Presentation
Elderly patient, morbidly obese, with history of recurrent infections. Recent left orbital/periorbital swelling, pain, redness.
Patient Data
- Note: This case has been tagged as "legacy" as it no longer meets image preparation and/or other case publication guidelines.

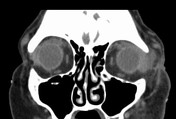
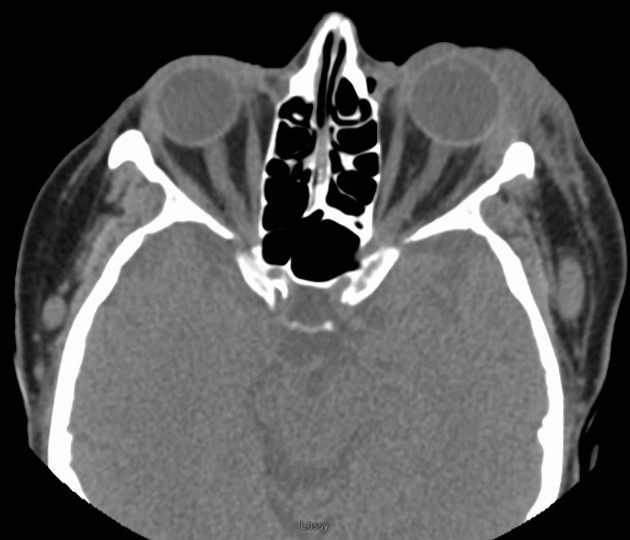
Stranding of left orbital pre-septal soft tissues reflecting cellulitis. Moderate edema of the left lacrimal with central hypo-attenuations favoring significant intra-glandular inflammatory edema. Mild anteromedial displacement of the ocular globe (slight proptosis). Mild retro-orbital/intraconal fat stranding reflecting cellulitis.
No left ocular globe or optic nerve sheath invasion. Intact osseous structures. No mass lesions.
Case Discussion
Approximately 50% of the lacrimal gland lesions are inflammatory. Lymphoma and salivary gland tumors come next (approximately 25% each).
If not treated promptly, these lesions quickly progress and cause ocular globe infection, thrombosis of the superior ophthalmic vein, orbital thrombophlebitis with risk of intracranial invasion via cavernous plexus. Intra-glandular abscess require immediate referral for surgical drainage.
Repeating CT or ultrasound after complete resolution of the inflammation may help exclude underlying lacrimal neoplasm. MRI of dacryoadenitis can show restricted diffusion on DWI/ADC and it may be difficult to distinguish from lymphoma which is hypercellular therefore restricts on DWI.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.