Presentation
Emergency CT brain in the ER following motor vehicle accident.
Patient Data
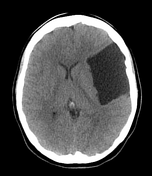

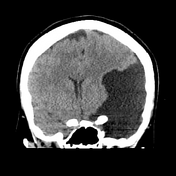

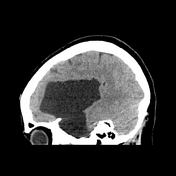

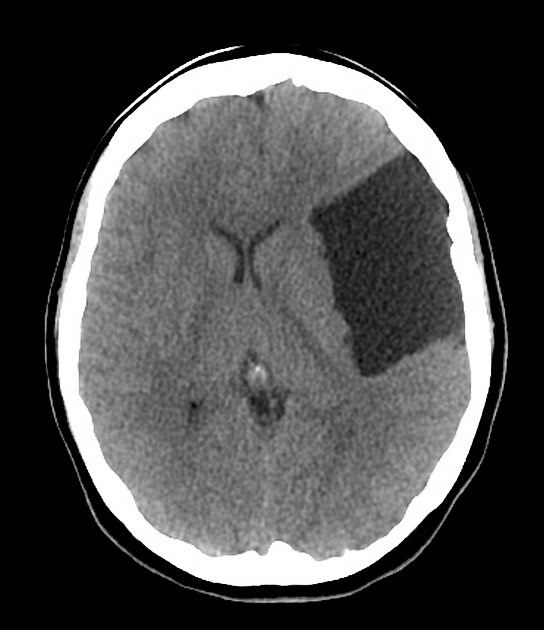
no intra-axial or extra-axial hemorrhage
no calvarial fracture
large extra-axial CSF attenuating lesion is seen occupying the left middle cranial fossa splaying the Sylvian fissure and displacing the frontal, parietal and temporal lobes
secondary mass effect is seen in the form of effacement of left cerebral hemispheric sulci, mild midline shift to right, effaced ipsilateral lateral ventricle
no transtentorial herniation
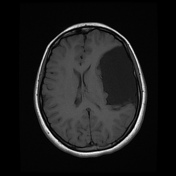

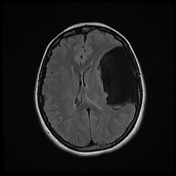

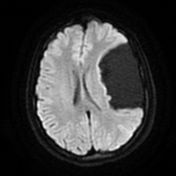



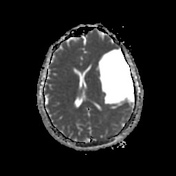

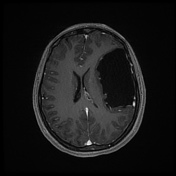

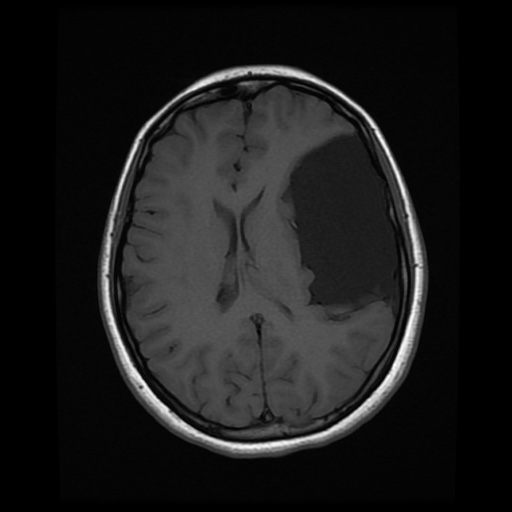
Contrast-enhanced MRI confirms
non-enhancing nature of the lesion
CSF signal on all sequences
-
extra-axial location
displaced cortical mantle and cortical vessels between the lesion and calvarium
no underlying white matter changes in the left cerebral hemisphere
Case Discussion
The most common site of an arachnoid cyst is in the middle cranial fossa, splaying the Sylvian fissure. Depending on the size and extent, it is classified by the Galassi classification. This is a type III variant.
They tend to be asymptomatic and discovered incidentally. The larger ones may cause symptoms secondary to mass effect.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.