Presentation
Incidental finding on postoperative control radiography.
Patient Data
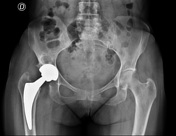
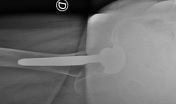
Postoperative radiograph in right total hip arthroplasty. Normal cortical thickness with no signs of stress shielding. There is large subchondral bone cyst in the right acetabulum.
Two years post-operative

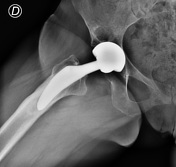
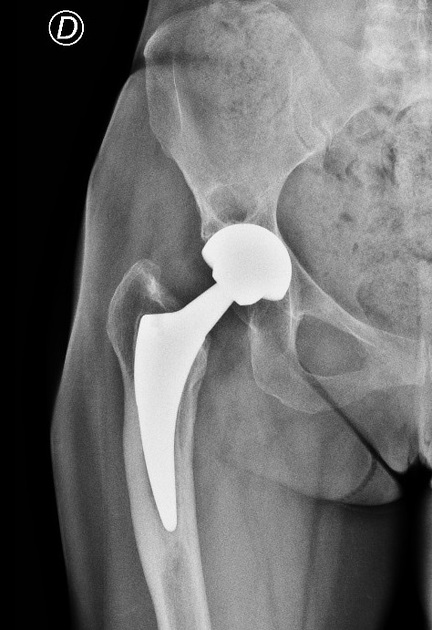
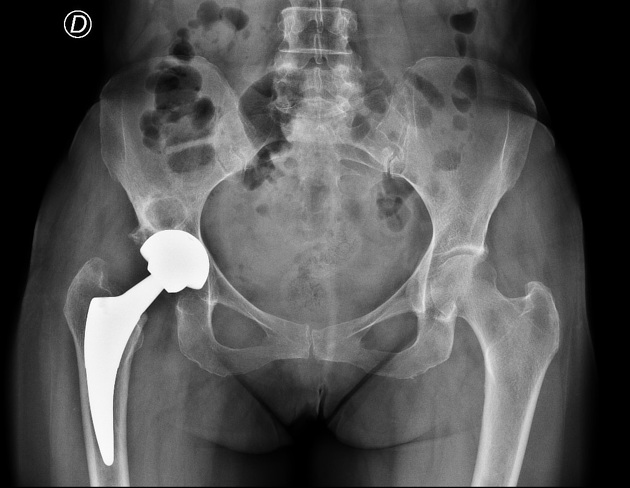
Two-year post-operative radiograph demonstrating distal cortical hypertrophy and proximal stress shielding (stress shielding of the proximal femur). There is a focal-type cortical hypertrophy to distal femoral, in Gruen zones 3-5. There is also stress shielding with loss of the medial cortex density below the minor trochanter (Gruen zone 7) and greater trochanter (Gruen zone 1) with calcar resorption as different parts of reactive bone remodeling. Unchanged the subchondral cyst of the right acetabulum.
Case Discussion
Cortical hypertrophy is a fusiform enlargements of the cortical bone in the bone-implant region, which appeared in Gruen zones 3 or 5 (DeLee & Charnley and Gruen zones), ‘the focal type,’ whereas if cortical hypertrophy appear in zones 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 as ‘the diffuse type’. Unloading of the proximal medial femoral cortex is usually associated with an increased bone strain at the distal part of the prosthesis, which may cause distal femoral cortical hypertrophy and then this pattern of abnormal loading might cause proximal osteopenia (Wolff’s law “where the bone is stressed it hypertrophies, where it is discharged it is reabsorbed”).




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.