Presentation
Asymmetric ascending spastic quadriparesis with dysphonia and sphincteric dysfunction.
Patient Data
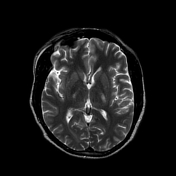

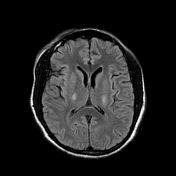

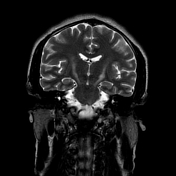



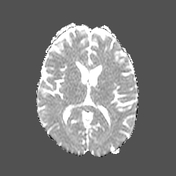

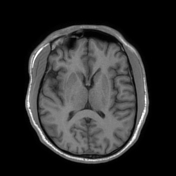



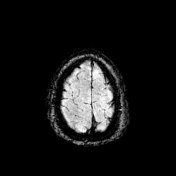


Bilaterally symmetric T1 hypointensities and T2/FLAIR hyperintensities in the centrum semi-ovale through the corona radiata down to the posterior limb of the internal capsule, ventral midbrain, pons and pyramids of the medulla (cortical spinal tracts). Restricted diffusion is noted along this pathway. No abnormal enhancement was noted. Similar intensities are noted tracking down along the lateral corticospinal tracts of the spinal cord on T2 coronal images. The motor band sign is not evident on SWI sequences. The rest of the brain parenchyma is unremarkable.
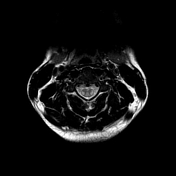

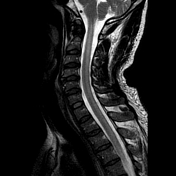

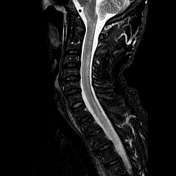

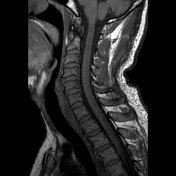



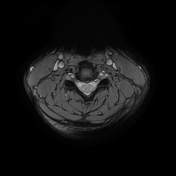

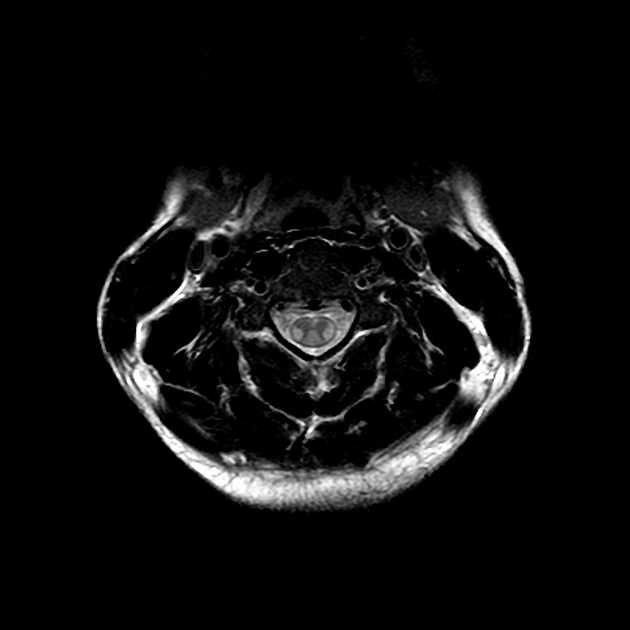
Bilaterally symmetric T1 hypointensities and T2/STIR hyperintensities along the lateral corticospinal tracts. No appreciable enhancement is noted post-gadolinium administration.
Case Discussion
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is the most common form of motor neuron disease resulting in progressive weakness and eventual death due to respiratory insufficiency. It is typically diagnosed in middle age with a recognized male predilection. The majority of the patients present with weakness of the limbs which is typically asymmetric and distal at the onset1. About a quarter present with bulbar symptoms which manifest as difficulty with speaking, chewing, or swallowing1. The earliest MR manifestation is hyperintensities on T2-weighted images in the corticospinal tracts.
Given the clinical presentation and classic MR findings, a diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis was made in this index patient. Unfortunately, the patient passed away 6 months after the first presentation from respiratory insufficiency.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.