Presentation
Head trauma following a fall from stairs.
Patient Data


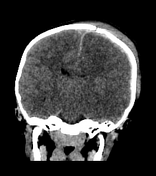

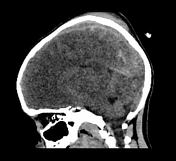

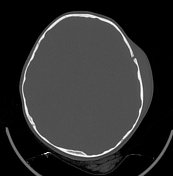

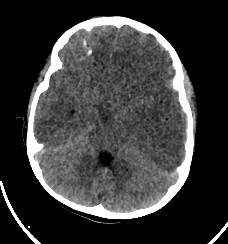
large left-sided cerebral hemispheric oedema with mass effect and left-to-right midline shift
loss of grey-white differentiation suggestive of an associated cytotoxic oedema
mild left uncal herniation
left acute subdural haematoma and subarachnoid haemorrhage
left frontal cerebral haemorrhagic contusion
left frontal and parietal bone fracture with subcutaneous haematoma

significant increase in the cerebral oedema
increased mass effect, midline shift, and left uncal herniation
onset of a left subfalcine herniation
increase in the size of the subdural and subarachnoid haemorrhage
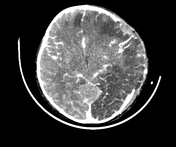

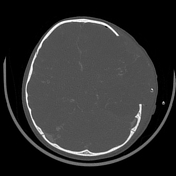

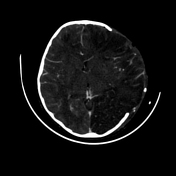

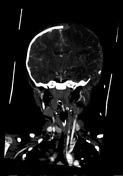

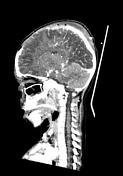

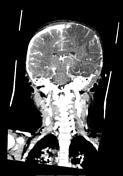

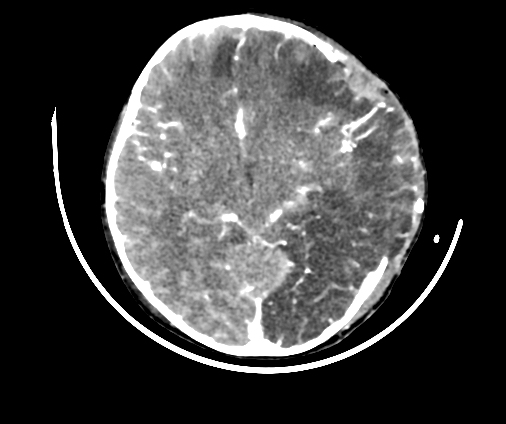
left frontal, parietal and temporal decompressive craniectomy
persistent massive brain swelling
decreased midline shift and uncal herniation
there is no sign of arterial occlusion or dissection
Case Discussion
Post-traumatic cerebral oedema is a combination of three types:
osmotic oedema - the contusion necrosis and expansion lead to local tissue osmolarity increase and subsequent oedema 1
vasogenic oedema - due to the traumatic rupture of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and to the liberation of neuroinflammation mediators 1
cytotoxic oedema - the raised intracranial pressure leads to a reduction of the cerebral perfusion pressure with subsequent ischaemia and cytotoxic oedema




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.