Presentation
Out of hospital cardiac arrest due to status asthmaticus. Blown pupils. Hypotensive and bradycardic.
Patient Data
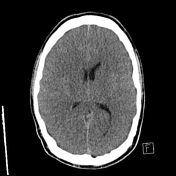

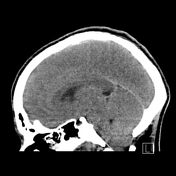

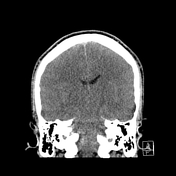


No acute intra or extra-axial hemorrhage or collection. There is diffuse cerebral edema with significant positive mass effect causing diffuse sulcal effacement and near complete effacement of the cisterns. Partial effacement of the ventricular system. No hydrocephalus. The cerebellar tonsils have herniated up to 9 mm below the level of the foramen magnum.
There is diffusely reduced supratentorial grey-white matter differentiation with apparent relative hyperattenuation of the subarachnoid spaces (pseudosubarachnoid hemorrhage) and the cerebellum (reversal sign).
The superior ophthalmic veins are prominent bilaterally, and the distal aspects of the optic nerve sheaths are also prominent. No acute skull fracture or surface collection. Mucosal thickening in the ethmoid air cells, maxillary sinuses, and sphenoid sinus. The frontal sinus and mastoid air cells are well pneumatized.
IMPRESSION
Features of diffuse cerebral edema due to diffuse hypoxic ischemic injury. Significant positive mass effect and cerebellar tonsillar herniation. No hydrocephalus.
Case Discussion
The patient died in ICU 4 days later.
Tonsillar herniation is typically a pre-terminal event.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.