Presentation
Ankle pain.
Patient Data



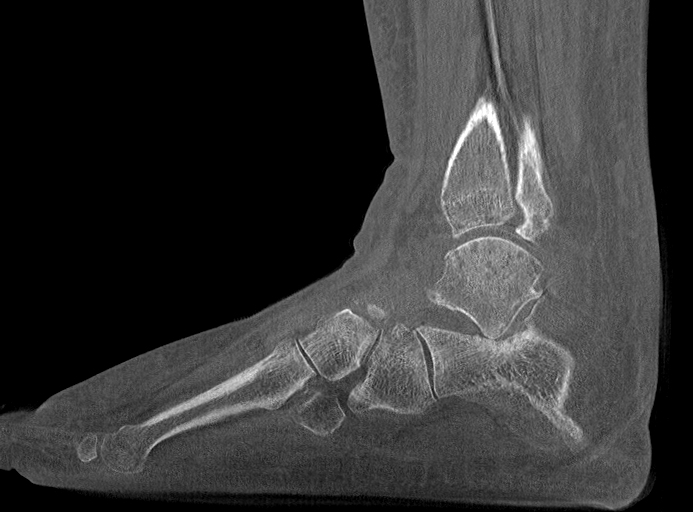
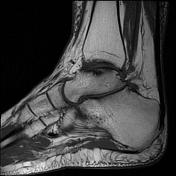
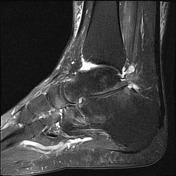
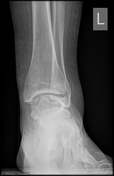
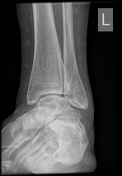
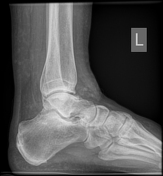
Ball and socket ankle joint. Flattened talar dome with lateral talar tilt. Mild degenerative changes at the ankle joint. Narrowing of the posterior subtalar joint as well as the talocalcaneal interval. Small ossicle at the anterior calcaneal process and adjacent to a dysplastic anterior subtalar joint.
Ossification of the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament. Heterotopic ossification in the superomedial spring ligament. Small ossicle adjacent to the lateral talus.
Longitudinal arch height is preserved. No hindfoot valgus. Midfoot joint spaces are preserved.


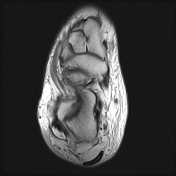

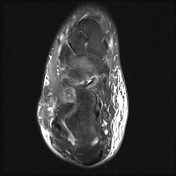

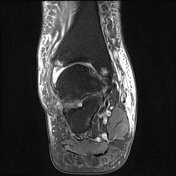

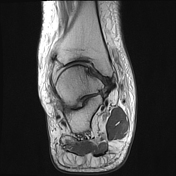

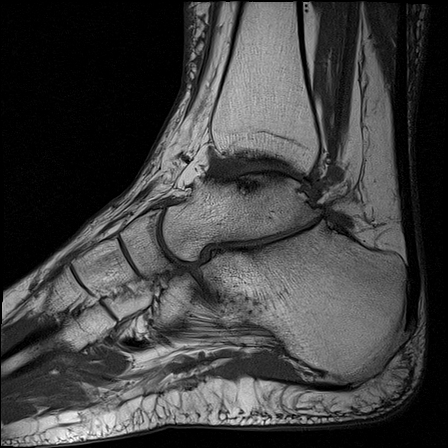
Ankle joint has a ball and socket morphology.
Both ankle and posterior subtalar joint effusions with synovial thickening suggestive of synovitis. Full-thickness chondral loss of the ankle joint medially with subchondral edema present; partial chondral thinning elsewhere.
Lateral tilt of the talus with narrowing of the sinus tarsi and talocalcaneal abutment at the angle of Gissane with mild subchondral signal change. Mild subchondral edema at the posterior subtalar joint, as well as through the midfoot lateral column. No findings of tarsal coalition. Extensive subcutaneous edema centered on the ankle joint.
No ligamentous injury.
Plantar fascia origin is normal. Achilles tendon insertion is intact.
Insertional tendinosis and tendon sheath effusion of tibialis posterior.
Case Discussion
This is an example of a ball and socket ankle joint with lateral talar tilt. Medial ankle joint impingement with degeneration, and extra-articular lateral talocalcaneal impingement. Further lateral foot marrow edema is likely reactive due to altered biomechanics, which is associated with tibialis posterior dysfunction.





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.