Presentation
Chronic shoulder pain. No history of previous trauma.
Patient Data


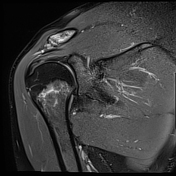

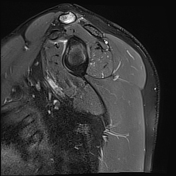

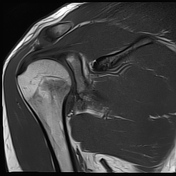

Bone marrow oedema and cortical thinning are visualised at the distal clavicle. Mild widening of the acromioclavicular joint and capsular oedema are noted.
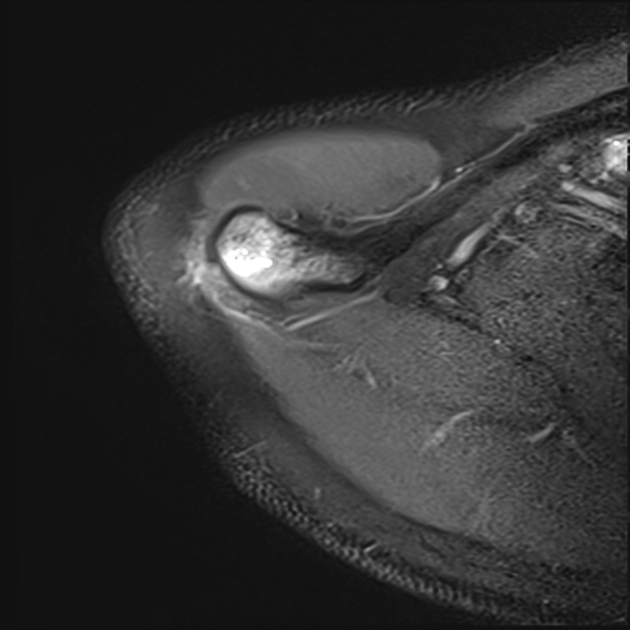
Intense bone marrow oedema is noticed at the humeral neck, associated with a transverse fracture line.
Buford complex is seen, as the absence of anterosuperior glenoid labrum and thickening of the middle glenohumeral ligament.
Mild glenohumeral effusion is visible.
Case Discussion
As a well-studied cause of adult shoulder pain, distal clavicular osteolysis (DCO) can be divided into two categories: post-traumatic and atraumatic.
Atraumatic DCO occurs as a result of repetitive stress. Main MRI findings include distal clavicular marrow oedema, cortical thinning and acromioclavicular widening.
Without a history of direct trauma, stress fractures are diagnosed on imaging with transverse or oblique fracture lines and bone marrow oedema at specific locations. They most commonly occur in the lower extremity. Proximal humeral stress fractures are less common.
This case represents two concomitant stress-induced injuries to the shoulder: atraumatic distal clavicular osteolysis and humeral neck stress fracture.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.