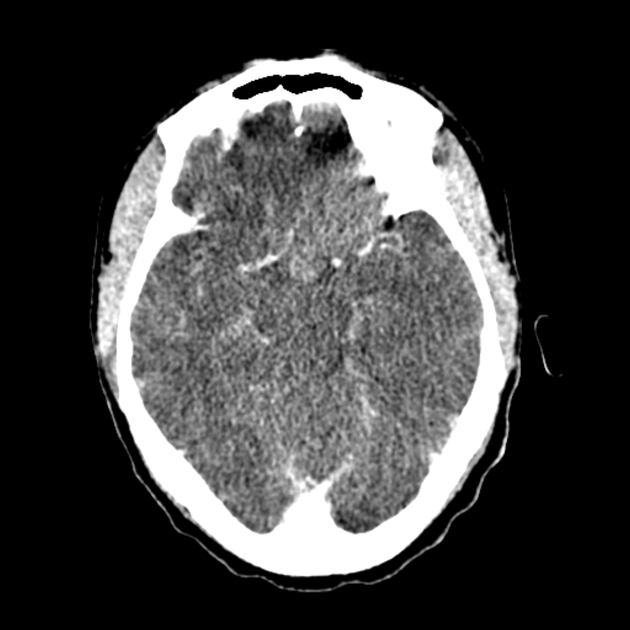
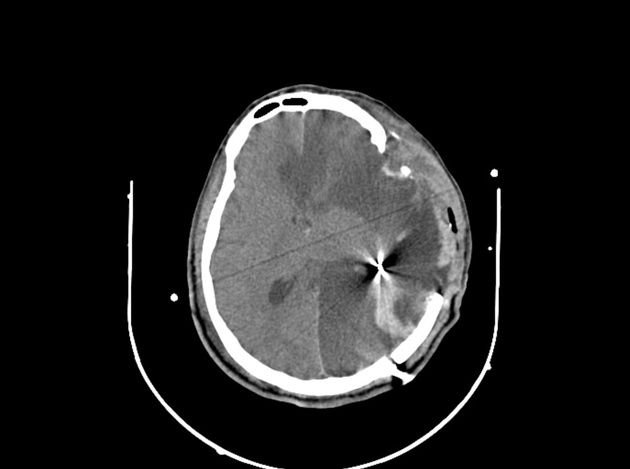
View Andrew Murphy's current disclosuresIn CT imaging, the windmill artifact is an image distortion in the axial plane, encountered during helical multidetector acquisitions. The telltale appearance is characterised by equally distanced bright streaks diverging from a focal high-density structure. The streaks seemingly rotate while scrolling back and forth through the affected slices - hence the name 1.
The windmill artifact is caused by inadequate data sampling in the z-plane, due to multiple detector rows intersecting the reconstruction plane during each rotation of the gantry. With increasing helical pitch, the number of detector rows intersecting the same image plane also increases, thus resulting in an increased amount of streaks 2. The windmill artifact can be therefore ameliorated by either decreasing the pitch or using axial acquisition technique instead 1.
References
- 1. Benjamin L. Triche, John T. Nelson Jr, Noah S. McGill, Kristin K. Porter, Rupan Sanyal, Franklin N. Tessler, Jonathan E. McConathy, David M. Gauntt, Michael V. Yester, Satinder P. Singh. Recognizing and Minimizing Artifacts at CT, MRI, US, and Molecular Imaging. (2019) RadioGraphics. 39 (4): 1017-1018. doi:10.1148/rg.2019180022 - Pubmed
- 2. Julia F. Barrett, Nicholas Keat. Artifacts in CT: Recognition and Avoidance1. (2004) RadioGraphics. 24 (6): 1679-91. doi:10.1148/rg.246045065 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Computed tomography
- computed tomography in practice
-
computed tomography overview
- iodinated contrast media
- CT IV contrast media administration
-
CT artifacts
- patient-based artifacts
- physics-based artifacts
- hardware-based artifacts
- ring artifact
- tube arcing
- out of field artifact
- air bubble artifact
- helical and multichannel artifacts
- CT technology
-
generations of CT scanners
- helical CT scanning
- step and shoot scanning
- ultra-high-resolution CT (UHRCT)
- CT x-ray tube
- CT fluoroscopy
- cone-beam CT
-
generations of CT scanners
- dual-energy CT
- CT image reconstruction
- CT image quality
- CT dose
-
CT protocols
- composite
- head & neck
- chest
- abdomen and pelvis
- CT abdomen-pelvis (protocol)
- CT abdominal aorta
- CT adrenals (protocol)
- CT cholangiography (protocol)
- CT colonography (protocol)
- CT enteroclysis (protocol)
- CT enterography (protocol)
- CT gastrography (protocol)
- CT kidneys, ureters and bladder (protocol)
- CT urography (protocol)
- CT Renal mass (protocol)
- CT angiography of the splanchnic vessels (protocol)
- CT renal split bolus
- CT pancreas (protocol)
- liver




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.