Presentation
Right chin progressive swelling.
Patient Data
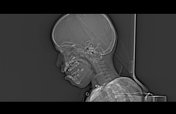
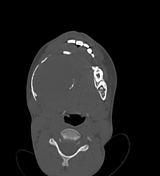

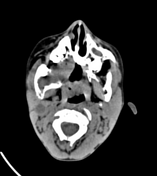

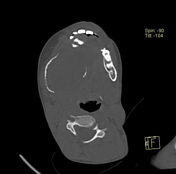

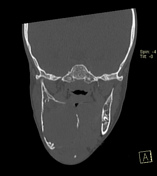

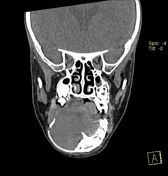

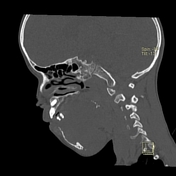

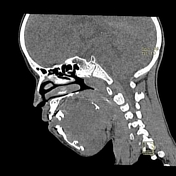



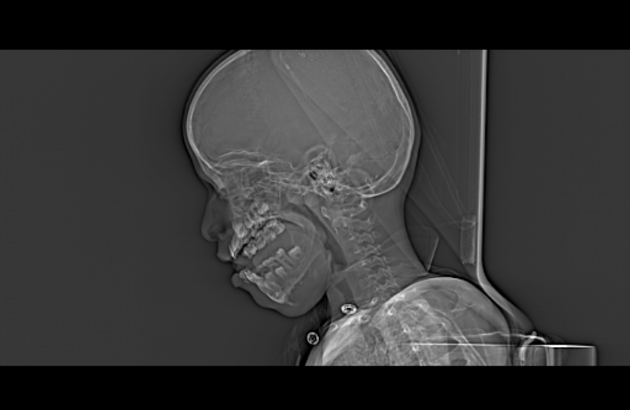
Right mandibular body, angle and ramus expansile lytic lesion showing marked cortical thinning and scalloping. The lesion shows small extra-ossoeus component along its lower aspect at the submental region. The inferior mandibular nerve canal is running along the lateral aspect of the lesion. The lesion compresses the tongue and submandibular gland medially.
Multiple enlarged upper deep cervical lymph nodes, numerous and larger on the right with node showing hypodense cystic center.
Radiological features were suggestive of giant cell granuloma versus odontogenic tumor.
Tru-cut biopsy
Microscopic appearance
Sections examined revealed cores of tumor tissue formed of hypocelluar spindle cells in thick collagenous bundles.
Immunohistochemsitry
tumor cells are weakly focally positive for SMA
tumor cells are positive for B-catenin
5% of tumor cells are positive for Ki67
Conclusion: findings are compatible with fibromatosis.
Case Discussion
Desmoplastic fibromas are extremely rare bone tumors that do not metastasize but may be locally aggressive. They are considered to be a bony counterpart of soft tissue desmoid tumors and are histologically identical.
Desmoplastic fibroma of bone is rare and mostly found in young adults and adolescents.
The most frequent locations of desmoplastic fibroma of bone include
long bones (femur, radius, tibia) usually located in the metaphysis or diametaphysis
pelvic bones
The diagnosis of desmoplastic fibroma is difficult to make radiologically.
CT will show a soft tissue density mass and will show cortical erosion possibly associated with infiltration of the surrounding tissues.
DDx:




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.