Presentation
Driver in car accident. Reduced GCS.
Patient Data
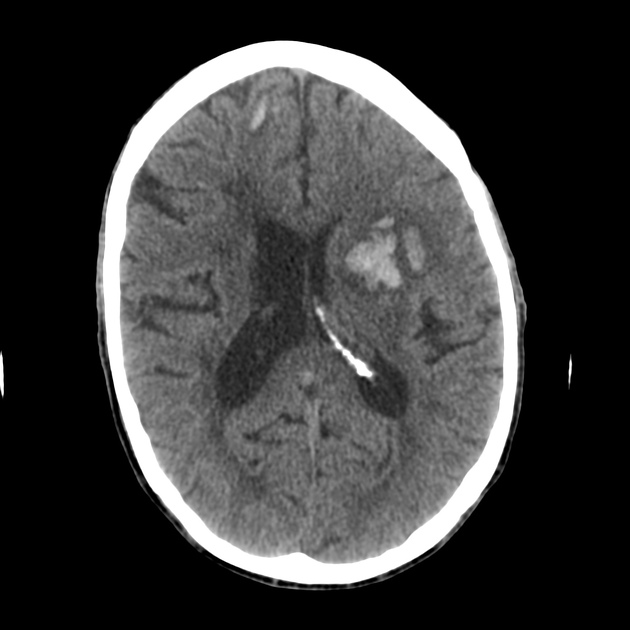
There are multiple intraparenchymal hemorrhages, the largest of which is centered within the left basal ganglia consistent with hypertensive etiology. The remaining smaller hemorrhages are located at the grey-white junction in the right frontal lobe and temporal lobe consistent with traumatic etiology.
Case Discussion
This case is radiologically cute in that the intraparenchymal hemorrhages have two separate etiologies. The patient most likely suffered a left basal ganglia hypertensive bleed whilst driving and then crashed his car receiving traumatic right frontal and temporal hemorrhages.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.