Presentation
Non-traumatic wrist pain on the radial side.
Patient Data

There is a cortical irregularity near the radial styloid process. There is no fracture/ dislocation. Mild soft tissue swelling is present along the radial side of the wrist.
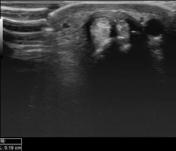
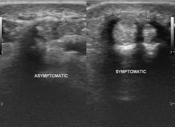
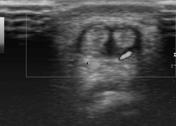

There is hypoechoic retinacular thickening involving both tendons of the 1st extensor compartment of the wrist which correlates with the site of the pain. A thickened hypoechoic intertendinous septum is present separating both tendons which are abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis. There is associated local hypervascularity in the retinaculum.
The asymptomatic side was examined for comparison. It does not show retinacular thickening. There is possibly a presence of the intertendinous septum.
Case Discussion
Retinacular thickening involving both tendons of the 1st extensor compartment on ultrasound in a patient with nontraumatic radial-sided wrist pain suggests the diagnosis of De Quervain tenosynovitis. An intertendinous septum is present which is one of the anatomical variants 1.
The presence of a focal radial styloid abnormality on x-ray is an indicator of de Quervain tenosynovitis of the wrist 2. However, such abnormalities do not affect the outcome of the management 3.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.